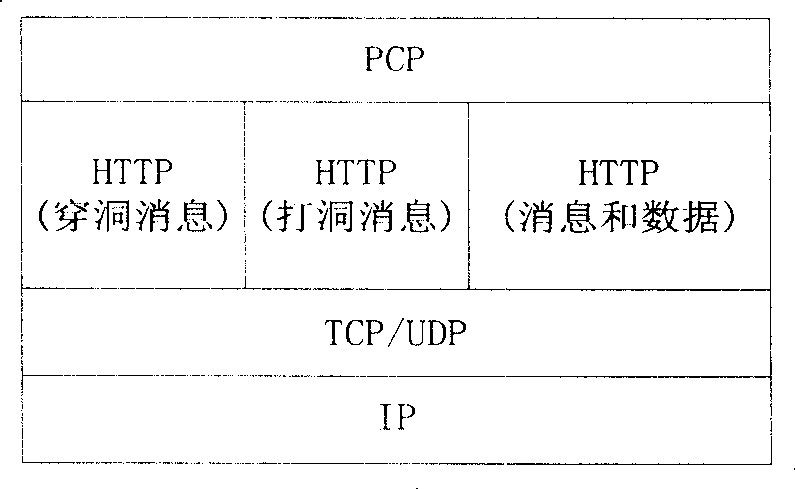
TCP NAT crossing method base on PCP protocol
A protocol and hole-piercing technology, applied in the field of TCP NAT traversal, which can solve the problems that peer nodes cannot directly connect and communicate, TCPNAT traversal, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
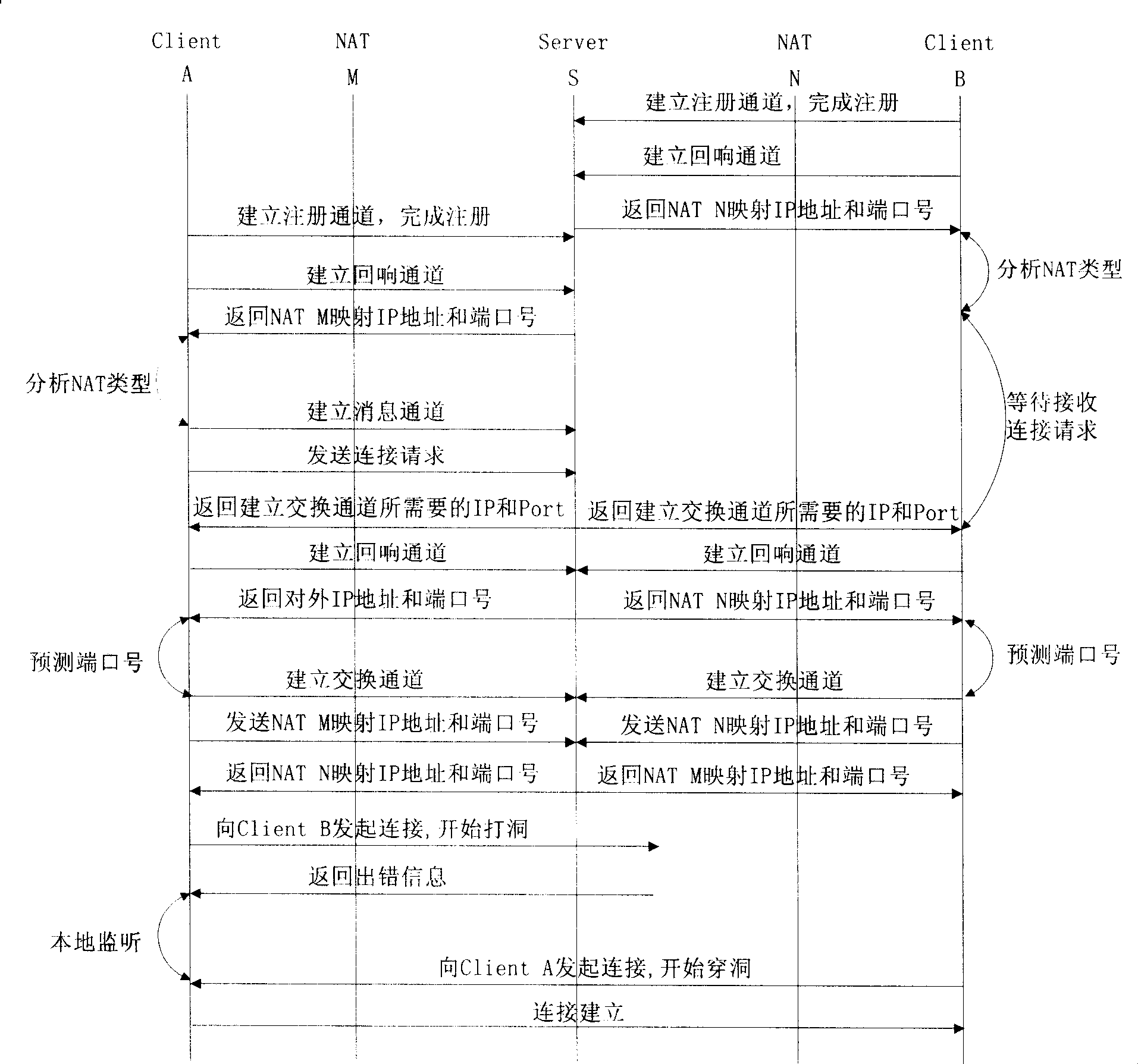
[0034] Assuming that client A is the initiator of the connection, client B is the connected party, and server S is the NAT traversal server, the process of realizing TCP NAT traversal can be divided into the following five steps:
[0035] 1) Client B first connects to server S, establishes a registration channel, and completes registration through this channel using the ID number that identifies the machine. After registration, if no NAT type detection has been performed before or if there is a change in the NAT configuration, it needs to be registered. NAT type detection, the detection process is as follows:
[0036] Client B initiates four consecutive connections to server S and establishes an echo channel, through which server S returns the corresponding NAT N mapped IP addresses and port numbers for the four connections. Server S analyzes and judges the results returned four times and saves them as records, and then client B waits to receive the connection request from cli...
Embodiment 2
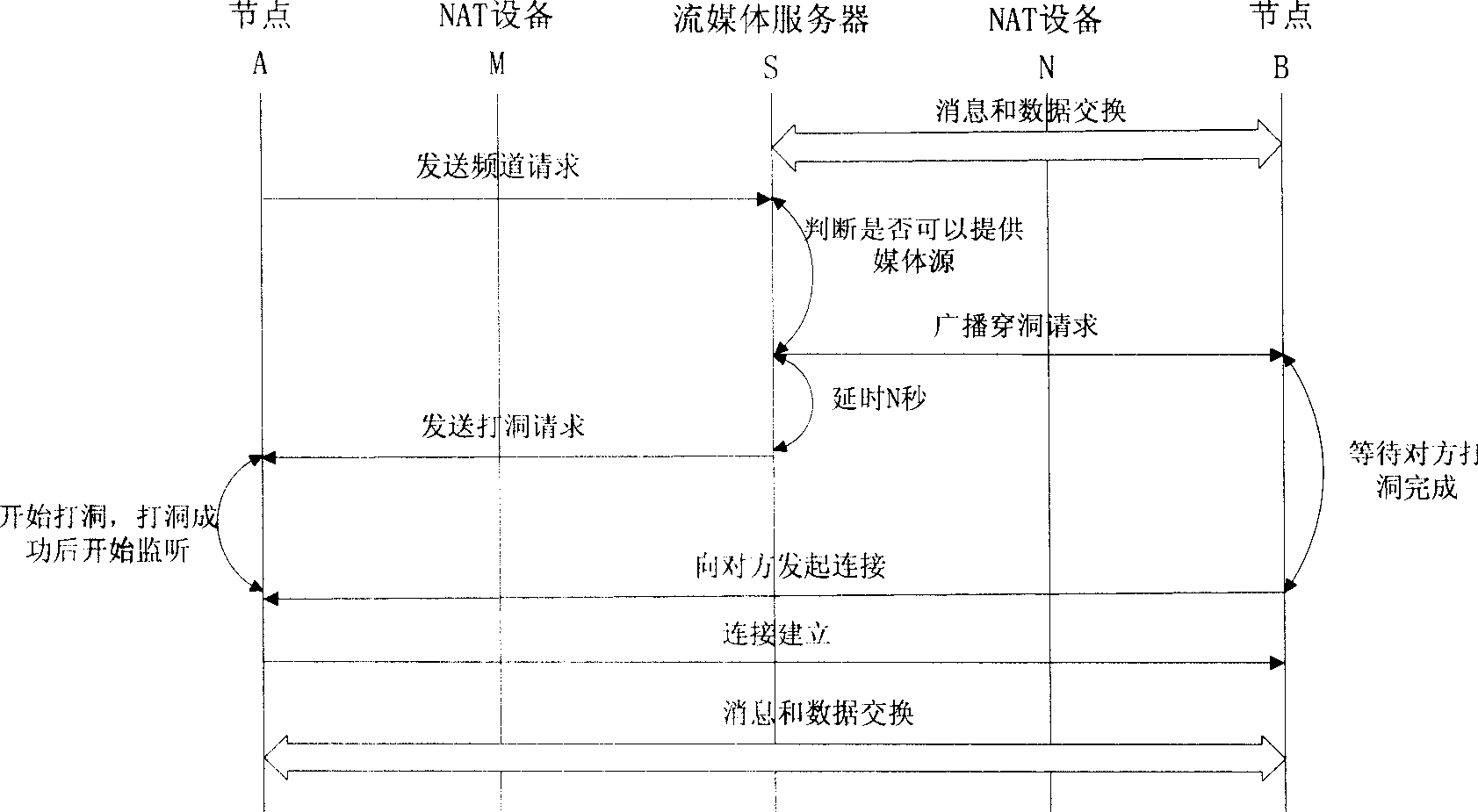
[0043] Combining the above TCP NAT traversal principle with the PCP protocol to realize TCP NAT traversal, the traversal process is shown in the figure below. Among them, node A and node B are hosts located in two private networks behind NAT M and NAT N respectively, S is a streaming media server, node B and streaming media server S have established a connection and can send and receive messages and media data normally, The implementation process is as follows:
[0044]When node A wants to play a certain channel, it will send a channel request to the streaming media server S. After receiving the request, the server S first judges whether the node A has a firewall or is behind a NAT M, and then judges whether the node A can provide media data for the node. If the server S cannot provide it, a node is selected from the node list of the channel. If the selected node is also behind a NAT or firewall, a broadcast hole-through request is sent to nodes such as B. Unicast the hole ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com