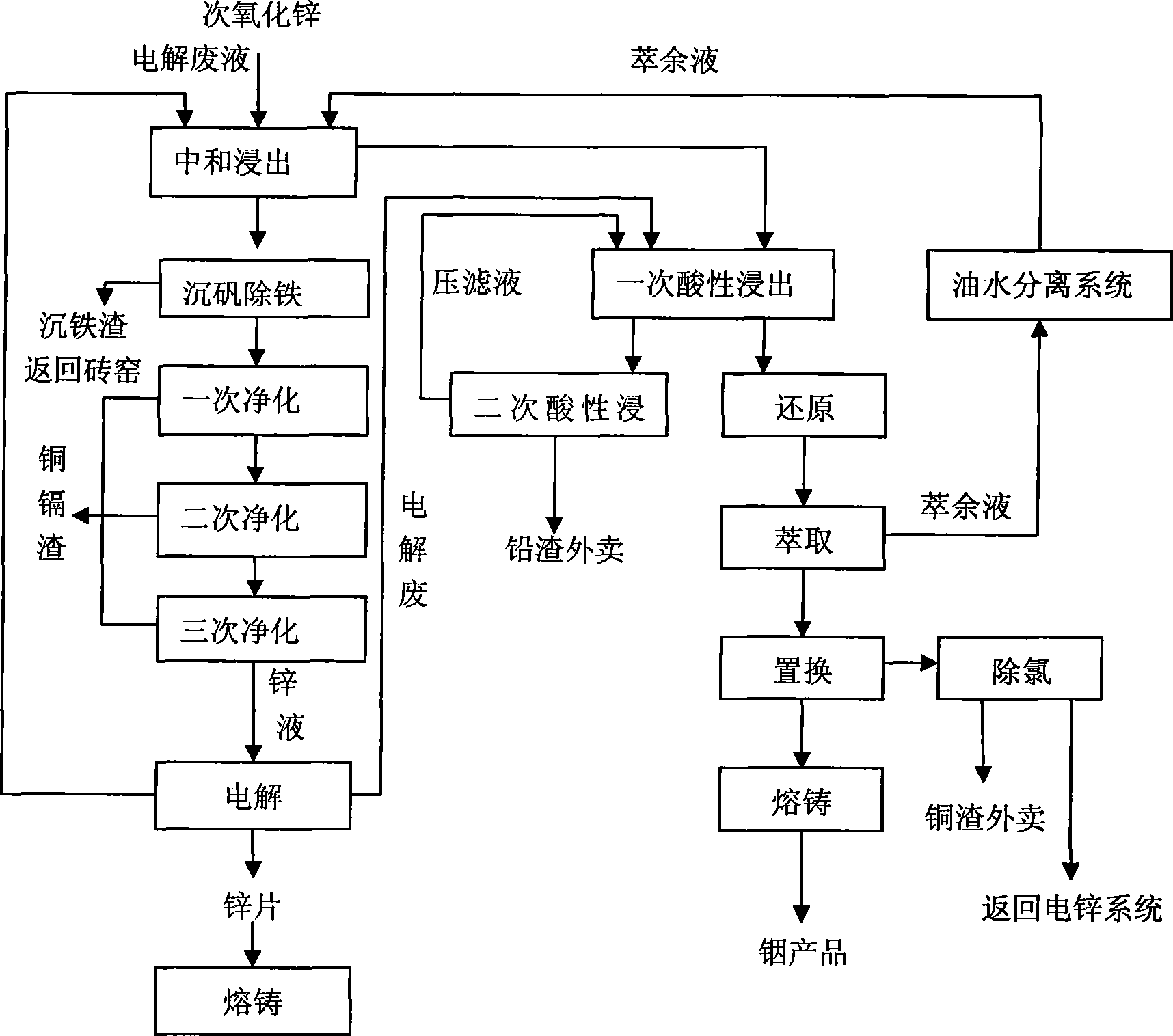
Process for comprehensively and efficiently recycling zinc and indium in indium raffinate
An indium raffinate and raffinate technology are applied in the field of raffinate recycling, can solve the problems of affecting the electrolytic zinc process, cannot be decomposed and destroyed by heavy metals, and have high processing costs, achieve significant environmental protection effects, and achieve environmental protection effects. Achieve emission-free results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
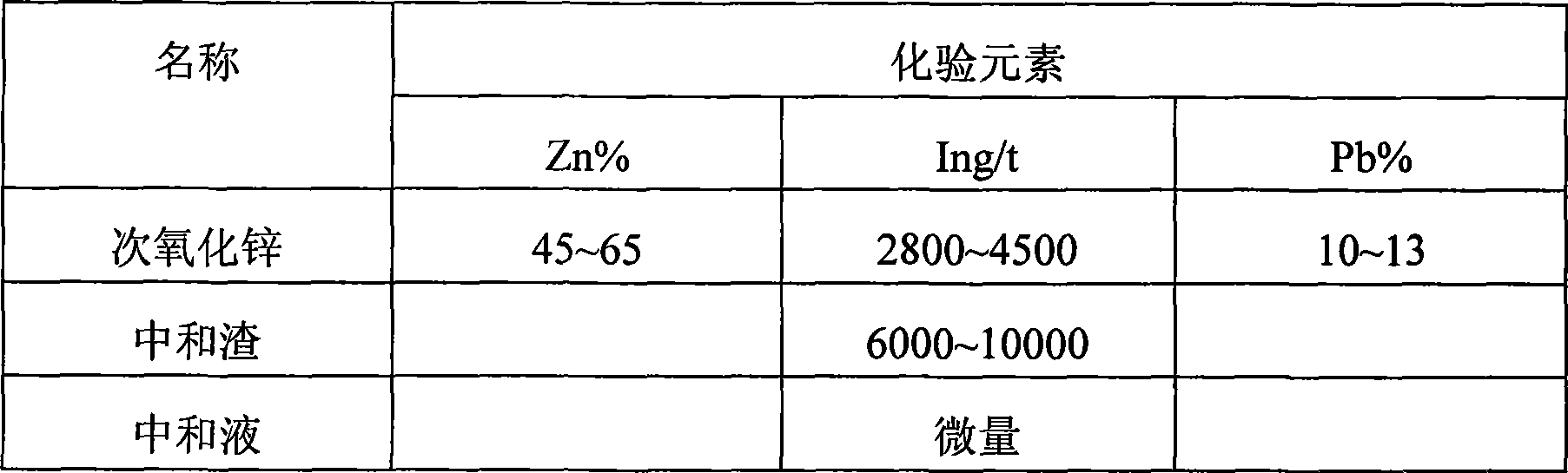
[0048] Raw material: secondary zinc oxide, the ingredients are as shown in Table 1
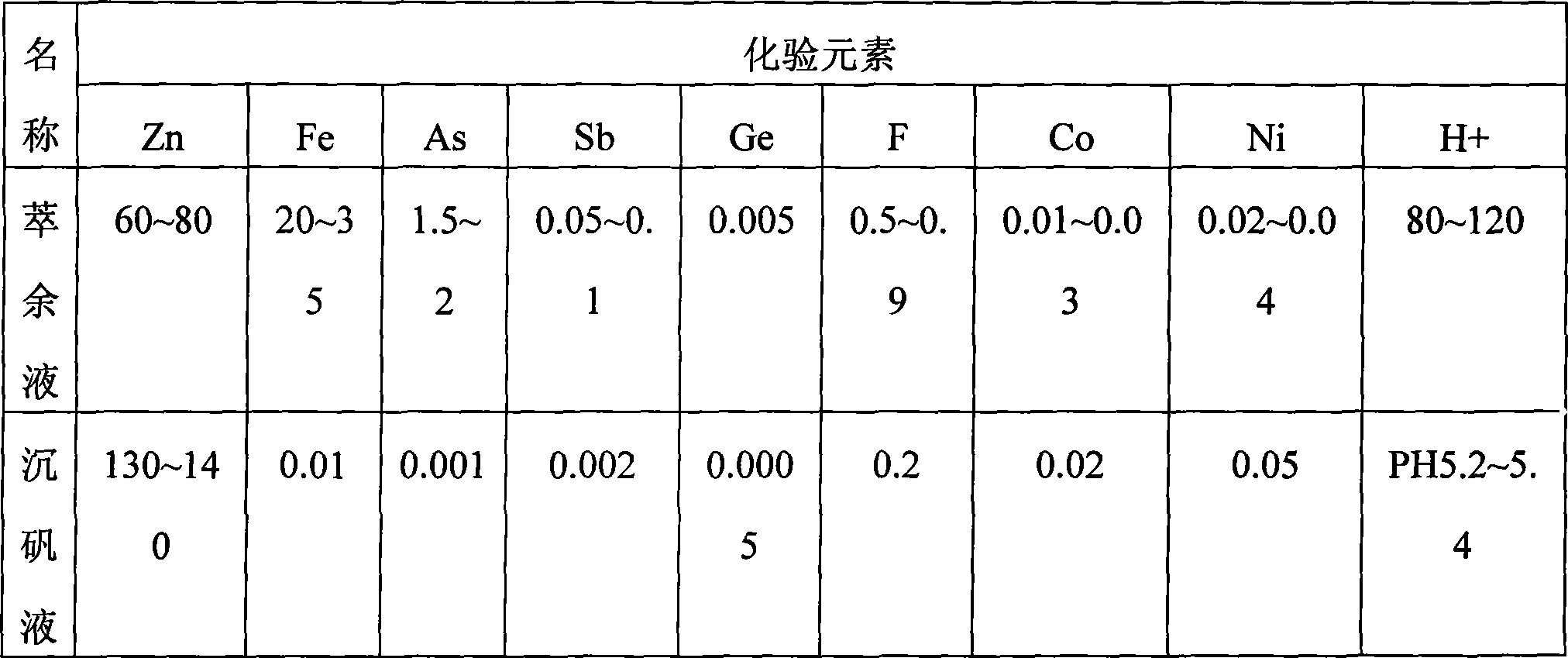
[0049] Indium raffinate, the composition is as follows Table 2
[0050] Electric zinc production process
[0051] 1. Neutralization and leaching
[0052] at 50m 3 In the mechanically stirred reaction tank, add sulfuric acid, remove the raffinate of the organic phase and the electrolytic waste liquid of electrolytic zinc when recovering indium, ensure the initial acid 150g / L, the liquid-solid mass ratio is 6:1, slowly add 8t of sub-zinc oxide, Raise the temperature to 60°C, react for 1.5 hours, and when the measured pH value reaches 4.5, press filter, and the press filter residue is subjected to acid leaching to extract indium, and the filtrate is sent to the iron precipitation process.
[0053] Table 1
[0054]
[0055] The results show that there is a small amount of indium in the solution, and most of the indium enters the slag.
[0056] 2. Alum sinking process
[0057] Inject the i...
Embodiment 2
[0088] 1. Neutralization and leaching
[0089] at 50m 3 Add sulfuric acid to the mechanically stirred reaction tank, add sulfuric acid, remove the raffinate of the organic phase, start acid 170g / L, slowly add zinc oxide 9t, liquid-solid volume ratio: 6:1, raise the temperature to 65°C, measure the pH value after 2 hours of reaction When it reaches 4.0, press filter, the press filter residue is acid leached to extract indium, and the filtrate is sent to the iron precipitation process.
[0090] 2. Alum sinking process
[0091] Pour the neutralizing solution into 50m 3 A mechanically stirred reaction tank with a volume of 45m 3 . Use the electrolytic waste solution to adjust the pH to 2.0, (stir evenly, take a sample for testing), raise the temperature to about 60°C, add manganese powder according to the iron test result, the liquid-solid volume ratio: 5:1, and raise the temperature to 90°C. Reaction 3h. When Fe≤0.02g / L is tested, add lime milk, adjust the pH value to 5.4, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com