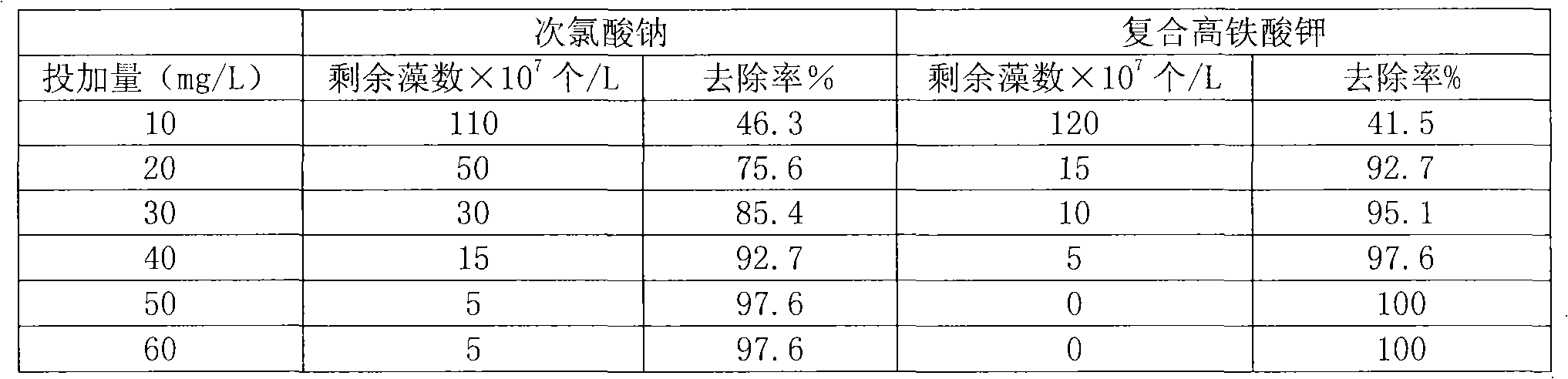
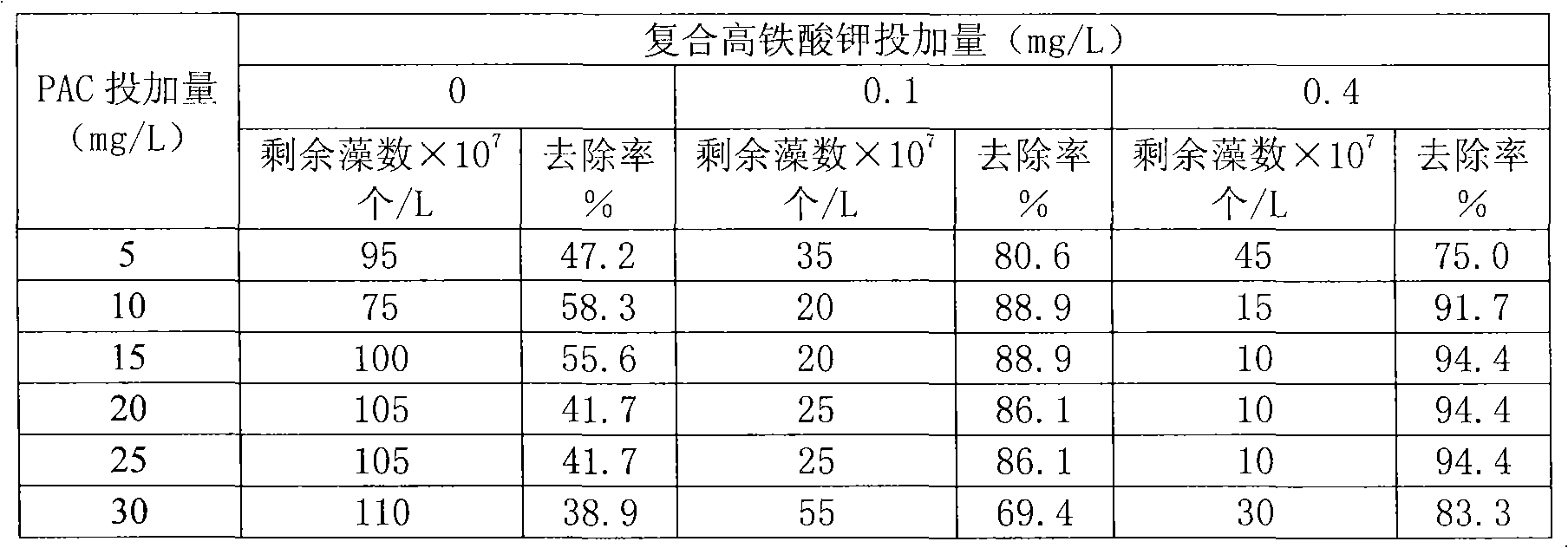
Method for preparing steady composite potassium ferrate solution
A potassium ferrate and solution technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, iron compounds, inorganic chemistry, etc., can solve problems such as preparation process optimization and screening, and achieve the effects of long storage time, difficult reduction of high iron content, and good stability.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] Take 120ml of 1.4mol / L sodium hypochlorite and 45.0g of sodium hydroxide in a reactor, control the temperature below 30°C with a water bath, suction filter after white matter is formed, and the obtained liquid is saturated alkaline sodium hypochlorite. Slowly add 25.1 g of finely ground ferric nitrate into the above liquid and stir, and control the reaction temperature at 25-35°C. After reacting for 1.5 hours, filter with suction to obtain sodium ferrate liquid. Add 40ml of saturated potassium hydroxide to the sodium ferrate solution, and stir for 10-15 minutes to obtain a composite potassium ferrate solution. Finally, add 1.7g of calcium hypochlorite, control the temperature in a water bath at 10-20°C, and stir for 10-20 minutes to obtain a stable composite potassium ferrate solution with a concentration of 0.16mol / L.
Embodiment 2
[0022] Take 180ml of 1.4mol / L sodium hypochlorite and 90.0g of sodium hydroxide in a reactor, control the temperature below 30°C with a water bath, and suction filter after white matter is formed, the obtained liquid is saturated alkaline sodium hypochlorite. Slowly add 40.1 g of finely ground ferric nitrate into the above liquid and stir, and control the reaction temperature at 25-35°C. After reacting for 1.5 hours, filter with suction to obtain sodium ferrate liquid. Add 40ml of saturated potassium hydroxide to the sodium ferrate solution, and stir for 10-15 minutes to obtain a composite potassium ferrate solution. Finally, add 2.5g of calcium hypochlorite, control the temperature in a water bath at 10-20°C, and stir for 10-20 minutes to obtain a stable composite potassium ferrate solution with a concentration of 0.17mol / L.
Embodiment 3
[0024] Take 150ml of 1.4mol / L sodium hypochlorite and 50.0g of sodium hydroxide in a reactor, control the temperature below 30°C with a water bath, and suction filter after white matter is formed, the obtained liquid is saturated alkaline sodium hypochlorite. Slowly add 30.0 g of finely ground ferric nitrate into the above liquid and stir, and control the reaction temperature at 25-35°C. After reacting for 1.5 hours, filter with suction to obtain sodium ferrate liquid. Add 50ml of saturated potassium hydroxide to the sodium ferrate solution, and stir for 10-15 minutes to obtain a composite potassium ferrate solution. Finally, add 2.20g of calcium hypochlorite, control the temperature in a water bath at 10-20°C, and stir for 10-20 minutes to obtain a stable composite potassium ferrate solution with a concentration of 0.24mol / L.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com