Method for manufacturing microlens and method for manufacturing solid-state image sensor
A manufacturing method and technology of microlens, applied in the direction of lens, semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of reducing sensitivity, reducing design freedom, increasing, etc., to improve convergence characteristics, reduce costs and reduce costs Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0053] A method of manufacturing a microlens according to an embodiment of the present invention is described below.
[0054] In the method of manufacturing a microlens according to an embodiment of the present invention, a microlens mold in which a reverse shape of a microlens has been formed is pressed on a microlens forming film formed on a substrate to convert the reverse shape of the microlens into onto the microlens-forming film to form microlenses.
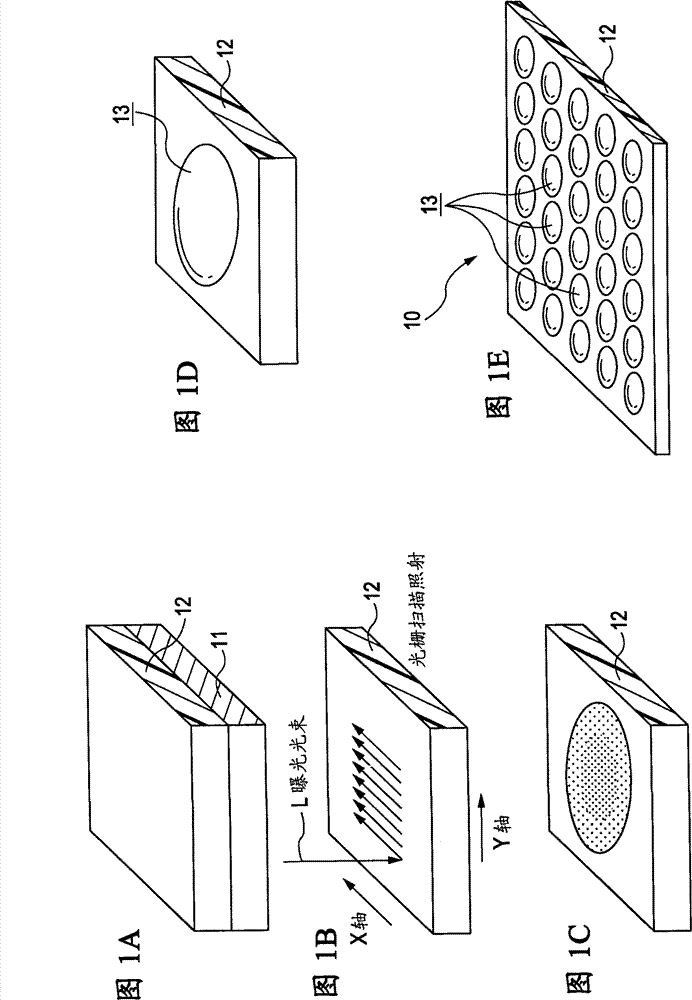
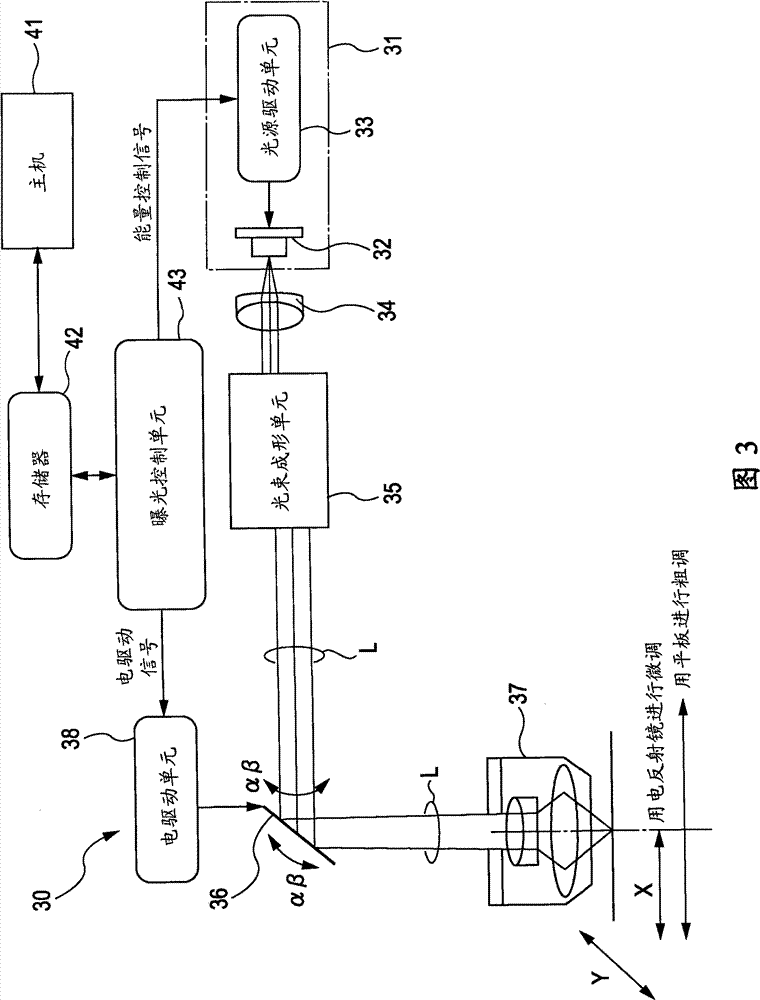
[0055] A process for forming a microlens mold is described with reference to FIGS. 1A to 1E and the process diagram of FIG. 2 .
[0056] As shown in FIG. 1A , an inorganic resist film 12 is formed on a mold substrate 11 . As the mold substrate 11, silicon dioxide (SiO 2 ) substrate or glass substrate. For the inorganic resist film 12, for example, a transition metal oxide is used. For example, tungsten oxide, molybdenum oxide, oxide of tungsten-molybdenum alloy, etc. are used. Such a material is formed on the substrate...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com