New process for preparing theaflavine
A technology of theaflavin and a new process, applied in the field of preparing theaflavin, can solve the problems of high content of theaflavin, inability to separate three phases, inability to filter, etc., to achieve increased yield and content, easy control of the fermentation process, and elimination of the The effect of waste water
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
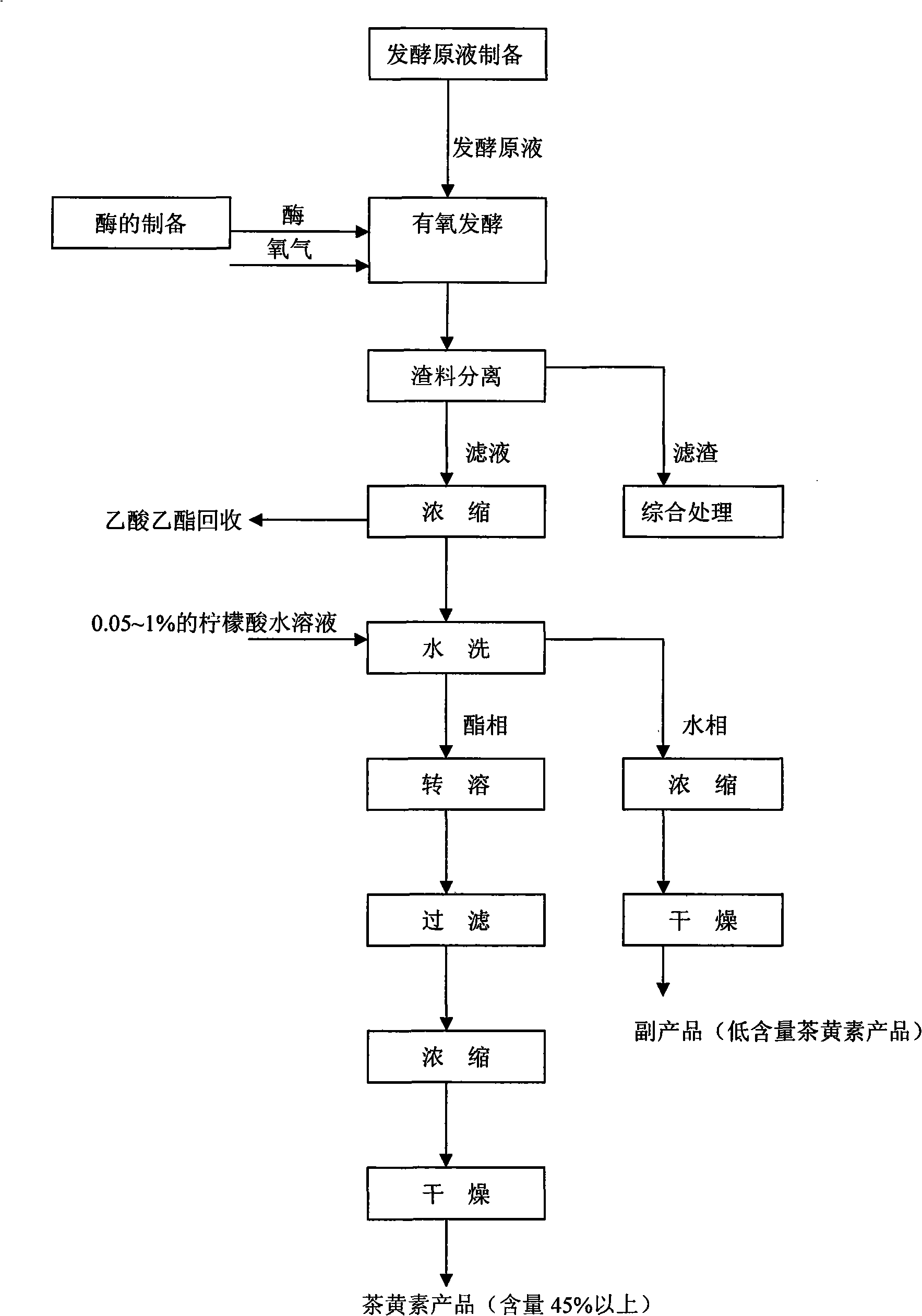
[0031] Embodiment 1: as figure 1As shown, a new process for preparing theaflavins, the process steps are as follows: put 100g of green tea into the extractor, then add 1000mL of ethyl acetate, control the temperature at 25-60°C, stir and extract for 30min, discharge the material, and then add Ethyl acetate 1000mL was extracted again in the same way, the extracts were combined, the above extracts were concentrated to a solid content of 1%, and cooled to room temperature as a fermentation stock solution; 120g of fresh fresh tea leaves were selected as raw materials for the enzyme, and the fresh tea leaves were used Wet it with pure water or 0.1% citric acid aqueous solution, place it below 0°C, freeze it for more than 2 hours, and immediately pulverize it after taking it out. The pulverization is carried out below room temperature, and the fresh tea leaves after pulverization are controlled to be above 80 mesh. After the treatment, the enzyme is used as a fermentation enzyme for...
Embodiment 2
[0032] Embodiment 2: as figure 1 As shown, a new process for preparing theaflavins, the process steps are as follows: put 100g of green tea into the extractor, then add 1500mL of ethyl acetate, control the temperature at 25°C-60°C, stir and extract for 30min, discharge, and then Add 1500 mL of ethyl acetate and extract again in the same way, combine the extracts, concentrate the above extracts to a solid content of 0.8%, cool to room temperature as a fermentation stock solution; select 180 g of fresh fresh tea leaves as raw materials for the enzyme, and fresh tea leaves Moisten it with pure water or 0.5% citric acid aqueous solution, place it below 0°C, freeze it for more than 2 hours, take it out and grind it immediately, and grind it below room temperature, and control the fresh tea leaves after grinding to 80 mesh or more , the treated enzyme is used as a fermented enzyme for later use (the storage time at room temperature shall not exceed 2 hours); 1500 g of the above-ment...
Embodiment 3
[0033] Embodiment 3: as figure 1 As shown, a new process for preparing theaflavins, the process steps are as follows: put 100g of green tea into the extractor, then add 3000mL of ethyl acetate, control the temperature at 25-60°C, stir and extract for 30min, discharge the material, and then add Ethyl acetate 3000mL is extracted once again in the same way, the extracts are combined, the above extracts are concentrated to a solid content of 0.5%, and cooled to room temperature as a fermentation stock solution; select fresh fresh tea leaves 180g as raw materials for the enzyme, and use fresh tea leaves Wet it with pure water or 1% citric acid aqueous solution, place it below 0°C, freeze it for more than 2 hours, and immediately grind it after taking it out. The grinding should be carried out below room temperature, and the fresh tea leaves after grinding should be controlled to be above 80 mesh After the treatment, the enzyme is used as a fermentation enzyme for later use (the sto...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com