Non-failure valve tripping criteria recognizing breaking point based on local measurement
A technology of fault-free tripping and distance, applied in the direction of automatic disconnection emergency protection devices, electrical components, circuit devices, etc., can solve problems such as too simple judgment of side tripping, misjudgment, and no good solution for segmented lines , to achieve the effect of accurate judgment and good applicability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
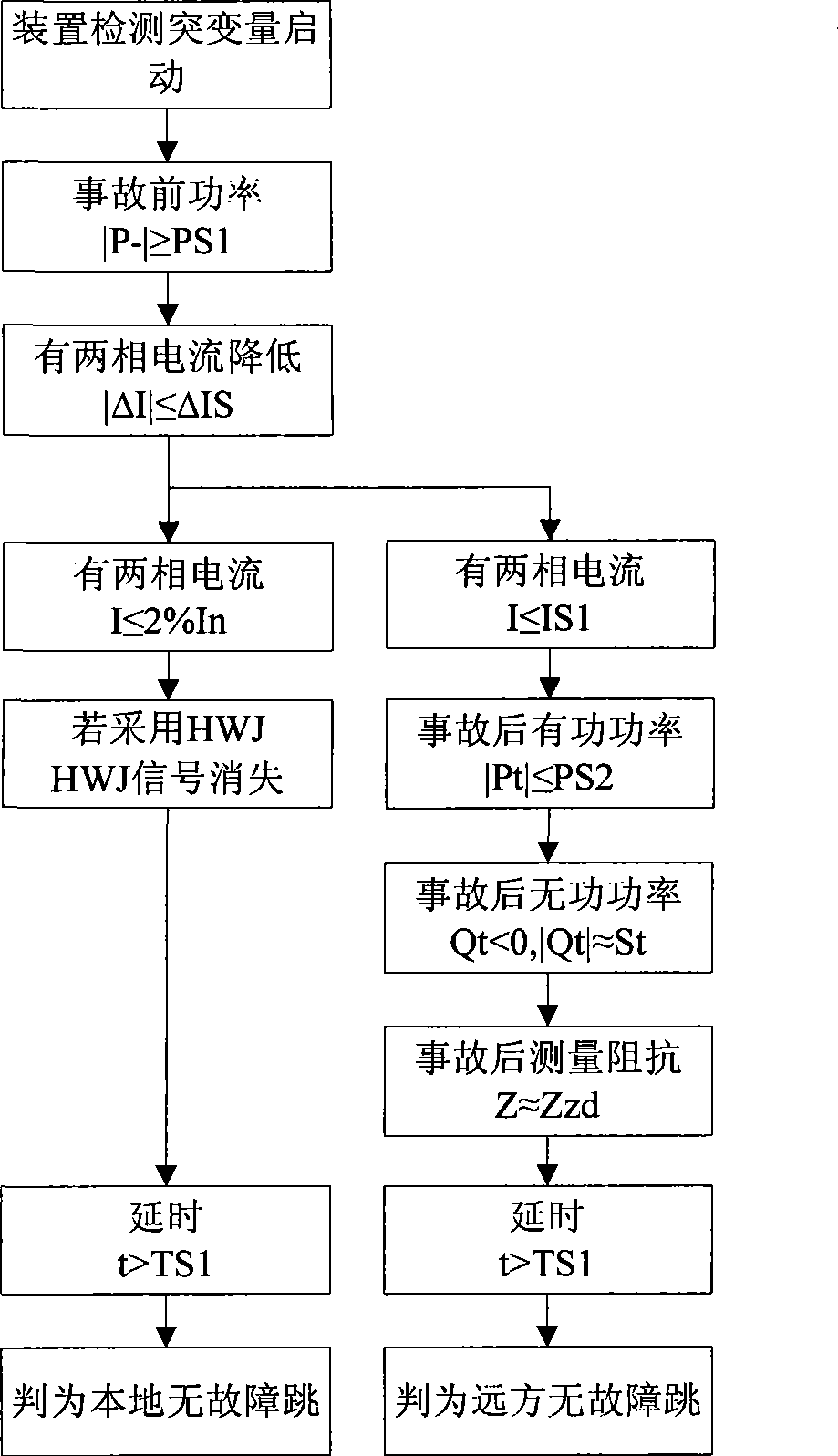
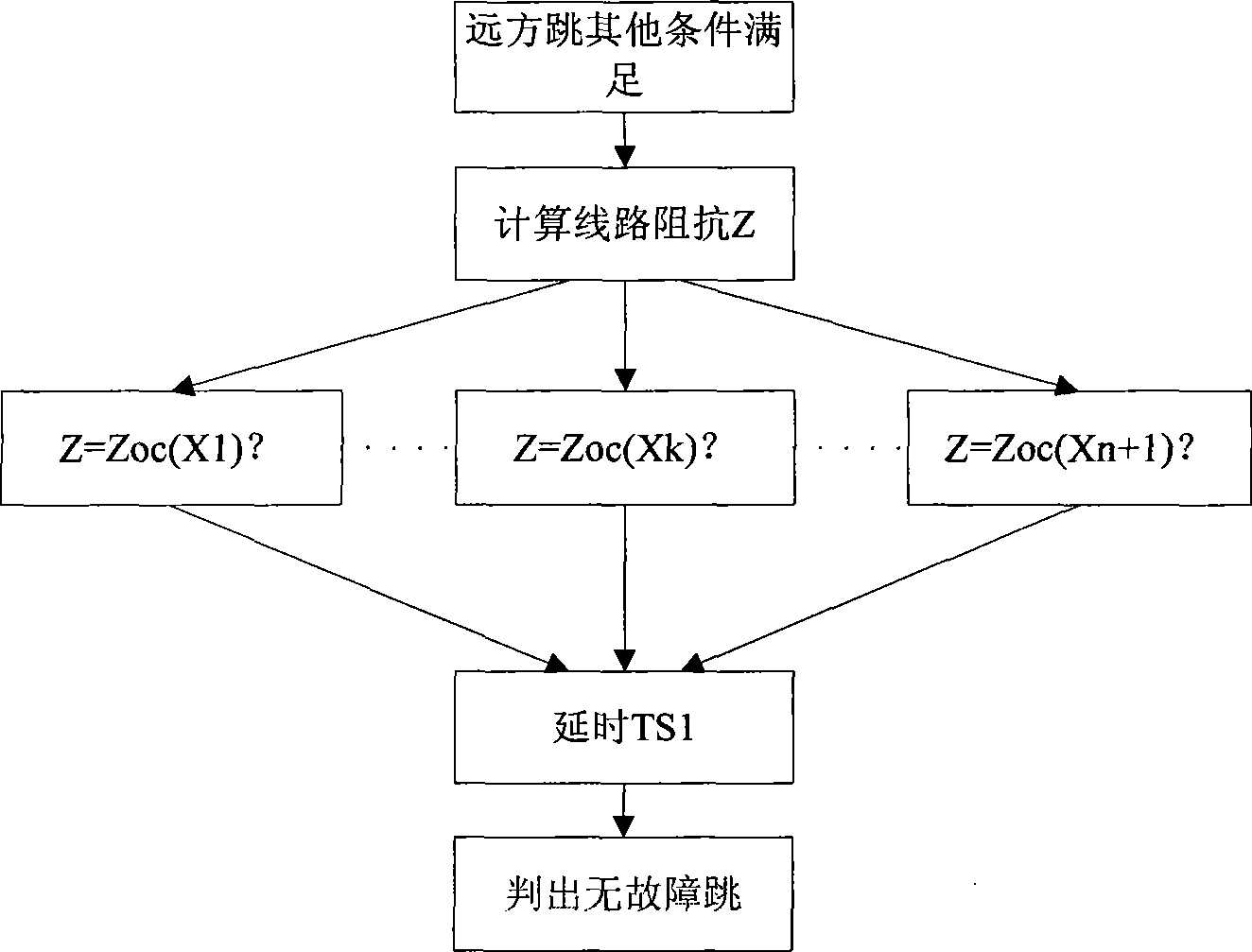
[0028] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with accompanying drawing. From attached figure 1 It can be seen from the figure that after the device collects the current and voltage, it first calculates the electrical quantities such as active power, reactive power, impedance, etc., and judges the start of the sudden change according to the sudden change of current or power, that is, the difference between the current current of any phase of the line and the instantaneous value 20ms ago If it is greater than the fixed value ΔIs, it will be considered that the current mutation has started after 5ms in a row; if the difference between the current power and the power before 0.2s is greater than the fixed value ΔPs (generally set between 5% and 10% of the rated power), it will be considered as continuous after 5ms. The power delta starts.
[0029] After entering the start-up state (keep for 5s), record the power before start-up, and judge whether it ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com