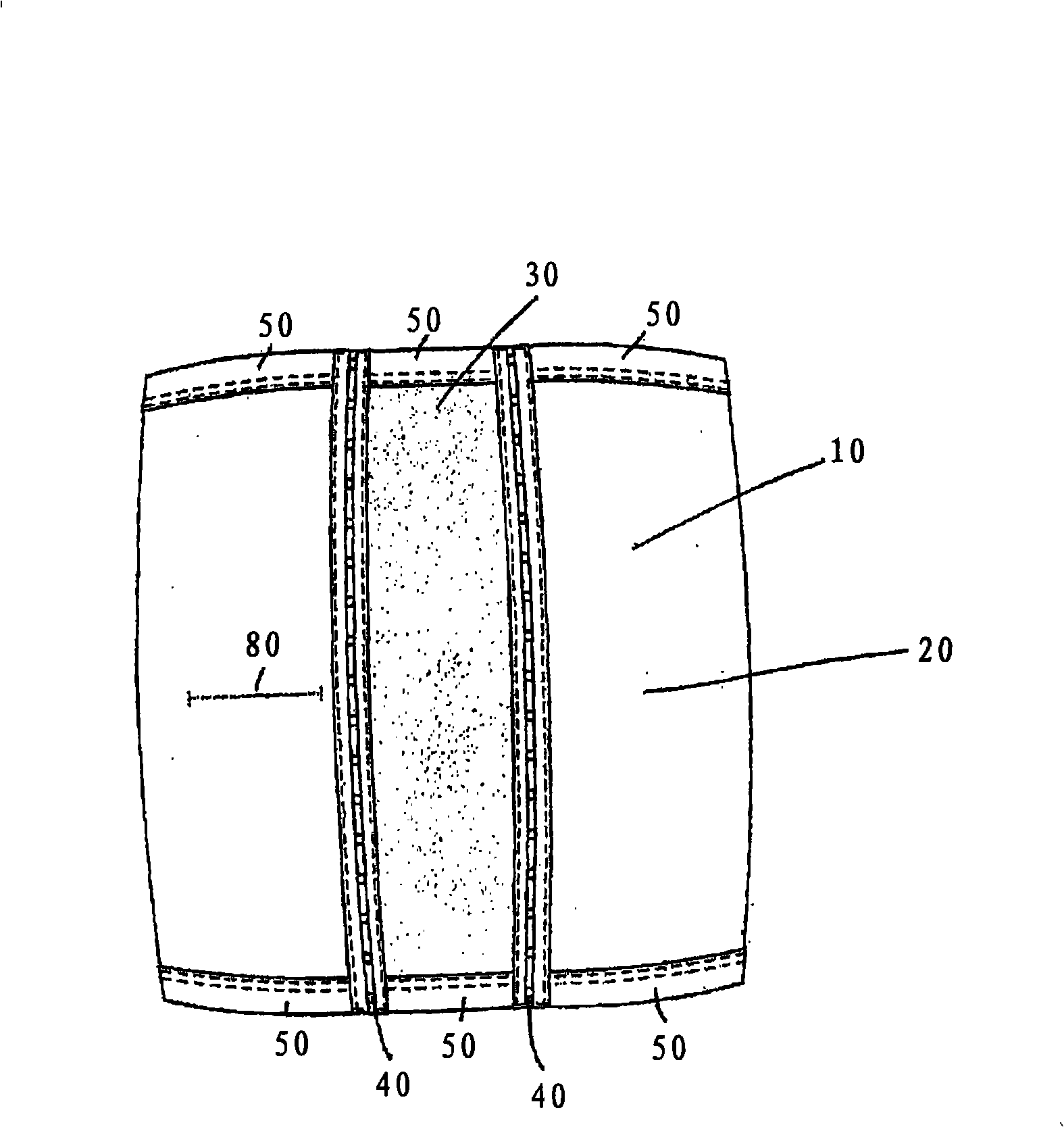
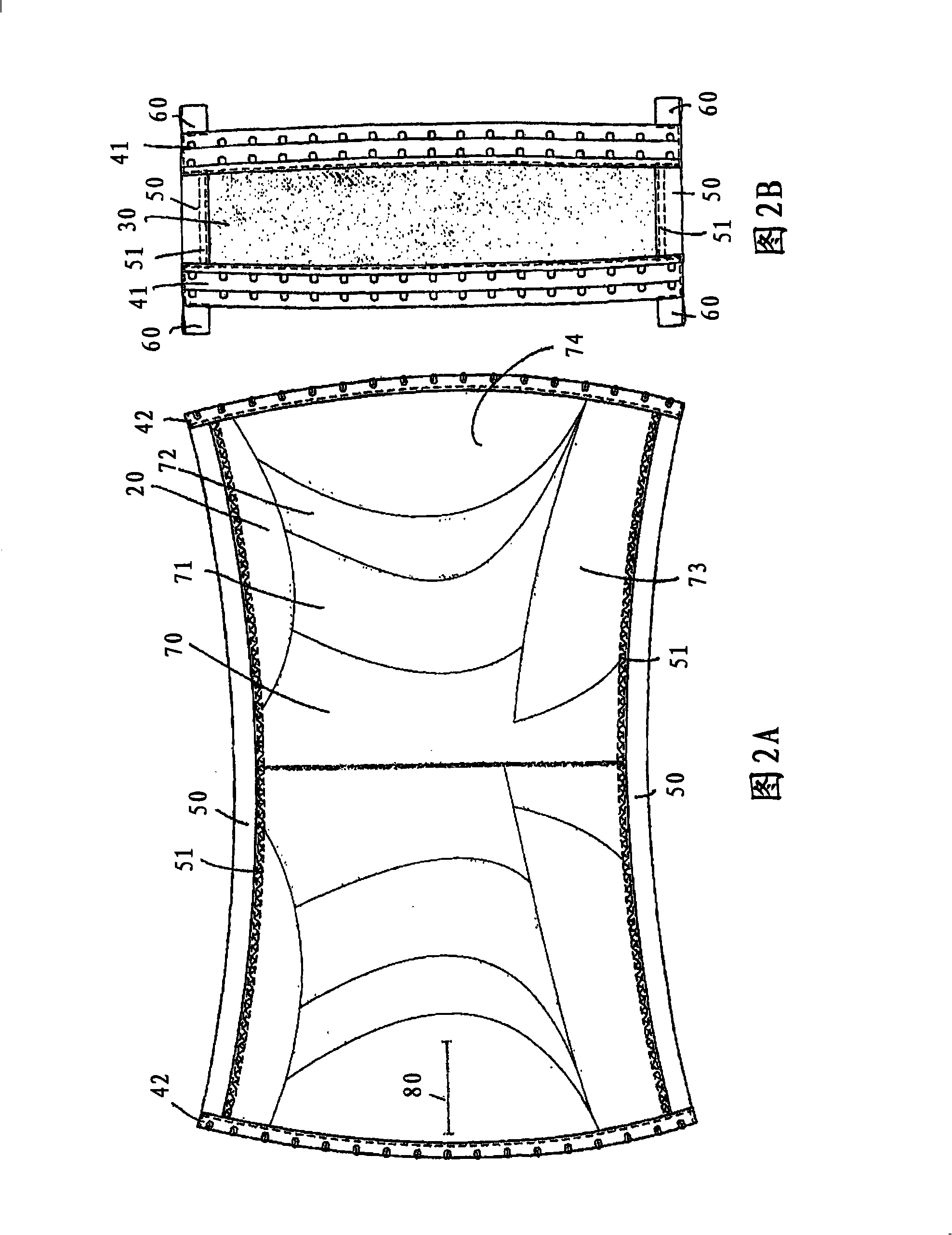
Abdominal compression
A technology for compressing clothing and abdominal girdle, used in medical science, bandages, etc., can solve problems such as non-compliance with postoperative procedures, increased risk of healing complications, patient discomfort, etc., to reduce incisional hernia formation, small elongation, Comfortable to wear
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0151] Example 1: Calculation of Tensile Test and Pressure
[0152] It is essential that the garment provides proper compression. However, there is no consensus on eg how to define abdominal compression and how it should be calculated. Most human torsos have a somewhat elliptical shape, which implies that the pressure provided eg by the abdominal girdle varies along the torso according to Laplace's equation. A distinction therefore needs to be made between local measurements, eg by probes, and the overall material properties. In the following, guidance is provided on how to measure elastic stress and the associated compression as defined here.
[0153] When an elastic material is stretched or elongated, the material exhibits elastic stress. This elastic stress depends on the elongation and fundamental properties of the elastic material. It can be measured by a standard mechanical tensile test well known in the art.
[0154] like Figure 11 A tensile test is performed by ...
example 2
[0186] Example 2: Materials
[0187] Material A: Padding fabric
[0188] warp knit fabric
[0189] Construction: Double bar raschel knit with a flat back and a pattern of holes (visible) on the front side.
[0190] Yarns: 100% polyester, filament yarns and monofilament pile yarns
[0191] Fabric Properties:
[0192] Thickness: 3.0mm (DIN EN ISO 5084)
[0193] Weight per unit area: 320g / m 2 (ISO3801:1997)
[0194] Compressive stress in transverse direction: 12.0kPa at 40% elongation (DIN 53 577)
[0195] This fabric is essentially an example of a non-stretchable pad fabric.
[0196] Material B: Warp knitted fabric, mesh fabric
[0197] warp knitted fabric
[0198] Structure: Single needle bar warp knitted fabric with hole structure
[0199] Yarn: 100% polyamide, filament yarn
[0200] Fabric Properties:
[0201] Thickness: 0.33mm (internal test method)
[0202] 2.2 holes per cm width, 3.5 holes per cm length
[0203] Weight per unit area: 65.0g / m 2 (ISO3801:1997) ...
example 3
[0252] Example 3: Elastic properties of Garment 1
[0253] In this example, the support portion is considered to be inextensible in its entirety when calculating the resulting pressure.
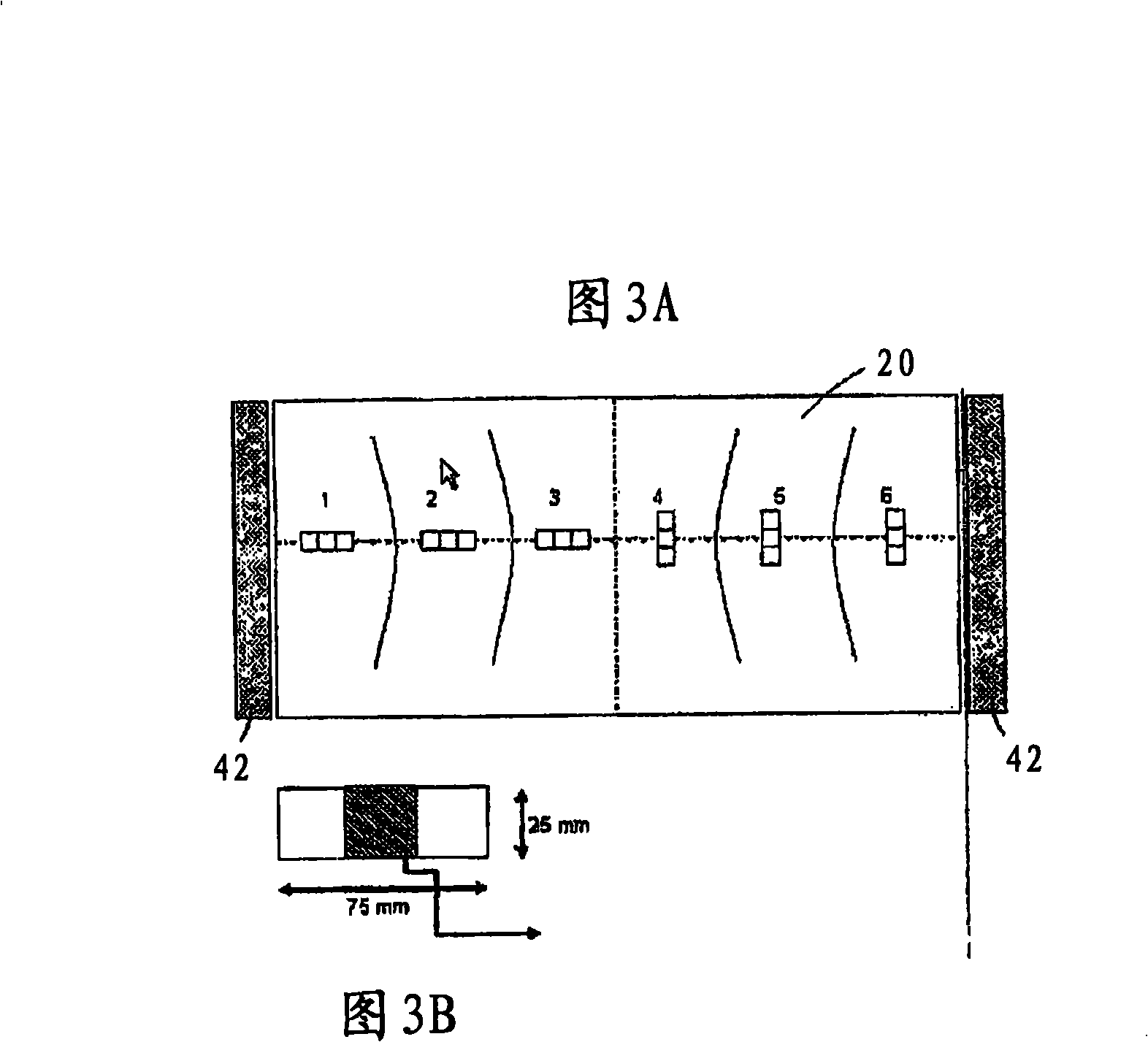
[0254] The abdominal belt shown in Figure 3A was used for the tensile test.
[0255] Test samples 1-6, each having a size of approximately 75 mm x 25 mm, were cut from the abdominal belt shown in FIG. 3A. Each 75 mm x 25 mm sample was then cut into three 25 mm x 25 mm pieces as shown in FIG. 3B and tensile tested as in Example 1 .
[0256] Figure 4 shows the mean stress-strain curves from the tensile tests of the test samples labeled 1 and 6 in Figure 3A corresponding to the elongation of the fabric variant C1 in the width direction (fill direction) and length direction (warp direction), respectively. Stress is defined as in Example 1 as the force per unit width of the sample. Figure 4 also shows the mean (width and length) stress-strain curves for fabric variant C1, linearly fitted to the...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com