Method of preparing alkali lignin modified phenolic resin
A technology of alkali lignin and phenolic resin, which is applied in the field of preparation of environmentally friendly alkali lignin modified phenolic resin, can solve the problems of few types of alkali lignin, no application path, and limited application range, etc. The effect of low glue cost and energy saving
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0021] 1): Add 100g of phenol, 44g of alkali lignin, 80g of the first batch of formaldehyde solution, 0.2g of calcium oxide, and 60g of water into a 500ml four-neck flask, heat up to 80°C, and react for 80min.
[0022] 2): Add the second batch of formaldehyde solution 60g, react at 85°C for 60min.
[0023] 3): Add 60g of the third batch of formaldehyde solution and 10g of the first batch of lye, and react at 85°C for 60min.
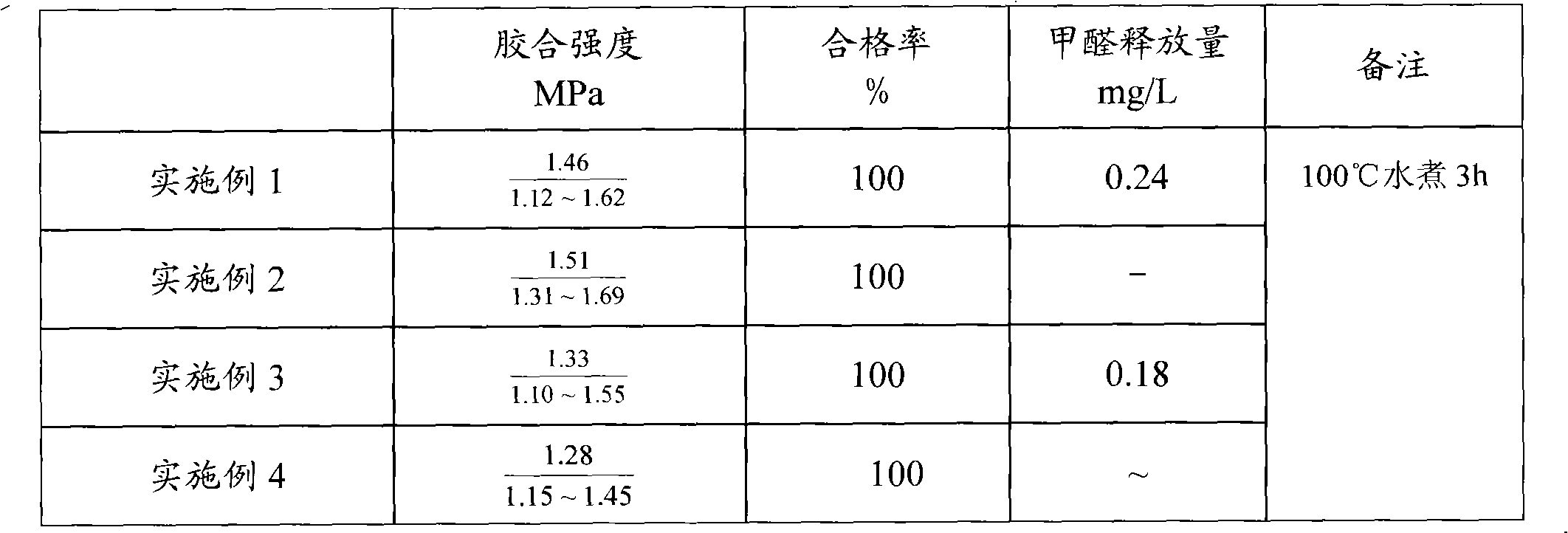
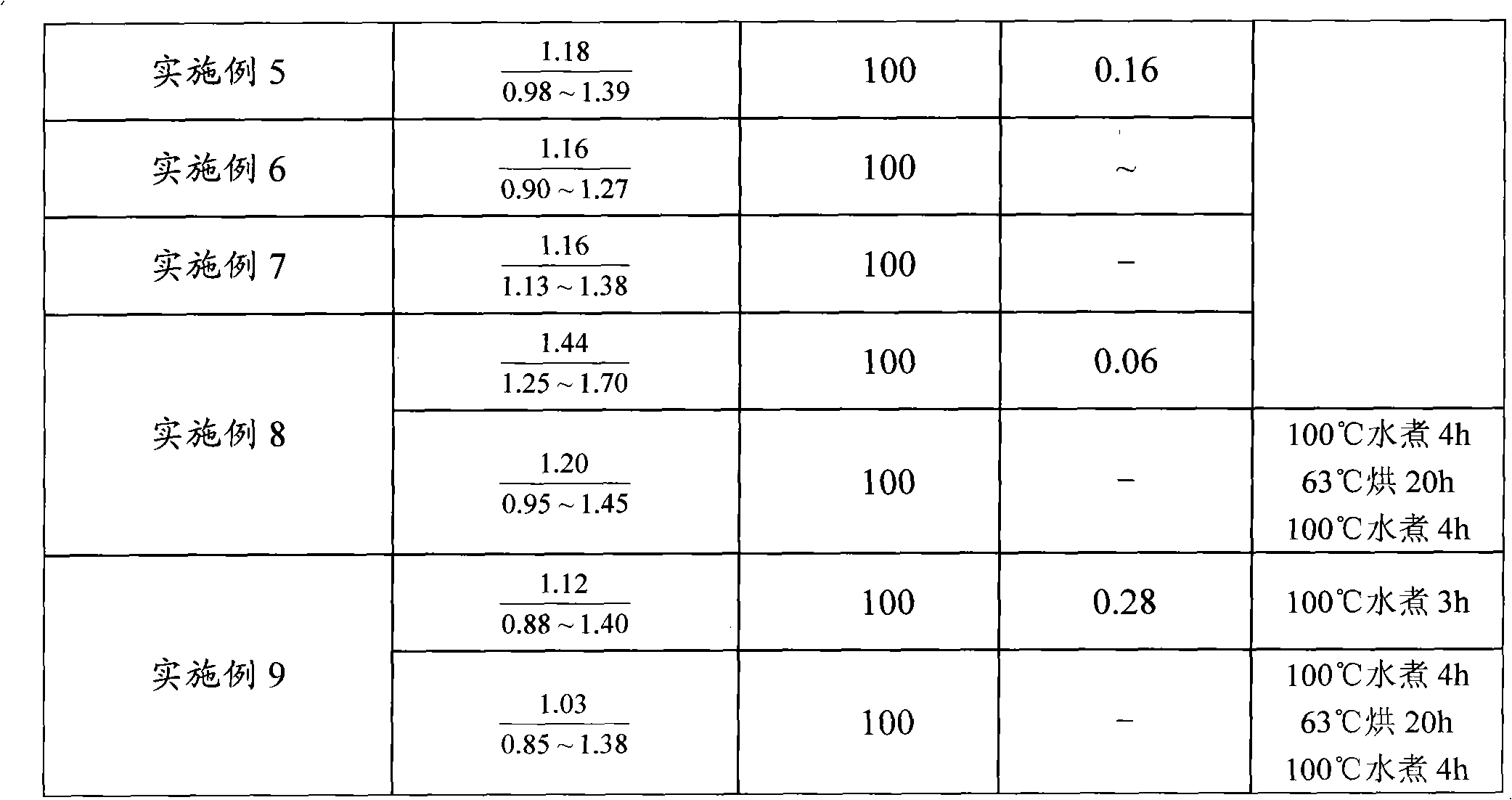
[0024] 4): Cool down to 70°C, add 8g of urea and 30g of the second batch of lye, react at 65°C for 30min, cool and discharge. Test their performance respectively, and the results are listed in attached table 2. Press poplar plywood, test its performance, the results are listed in attached table 3.
Embodiment 2
[0026] 1): Add 100g of phenol, 44g of alkali lignin, 75g of formaldehyde solution, 0.5g of calcium oxide, and 60g of water into a 500ml four-neck flask, heat up to 75°C, and react for 70min.
[0027] 2): Add the second batch of formaldehyde solution 60g, react at 80°C for 70min.
[0028] 3): Add 60g of the third batch of formaldehyde solution and 8g of the first batch of lye, react at 85°C for 60min.
[0029] 4): Cool down to 70°C, add 8g of urea and 30g of the second batch of lye, react at 65°C for 20min, cool and discharge. Test their performance respectively, and the results are listed in attached table 2. Press poplar plywood, test its performance, the results are listed in attached table 3.
Embodiment 3
[0031] 1): Add 100g of phenol, 66g of alkali lignin, 80g of formaldehyde solution, 0.2g of calcium oxide, and 90g of water into a 500ml four-neck flask, heat up to 80°C, and react for 60min.
[0032] 2): Add the second batch of formaldehyde solution 60g, react at 85°C for 70min.
[0033] 3): Add 60g of the third batch of formaldehyde solution and 10g of the first batch of lye, and react at 85°C for 60min.
[0034] 4): Cool down to 70°C, add 8g of urea and 30g of the second batch of lye, react at 70°C for 30min, cool and discharge. Test their performance respectively, and the results are listed in attached table 2. Press poplar plywood, test its performance, the results are listed in attached table 3.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com