Magnetostrictive material and preparation method thereof
A technology of magnetostrictive materials and raw materials, which is applied in the direction of material selection, device material selection, magnetic layer, etc. for magnetostrictive devices, can solve the problems of poor plasticity of alloy materials, complex manufacturing process, poor oxidation resistance, etc. Achieve good oxidation resistance, good consistency and good toughness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
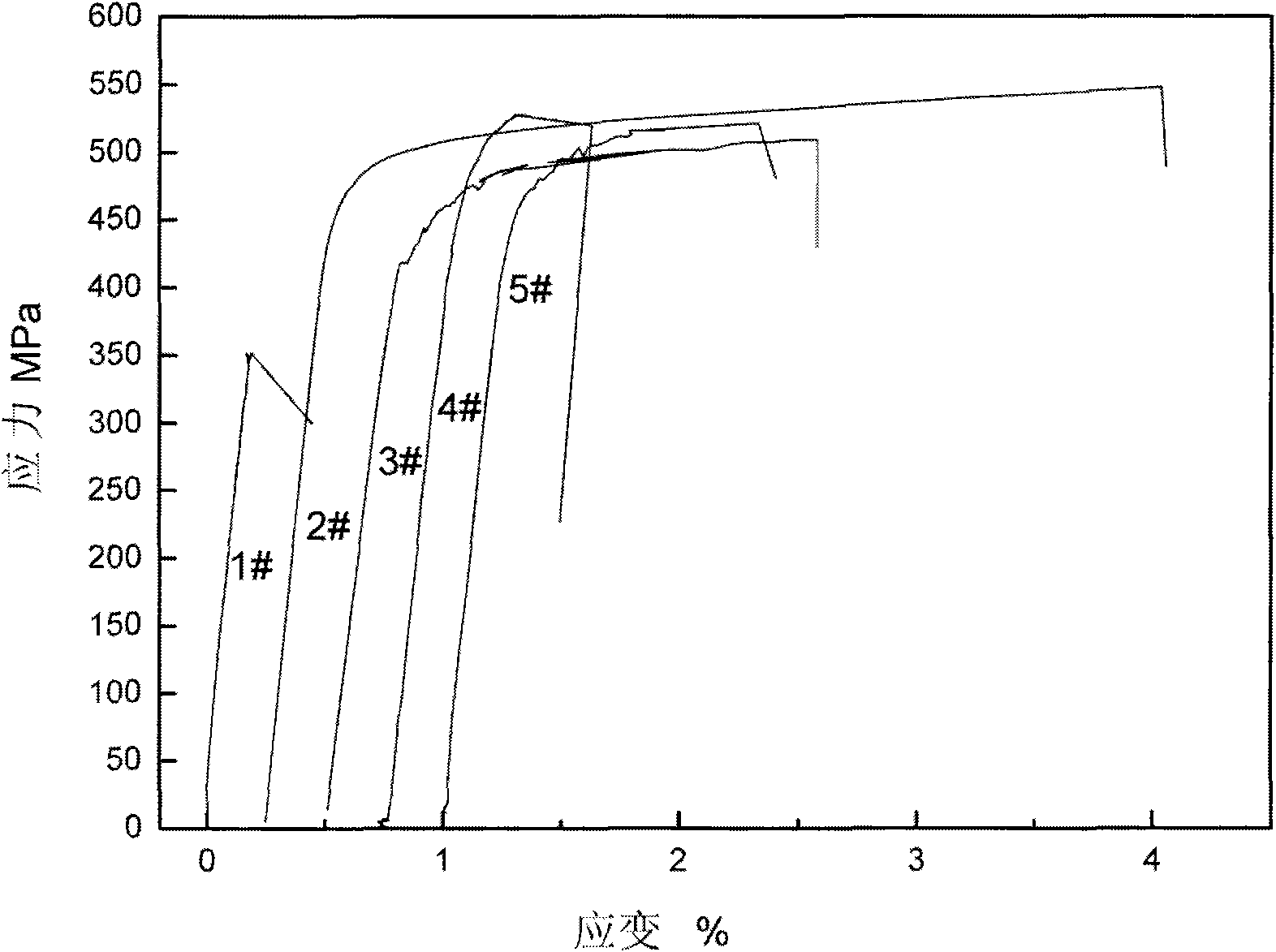
[0046] Embodiment 1: prepare Fe with rolling method 80 Ga 16.5 Al 1.5 Cr 2 Thin sheet magnetostrictive alloy material
[0047] Use an electronic balance to weigh the raw materials required for the design, use an iron source with a purity greater than 99.5%, and add 3% more Ga burning loss, put the prepared raw materials into the crucible of the vacuum induction furnace, and evacuate to 5× 10 -3 After Pa, fill it with argon gas to 0.5MPa to protect the raw materials from oxidation, and start smelting. After it is completely melted, it can be refined for 3 minutes, and then cast into alloy ingots in the furnace;
[0048] The as-cast alloy ingot is forged at 900°C into a rectangular billet with a thickness of 6.5mm, and the deformation is about 70%;
[0049] The forging billet is hot rolled at 950°C, and the deformation is about 80%. Control the deformation rate and pass interval time, and roll to a thickness of 1.3mm;
[0050] The hot-rolled slab is cold-rolled at room te...
Embodiment 2
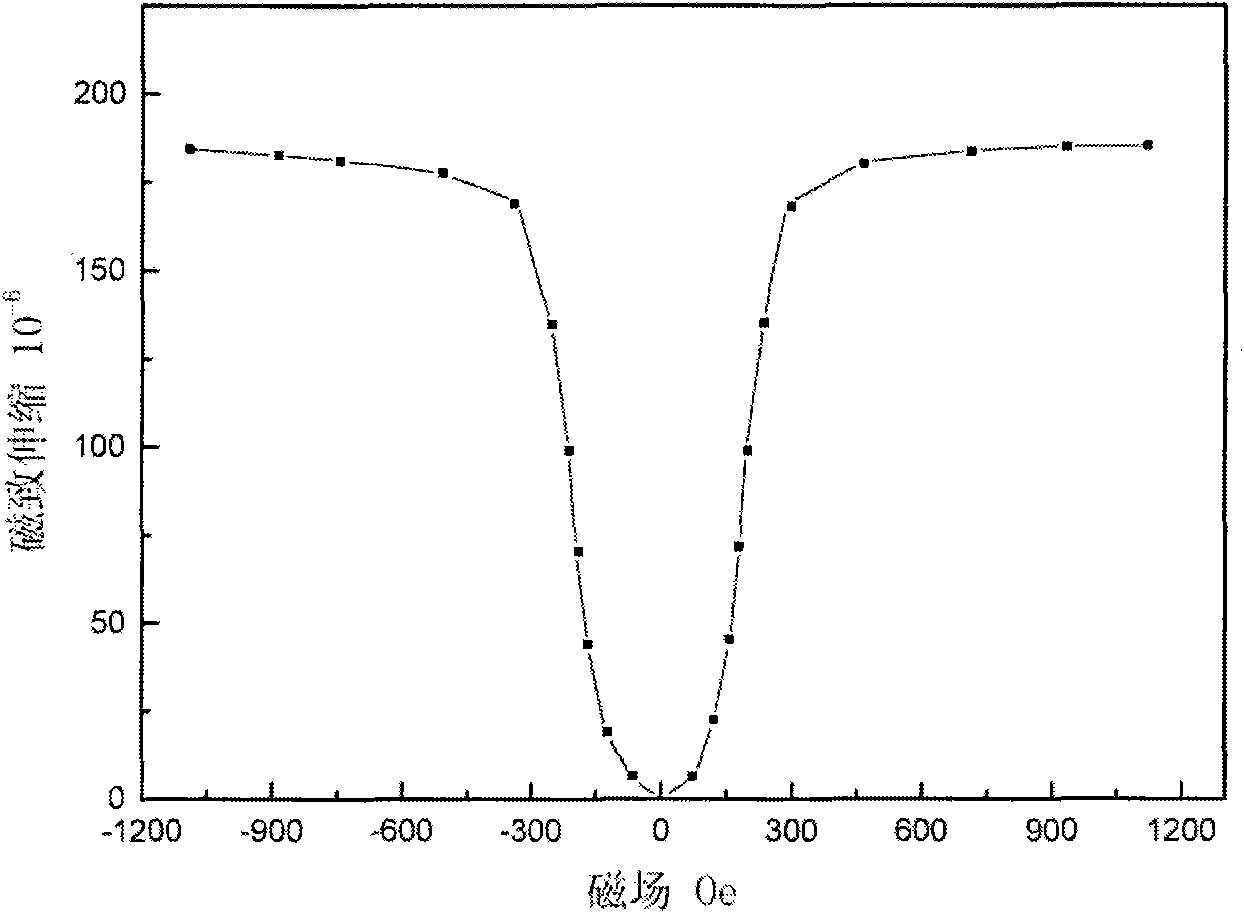
[0054] Embodiment 2: prepare Fe with rolling method 81 Ga 16.5 Al 1.1 Zr 0.9 sn 0.5 Thin sheet magnetostrictive alloy material
[0055] Weigh the required raw materials, use an iron source with a purity greater than 99.5%, and add 2% more Ga burning loss, put the prepared raw materials into the crucible of the vacuum induction furnace, and evacuate to 5×10 -3 Pa filled with argon to 0.5MPa to protect raw materials from oxidation, smelting and casting into alloy ingots;
[0056] The as-cast alloy ingot is forged at 950°C into a rectangular billet with a thickness of 6.2mm, and the deformation is about 65%;
[0057] The forged blank is hot rolled at 950°C, and the deformation is about 75%. Control the deformation rate and pass interval time, and roll to a thickness of 1.6mm;
[0058] The hot-rolled slab is cold-rolled at room temperature for 15 passes, with a deformation of about 70%, and finally rolled to 0.48mm;
[0059] The as-rolled alloy was kept at 1200°C for 4 hou...
Embodiment 3
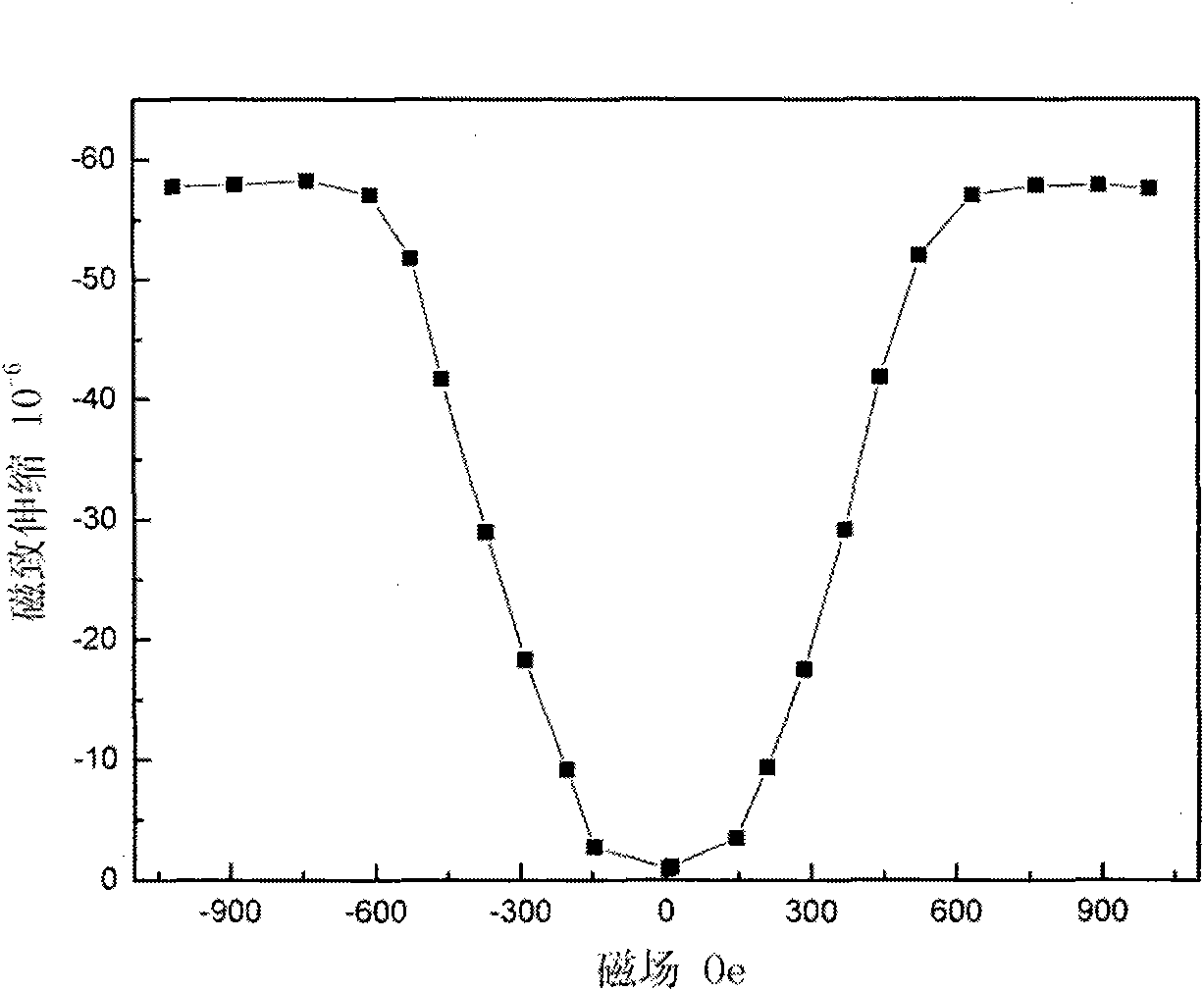
[0062] Embodiment 3: prepare Fe with rolling method 79.8 Ga 17 Al 1.2 V 1.5 Sb 0.5 Thin sheet magnetostrictive alloy material
[0063] Weigh the required raw materials, use an iron source with a purity greater than 99.5%, and add 4% more Ga burning loss, put the prepared raw materials into the crucible of the vacuum induction furnace, and evacuate to 5×10 -3 Pa filled with argon to 0.5MPa to protect raw materials from oxidation, smelting and casting into alloy ingots;
[0064] The as-cast alloy ingot is forged at 1000°C into a rectangular billet with a thickness of 5.6mm, and the deformation is about 70%;
[0065] The forging billet is hot rolled at 1000°C, and the deformation is about 70%. Control the deformation rate and pass interval time, and roll to a thickness of 1.7mm;
[0066] The hot-rolled slab is cold-rolled at room temperature for 18 passes, with a deformation of about 80%, and finally rolled to 0.34mm;
[0067] The as-rolled alloy was kept at 1150°C for 6 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com