Method for lowering olefine content in gasoline in secondary processing
A secondary processing, olefin content technology, applied in hydrotreating process, petroleum industry, treatment of hydrocarbon oil, etc., to achieve the effect of small octane loss, more operational flexibility, and high gasoline yield
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
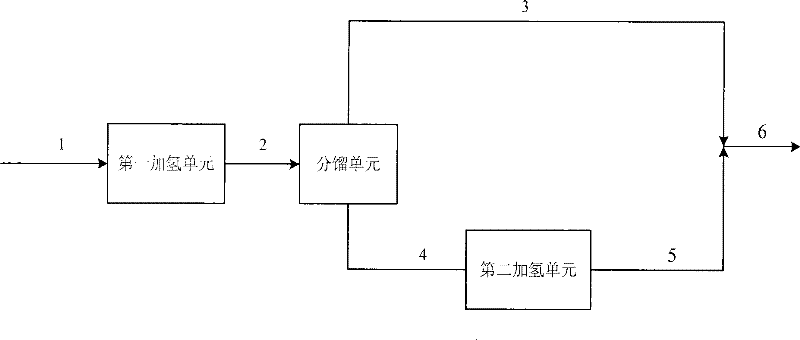
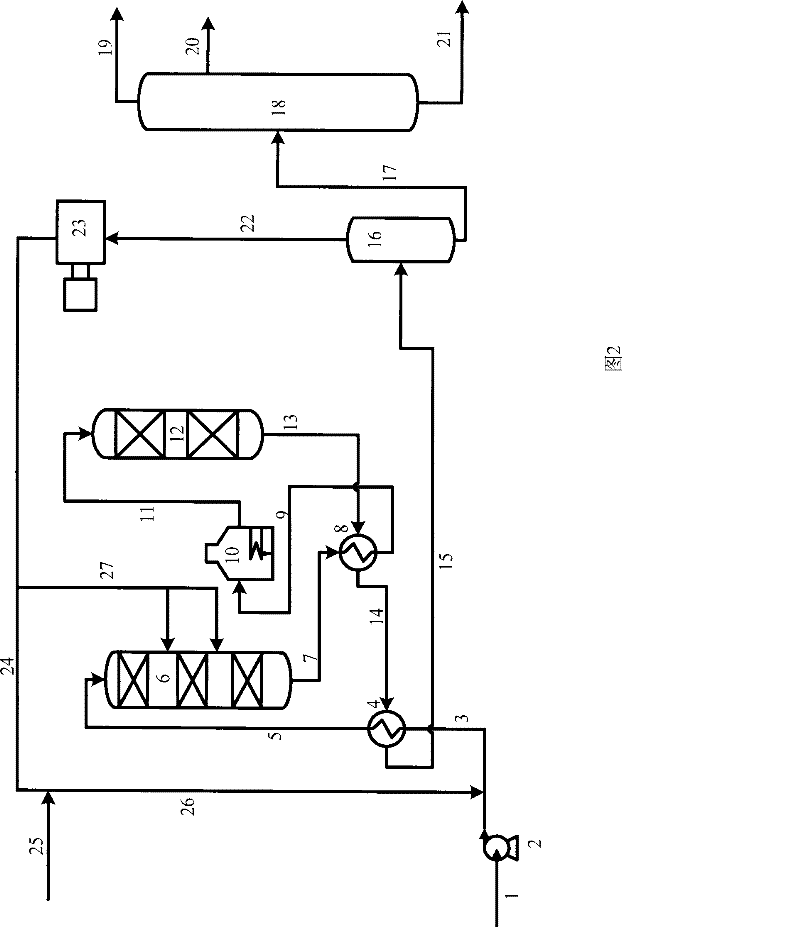
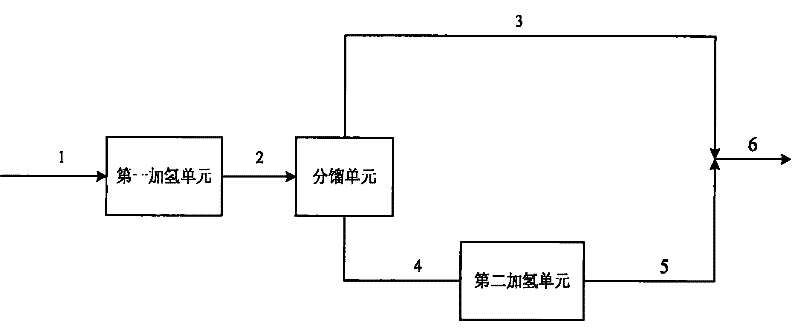
[0038] The properties of the raw materials used in Example 1 are shown in Table 1. The raw material oil A and hydrogen are successively contacted with hydrogenation protecting agent I, hydrogenation protecting agent II and hydrogenation protecting agent III in the first hydrogenation unit to remove most of the diolefins in the raw material. The hydrogenation process conditions and product properties are shown in Table 2. It can be seen from Table 2 that after the first hydrogenation unit, the diene value of the product is less than 0.2gI / 100g, and the stability of gasoline is greatly improved.
Embodiment 2
[0040] The product obtained in Example 1 was subjected to fractional distillation with 90° C. as the fractionation point, wherein the mass ratio of the heavy fraction was 60% by weight. The light distillate is not treated; the heavy distillate and hydrogen are sequentially contacted with a hydrofinishing agent and an octane number recovery catalyst, and are hydrogenated and upgraded under the reaction conditions of a hydrogen partial pressure of 3.2MPa and a reaction temperature of 375°C. The hydrogenated heavy fraction is mixed with the light fraction to obtain gasoline products. The process conditions of heavy fraction hydrogenation and the properties of whole fraction products are shown in Table 2. It can be seen from Table 2 that the olefin content decreased from 55.9% by volume to 24.2% by volume, and the product RON lost 1.2 units.
Embodiment 3
[0042] The product obtained in Example 1 was subjected to fractional distillation with 80° C. as the fractionation point, wherein the mass ratio of the heavy fraction was 68% by weight. The light distillate is not treated; the heavy distillate and hydrogen are sequentially contacted with a hydrofinishing agent and an octane number recovery catalyst, and are hydrogenated and upgraded under the reaction conditions of a hydrogen partial pressure of 3.2MPa and a reaction temperature of 380°C. The hydrogenated heavy fraction is mixed with the light fraction to obtain gasoline products. The process conditions of heavy fraction hydrogenation and the properties of whole fraction products are shown in Table 2. It can be seen from Table 2 that the olefin content decreased from 55.9% by volume to 17.8% by volume, and the product RON lost 1.5 units.
[0043] Table 1
[0044] raw material name
A
Density (20℃), g / cm 3
0.7474
Diene value, gI / 100g
...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com