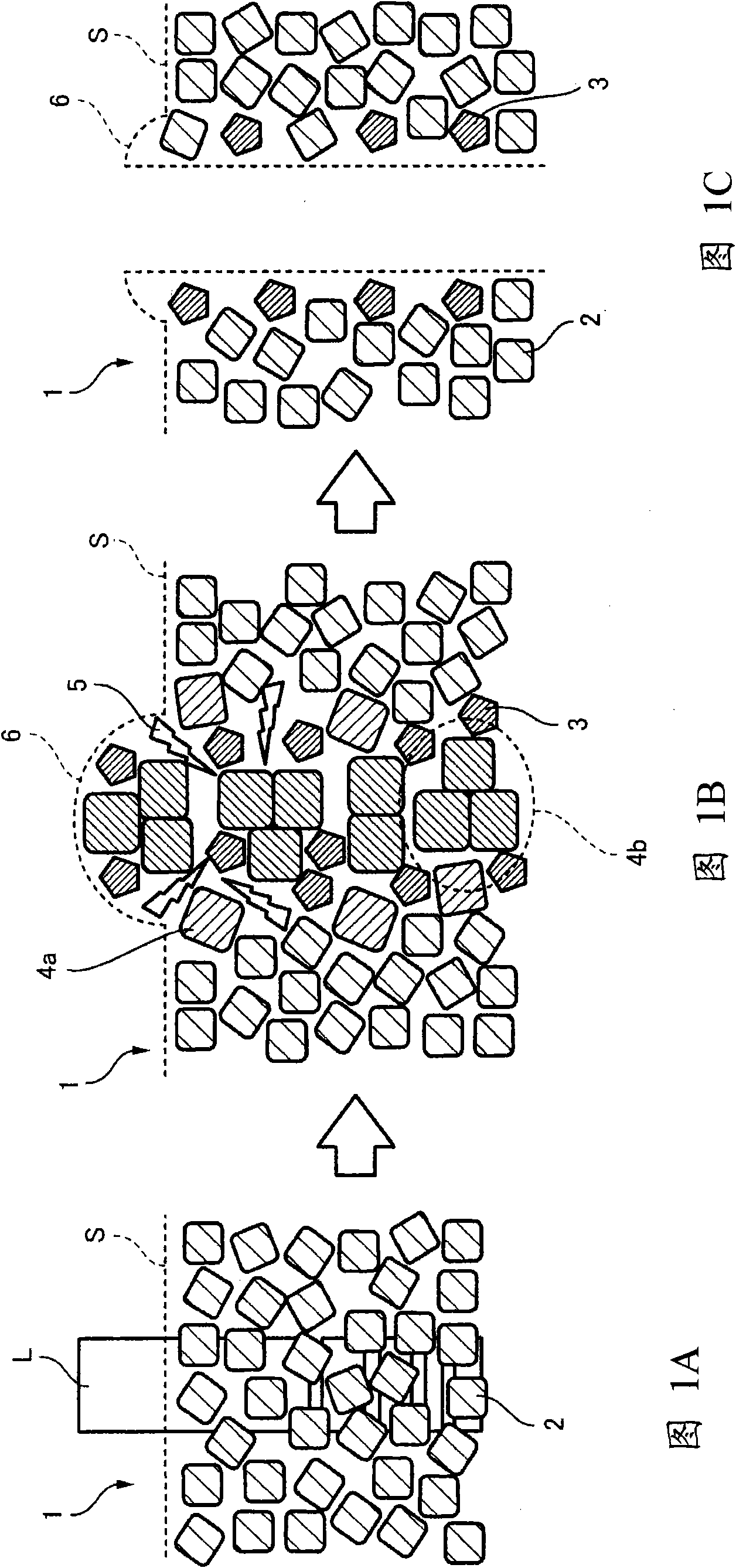
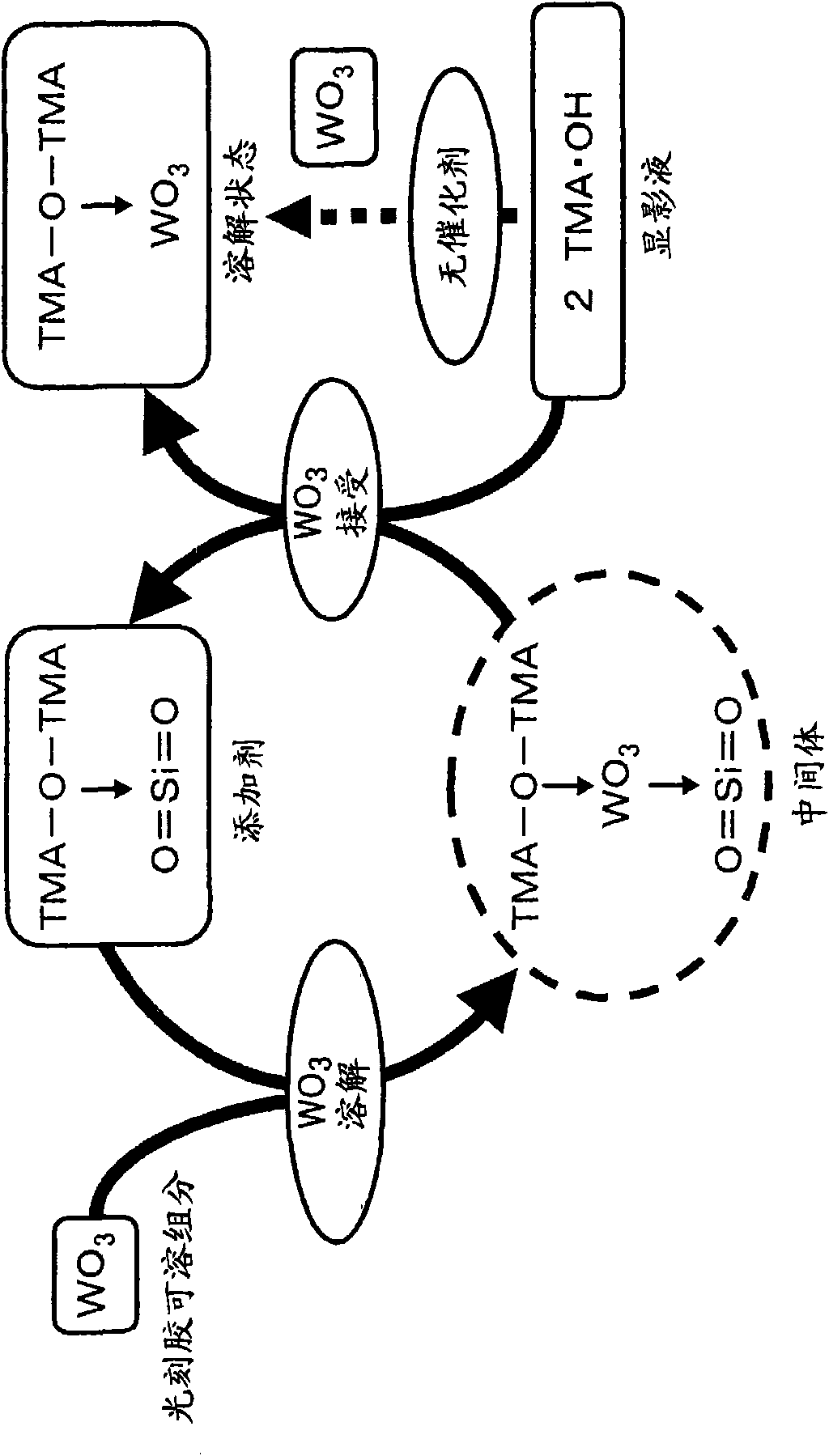
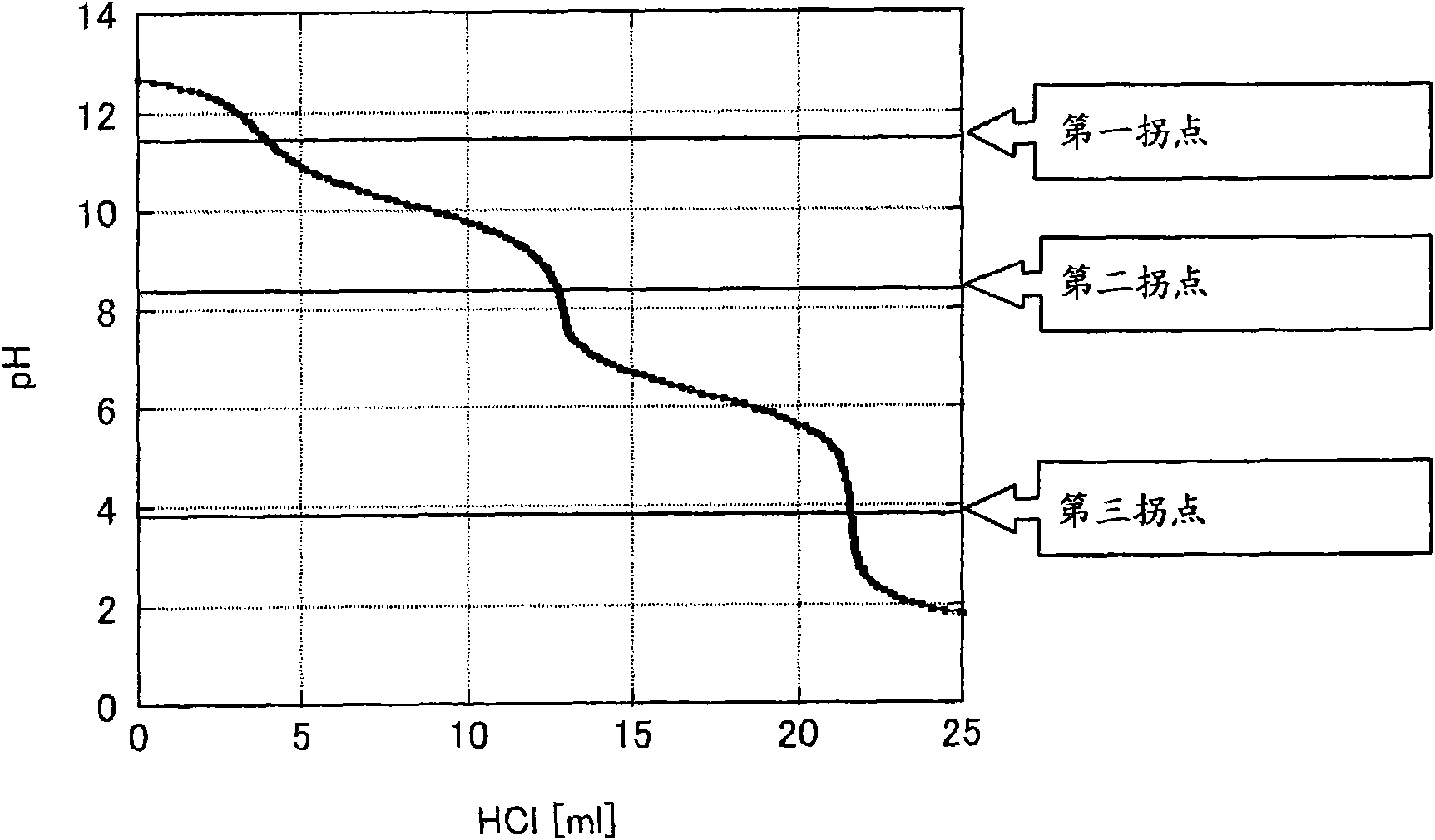
Developing solution and method for production of finely patterned material
A technology of developing solution and development accelerator, which is applied in the field of developing solution, can solve the problem of lower dissolution rate of photoresist and achieve the effect of shortening the developing time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach
[0119] (1-1) Inorganic photoresist
[0120] (1-2) Developer
[0121] (1-3) Reaction mechanism of inorganic photoresist
[0122] (1-4) Reaction of inorganic photoresist and developer
[0123] (1-5) Preparation method of photoresist master
[0124] (1-6) Method of monitoring developer
no. 2 approach
[0126] (2-1) Developer solution
[0127] (2-2) Reaction of inorganic photoresist and developer
no. 3 approach
[0129] (3-1) Developer solution
[0130] (3-2) Reaction between inorganic photoresist and developer
[0131] (1) First Embodiment
[0132] (1-1) Inorganic photoresist
[0133] First, the inorganic photoresist used in the first embodiment of the present invention will be described.
[0134] In photolithographic methods, inorganic photoresists are known to have better thermal stability compared to organic photoresists, and in addition, significantly higher gamma properties are easily obtained when using inorganic photoresists. For example, organic photoresists such as polystyrene (PS), polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), polymethacrylic Glycidyl ester-chlorostyrene copolymer (GMC), poly(butene-1-sulfone) (PBS) and benzaldehyde novolac (novolac), etc., usually only give a gamma property of 3 or less after development . In addition, γ=l / (log δ1-log δ0) (wherein δ0 is the minimum exposure amount required to sensitize the photoresist; δ1 is the exposure amount required to fully sen...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com