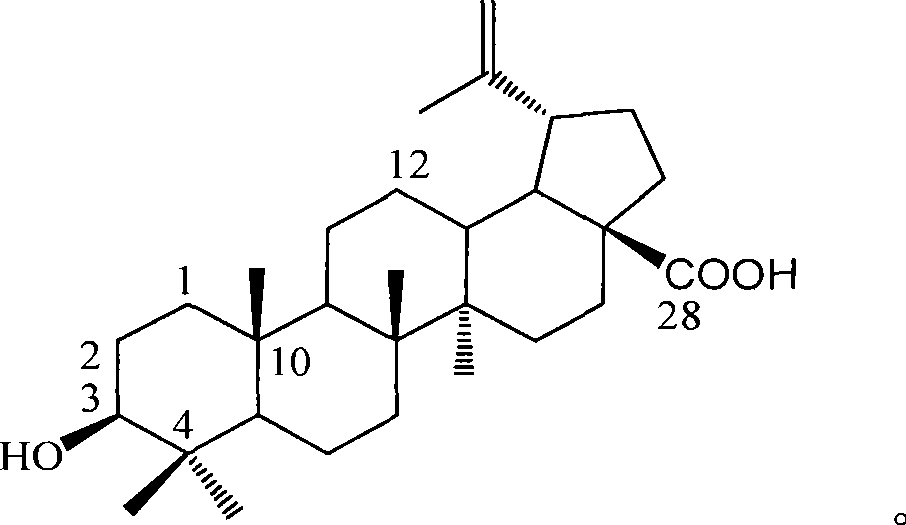
Use of betulinic acid in preparing glycosidase inhibitor medicine
The technology of a glycosidase inhibitor, betulinic acid, is applied in the field of natural medicinal chemistry to achieve the effects of simple preparation process, improved economic efficiency and environmental friendliness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0018] Example 1 : Preparation of betulinic acid from dry leaves of Lagerstroemia tomentosa
[0019] 1.1 Instruments and reagents
[0020] H NMR spectrum ( 1 H-NMR), carbon nuclear magnetic resonance spectrum ( 13 C-NMR) and two-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance spectrum (2D NMR) were measured by INOVA type superconducting nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer (VARIANINOVA-400MHz) (tetramethylsilyl ether as internal standard); electrospray mass spectrometry (ESI-MS) was determined by Bruker Esquire 3000+ mass spectrometer, silica gel (100-200, 200-300) for column chromatography and silica gel GF254 (10-40 mesh) for thin layer chromatography were purchased from Qingdao Ocean Chemical Factory; all reagents used were analytically pure, The boiling range of petroleum ether is 60-90° C.; the thin plate (TLC) detection uses 254nm and 365nm ultraviolet lamps; the color developer uses 10% sulfuric acid-ethanol and bromocresol green solution.
[0021] 1.2 Plant source and id...
Embodiment 2
[0029] Example 2 : Preparation of betulinic acid from fresh leaves of Lagerstroemia tomentosa
[0030] 2.1 Instruments and reagents: Same as Example 1.
[0031] 2.2 Plant source and identification: Same as Example 1.
[0032] 2.3 Extraction and separation
[0033] The sample (fresh leaves of Lagerstroemia tomentosa, weighing 0.5 kg) was immediately minced with a knife and extracted twice at room temperature with 95% ethanol for 24 hours each time. The extracts were cooled and combined, and concentrated under reduced pressure to obtain 35 grams of brown Black viscous crude extract. Dissolve the crude extract in 2 liters of hot water, extract with petroleum ether (2 liters / time, 3 times in total), evaporate the solvent under reduced pressure, and use 10 grams of 100-200 mesh silica gel to obtain the petroleum ether extract (10.1 grams) Mix the sample, and use a silica gel column (200-300 mesh, 150 g) for column chromatography, and use petroleum ether-ethyl acetate (100:0-0:...
Embodiment 3
[0035] Example 3 : Preparation of betulinic acid (betulinic acid) in crape myrtle tomentosa stems and root bark
[0036] 3.1 Instruments and reagents: Same as Example 1.
[0037] 3.2 Plant source and identification: Same as Example 1.
[0038] 3.3 Extraction and separation
[0039] The sample (crape myrtle tomentosa stems and root bark, dry weight 0.5 kg) was pulverized and extracted twice at room temperature with 95% ethanol for 24 hours each time. The extracts were cooled and combined, and concentrated under reduced pressure to obtain 43 grams of brown viscous crude extract. Dissolve the crude extract in 2 liters of hot water, extract with petroleum ether (2 liters / time, 3 times in total), evaporate the solvent under reduced pressure, and use 10 grams of 100-200 mesh silica gel to obtain the petroleum ether extract (12.2 grams) Mix the sample, and use a silica gel column (200-300 mesh, 150 g) for column chromatography, and use petroleum ether-ethyl acetate (100:0-0:100)...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com