Detection kit for distinguishing cow pathogenic mycobacteria infection from non-pathogenic mycobacteria infection and method thereof
The technology of Mycobacterium bovis and reagents is applied in the field of immunodetection, which can solve the problems of false positives, complex antigen components, and low sensitivity of serological detection methods, and achieve the effect of strong specificity and sensitivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] Example 1 Construction of recombinant plasmid pET-E6-M63-H70
[0028] 1.1 Extraction of Mycobacterium bovis genomic DNA
[0029] Refer to the method described in the instructions of the bacterial genomic DNA small amount rapid extraction kit (purchased from Beijing Broadtech Gene Technology Co., Ltd.).
[0030] 1.2 Design of primers
[0031] Specific primers were designed according to the ESAT-6, MPB63 and HSP70 gene sequences of Mycobacterium bovis genomic DNA (accession number BX248333) in GenBank. The primers were synthesized by Shanghai Shenggong Biotechnology Co., Ltd. The sequence is shown in Table 1 (the underlined is the enzyme Cut site, the shaded place is Linker).
[0032] Table 1 PCR primer name, sequence and size of amplified product
[0033]
[0034] 1.3 PCR amplification and product recovery of the target gene
[0035] Using M. bovis genomic DNA as a template, LA Taq DNA polymerase was used to amplify the ESAT-6, MPB63 and HSP70 genes. The specific reaction ...
Embodiment 2
[0048] Example 2 Expression and purification of Mycobacterium bovis recombinant fusion protein rE6-M63-H70
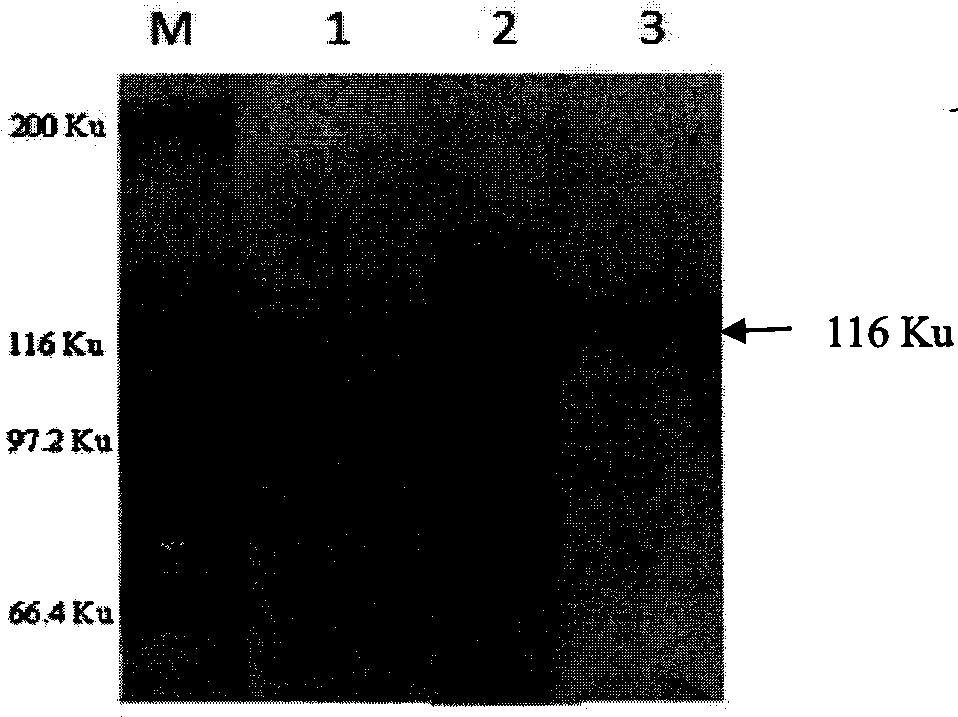
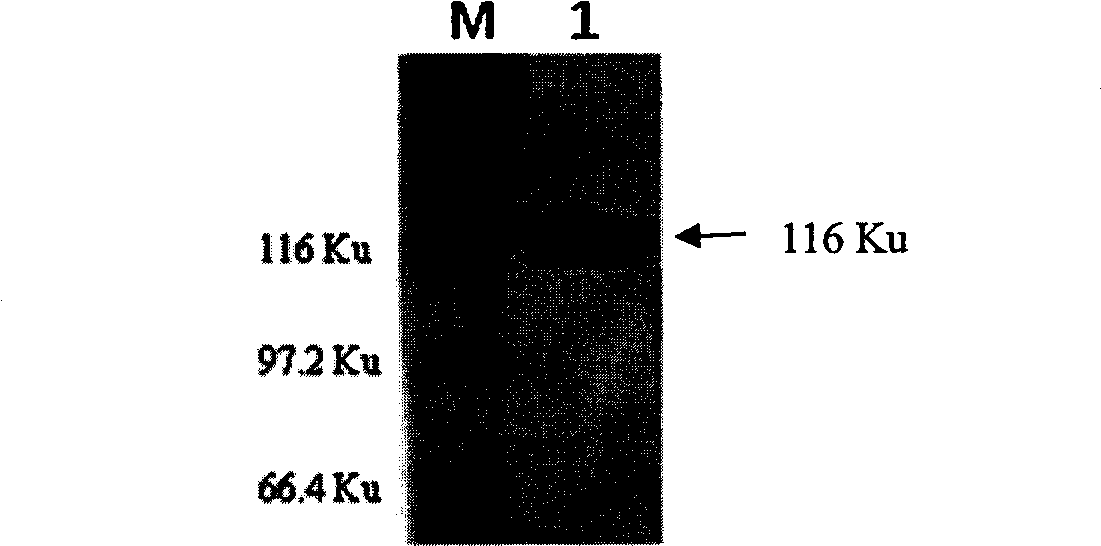
[0049] 2.1 Induced expression, purification, SDS-PAGE and Western-blot analysis of recombinant fusion protein
[0050] The recombinant plasmid pET-E6-M63-H70 prepared in Example 1 was transformed into BL21(DE3) competent cells, and a single colony was picked and inoculated into 200 mL of LB medium containing a final concentration of 25 μg / ml ampicillin at 37°C. Incubate in bed to OD600 = 0.7, add IPTG with a final concentration of 1 mM, induce culture at 30°C, 160 rpm shaker for 10 hours, centrifuge at 9000 rpm for 10 minutes to collect the bacteria, resuspend the bacteria in 60 mL PBS (pH 7.4), and ultrasonically break the bacteria in an ice bath After crushing, the mixture was centrifuged at 12000 rpm, 4°C for 30 min, and then the supernatant was taken. Press His Link TM Protein Purification Resin (purchased from Beijing Zeping Technology Co., Ltd.) operation manual to pu...
Embodiment 3
[0052] Example 3 Establishment of detection method for Mycobacterium bovis
[0053] 3.1 Collection and cultivation of whole blood from cattle to be inspected
[0054] ① Collect 5ml of bovine heparin anticoagulant whole blood under aseptic conditions, transport it to the laboratory at room temperature (22±5℃) and culture within 8 hours after blood collection. ②Add anticoagulant blood to a 24-well tissue culture plate, 1.5ml / well, 2 wells for each cow to be inspected, and then sterilely add 50μl Tris-Cl (100mM, pH8.0, as a negative control stimulus), 50μl Put the solution (20μg) containing rE6-M63-H70 into the corresponding well, mix well, 37℃ CO 2 Incubate for 24h in an incubator. ③After incubation, carefully draw 400μl of upper plasma and transfer it into a 1.5ml centrifuge tube (plasma can be stored at 2-8°C for 7 days, -20°C for several months), and 50μl of plasma can be drawn from each tube as the sample to be tested. ELISA detection of the release level of bovine IFN-γ.
[005...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com