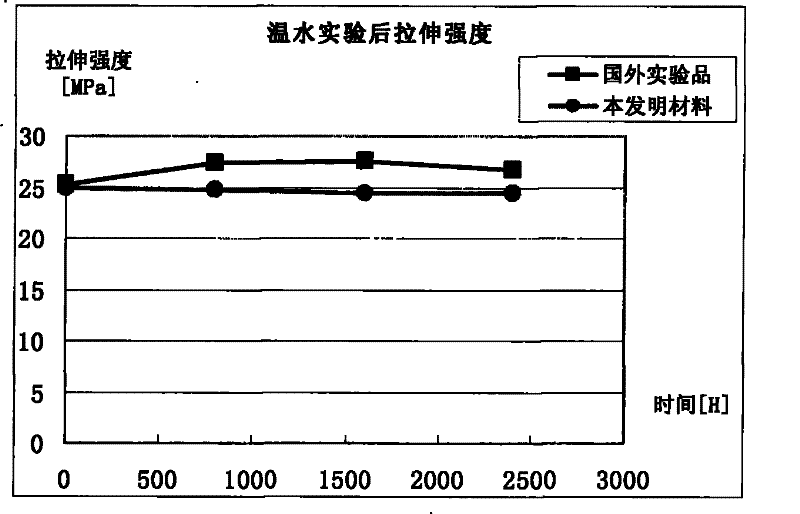
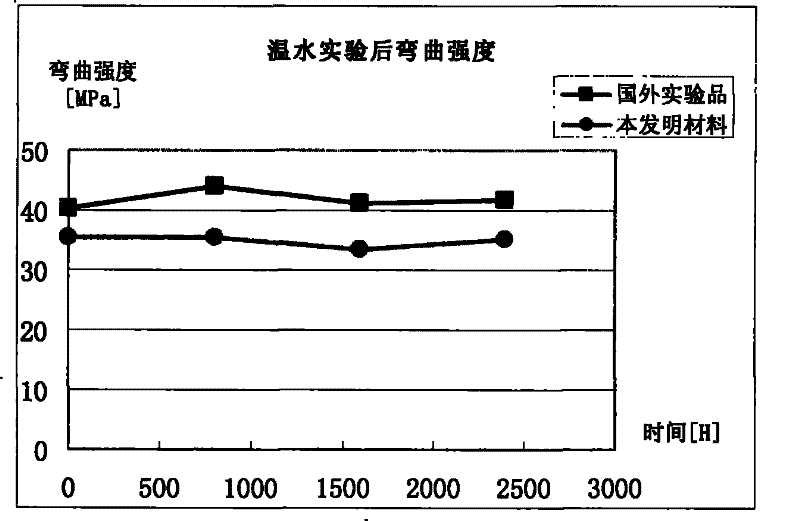
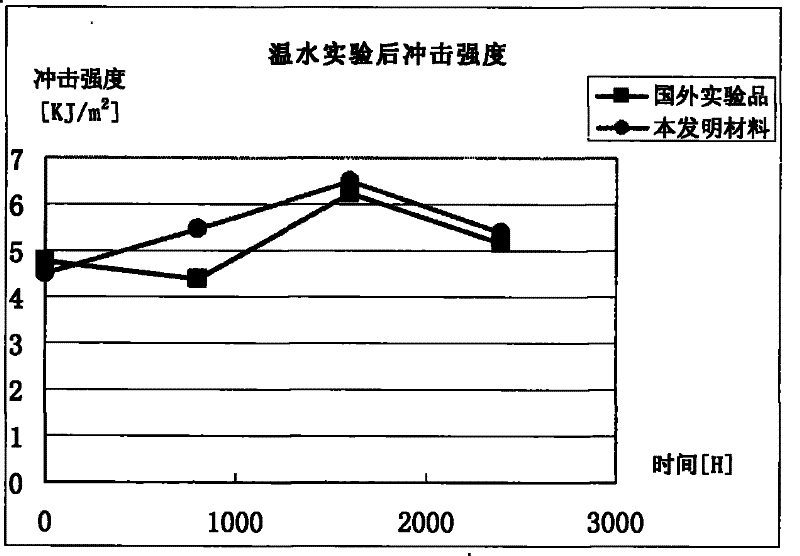
Polypropylene modified material and production method thereof
A technology for modifying materials and production methods, applied in the field of organic materials, can solve problems such as mechanical properties, thermal oxidation resistance, insufficient processing technology, and increase production costs, and achieves low cost, low production cost, and good mechanical properties. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0049] 1. First treat 20 parts of talc powder with 0.3 parts of silane coupling agent KH550, and set aside;
[0050] 2. Add 60 parts of copolymerized polypropylene and 20 parts of homopolypropylene into the high-mixing tank in turn, mix thoroughly, and then add the talcum powder treated in step (1), antioxidant, 0.2 parts of metal blunt into the high-mixing tank Chemicalizing agent MD1024, 0.2 parts of nucleating agent ZC-3 and 0.1 parts of calcium stearate, wherein the antioxidant consists of 0.3 parts of antioxidant 1010, 0.3 parts of antioxidant 1076, 0.2 parts of antioxidant 168 and 0.2 parts of antioxidant Composition of agent 802FD, mixed in a high mixer for 4 minutes, mixed fully and put into the lower hopper to mix and melt with a twin-screw machine. The mixing and melting temperature is: 185°C for the first section, 205°C for the second section, and 215°C for the third section , The fourth section is 210°C, the fifth section is 200°C, the sixth section is 205°C, the s...
Embodiment 2
[0053] 1. First treat 15 parts of talc powder with 0.2 parts of silane coupling agent, and set aside;
[0054] 2. Add 55 parts of copolymerized polypropylene and 15 parts of homopolypropylene into the high-mix tank in turn, mix thoroughly, and then add the talcum powder treated in step (1), antioxidant, 0.1 part of metal Passivator, 0.1 part of nucleating agent and 0.05 part of calcium stearate, wherein antioxidant consists of 0.2 part of antioxidant 1010, 0.2 part of antioxidant 1076, 0.1 part of antioxidant 168 and 0.1 part of antioxidant 802FD , mixed in the high mixer for 3 minutes, mixed fully and put into the lower hopper to mix and melt with a twin-screw machine. Section 208°C, fifth section 198°C, sixth section 203°C, seventh section 203°C, melt temperature 203°C and die temperature 198°C;
[0055] 3. Extrude the strands from the twin-screw machine, cool the strands with water, dry the water on the surface of the strands, and then cut into pellets.
Embodiment 3
[0057] 1. First treat 25 parts of talcum powder with 0.4 parts of silane coupling agent KH550, and set aside;
[0058] 2. Add 65 parts of copolymerized polypropylene and 25 parts of homopolypropylene into the high-mixing tank in turn, mix thoroughly, and then add the talcum powder treated in step (1), antioxidant, 0.3 parts of metal Passivator MD1024, 0.3 part of nucleating agent ZC-3 and 0.2 part of calcium stearate, wherein the antioxidant consists of 0.3 part of antioxidant 1010, 0.3 part of antioxidant 1076, 0.3 part of antioxidant 168 and 0.3 part of antioxidant Composition of oxygen agent 802FD, mixed in high mixer for 5 minutes, mixed fully and put into lower hopper to mix and melt with twin-screw machine, mixing and melting temperature: 187°C for the first section, 207°C for the second section, 217°C for the third section ℃, the fourth section 212°C, the fifth section 202°C, the sixth section 207°C, the seventh section 207°C, the melt temperature 207°C and the die temp...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com