Method for testing sequence of nucleic acid single molecule
A single-molecule sequencing and nucleic acid technology, which is used in biochemical equipment and methods, material excitation analysis, and microbial determination/inspection. The effect of high quality and low measurement cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] DNA fragment sequencing
[0021] Step 1, detection of dNMPs handwriting
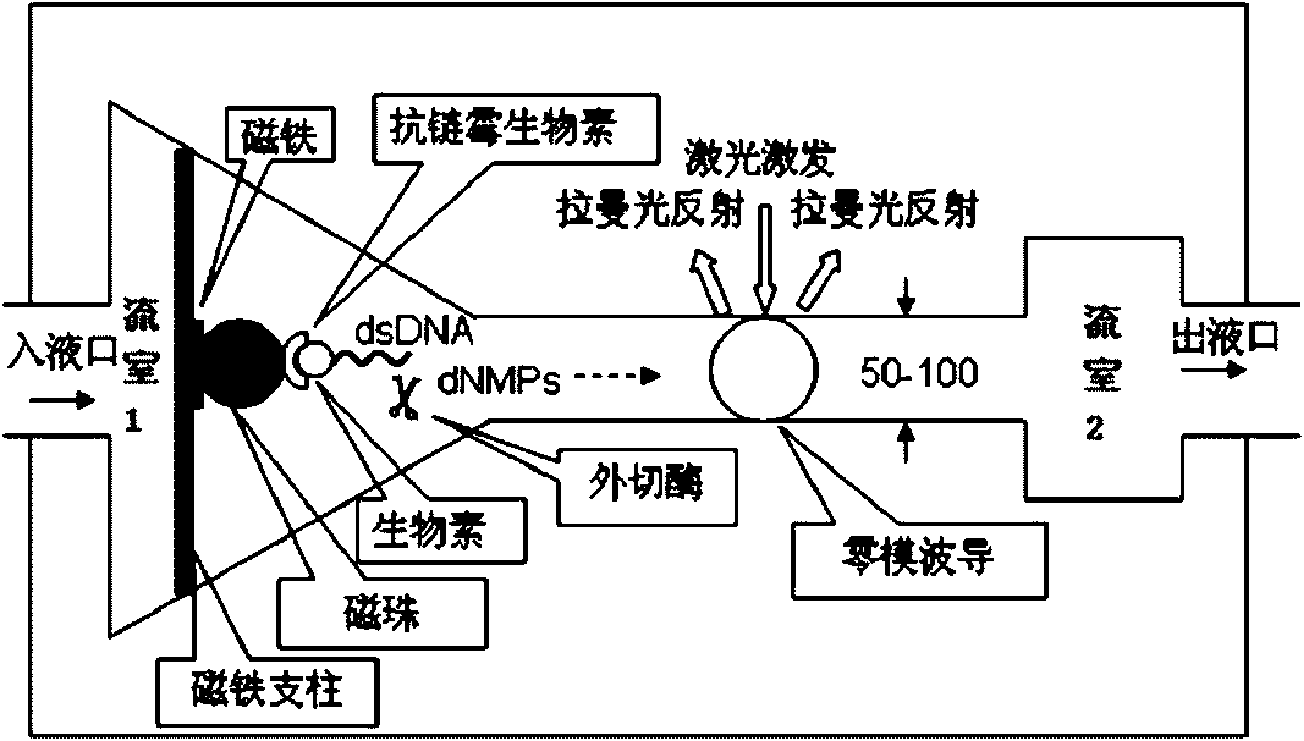
[0022] Add water or aqueous solution to the flow chamber 1 connected by nanochannels embedded with zero-mode waveguides, and only add one ultra-diluted nucleotide each time, turn on the vacuum pumping and Raman spectroscopy detection system to record when a single nucleotide passes through the ZMW In this way, the Raman spectrum signals of various nucleotides are detected, and finally the characteristic spectra of their specific phonon vibrations are determined, a standard curve is established, and software is written.
[0023] Step 2, immobilization of single-molecule DNA fragments
[0024] A magnetic bead carrying a target nucleic acid molecule is fixed to the magnet of the flow chamber 1 of the sequencing unit, so that one end of a target nucleic acid is fixed. The sequencing unit is made into an array, and finally each sequencing unit of the entire array has a target nucleic acid.
[0025] ...
Embodiment 2
[0030] Complete Chromosome Sequencing
[0031] Step 1, single-molecule operation: with the aid of an optical microscope, flow cytometer or other methods, a single chromosome is extracted, histones are removed, and the chromosome is immobilized on magnetic beads according to the method in Example 1.
[0032] Step 2, Chromosome fixation: fix the magnetic beads with 1 complete chromosome on the magnet installed in the flow chamber 1 of a sequencing unit to make an array, and finally make each sequencing unit of the entire array have a chromosome.
[0033] Step 3, sequence detection: add exonuclease and buffer in flow chamber 1, after a single enzyme molecule binds to DNA, add magnesium ions, immediately turn on the vacuum device, collect Raman spectrum signals, and use software to read the DNA sequence .
[0034] The implementation effect of this embodiment: the whole chromosome is used as the substrate for sequencing, although the effect of the array cannot be fully exerted as ...
Embodiment 3
[0036] RNA sequencing
[0037] Step 1, the detection of rNMPs handwriting is the same as in Example 1, and a standard curve is established according to the specific Raman spectrum signals generated by them.
[0038] Step 2, according to the method of Example 1, fix the RNA single molecule to the flow chamber 1, use RNA exonuclease to degrade the nucleotides one by one, when the nucleotide passes through the ZWM, record the Raman spectrum data, and convert the Raman spectrum according to the standard curve The signal is converted into sequence information.
[0039]In step 3, RNA can also be used as a template to synthesize cDNA (complementary DNA) by reverse transcriptase, and then follow the steps in Example 1 to obtain the RNA sequence.
[0040] Implementation effect of this embodiment: suitable for the RNA / DNA exonuclease activity of this embodiment is 1000nts / second, such as detection of mRNA sequence, according to the average length of mRNA of 1000nts, the array of 100 * ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com