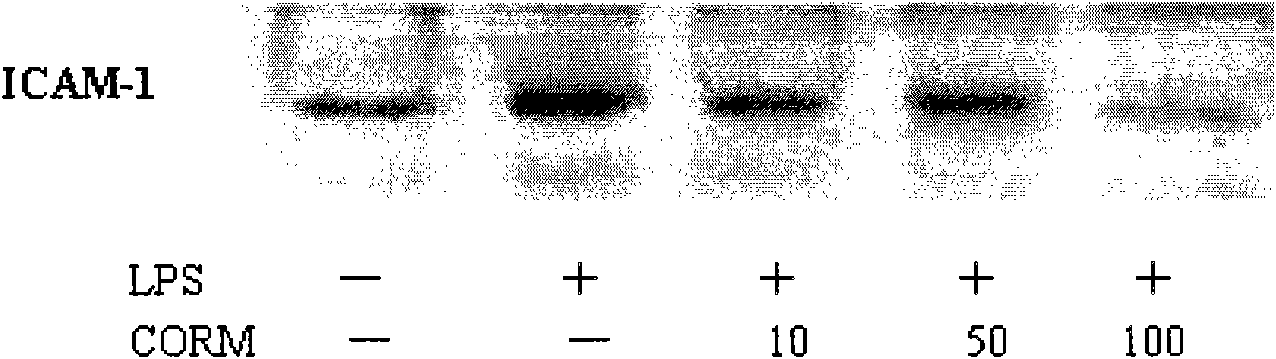Application of carbon monoxide release molecules in preparing medicament for treating early sepsis
A carbon monoxide and sepsis technology, used in the treatment of sepsis, the early application of carbon monoxide release molecules, can solve the problems of exogenous CO administration mode and concentration control difficulties, unfavorable long-term observation of experimental results, etc., to achieve concentration control and correct , to meet the clinical application, the effect of easy concentration control
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] 1. By measuring the carbon monoxide hemoglobin (COHb) in the blood, the binding degree of carbon monoxide (CO) and Hb can be judged. The method specified in the literature of Steina AB et al. (J Mol Cell Cardiol 38: 127-34, 2005) was used to measure the COHb detection results after using CORM-2 in animals (see Table 1).
[0025] Table 1 COHb detection results after use of CORM-2 in animals
[0026]
[0027] 2. The dosage of CORM-2 in this animal experiment study is 8 mg / kg bw.
Embodiment 2
[0029] Dissolve the carbon monoxide releasing molecule in DMSO solvent, and use the following method to test:
[0030] (1) In cell experiments, the final concentration of CORM-2 is 10M, 50M, and 100M solutions; in animal experiments, the dose of CORM-2 is 8mg / kg bw;
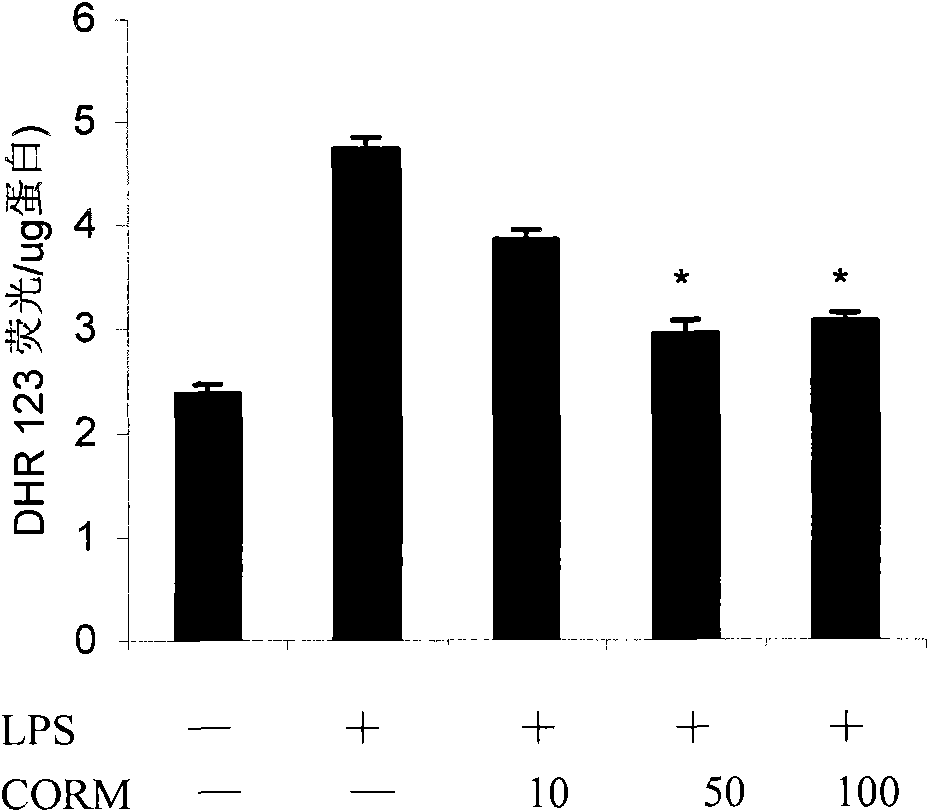
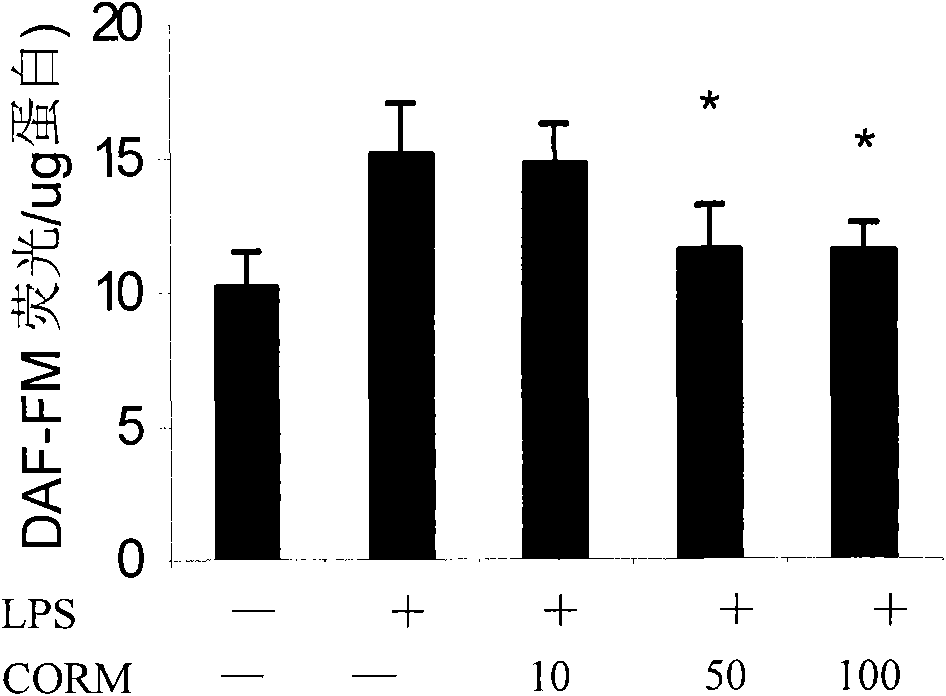
[0031] (2) Effects of different working concentrations of CORM-2 on LPS-induced oxidative stress (DHR 123) and NO production (DAF-FM) in HUVEC cells;
[0032] (3) The effect of different working concentrations of CORM-2 on the expression of LPS-induced HUVEC cell adhesion molecule ICAM-1;
[0033] experiment method:
[0034] Cells: human umbilical cord endothelial cells (passage 3-8), stimulated with LPS (final concentration 10g / ml) for 4 hours, and collected cells;
[0035] Extraction of nuclear and cytoplasmic proteins: Grind tissue samples in liquid nitrogen, then place in 300 l of buffer E (10mmol / L HEPES (pH7.9), 10mmol / L KCl, 1.5mmol / L MgCl2, 1% NP -40, 0.5mmol / L DTT, 0.5mmol / L PMSF, 10g / ml aprotinin, 10...
Embodiment 3
[0041] Inhibitory effect of CORM-2 on hepatic inflammatory response in septic mice.
[0042] experiment method:
[0043] (1) Animal and CLP sepsis model
[0044] Male C57BL / 6 mice, 6-8 weeks old, weighing 18±2 grams, were raised in a general laboratory (commercial dry block feed, free access to water). The experimental animals were divided into five groups according to the random number table method: Sham group (n=9), Sham+CORM-2 group (n=9), CLP group (n=9), CLP plus CORM-2 group (n=9) and CLP+DMSO group (n=9). Under isoflurane inhalation anesthesia, the mice in the CLP group were subjected to cecal ligation and perforation, and 1.5 ml of normal saline was injected intraperitoneally after injury to resist shock; the mice in the CLP plus CORM-2 group were injected with CORM-2 (8 mg / kg) into the tail vein after CLP. ). All animals were sacrificed with isoflurane inhalation 24 hours after injury and collected specimens.
[0045] (2) Detection indicators
[0046] Detection ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com