Method for marking non-heading cabbage molecule by utilizing SAMPL technique
A technology of head cabbage and molecular markers, applied in the direction of biochemical equipment and methods, microbial determination/inspection, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
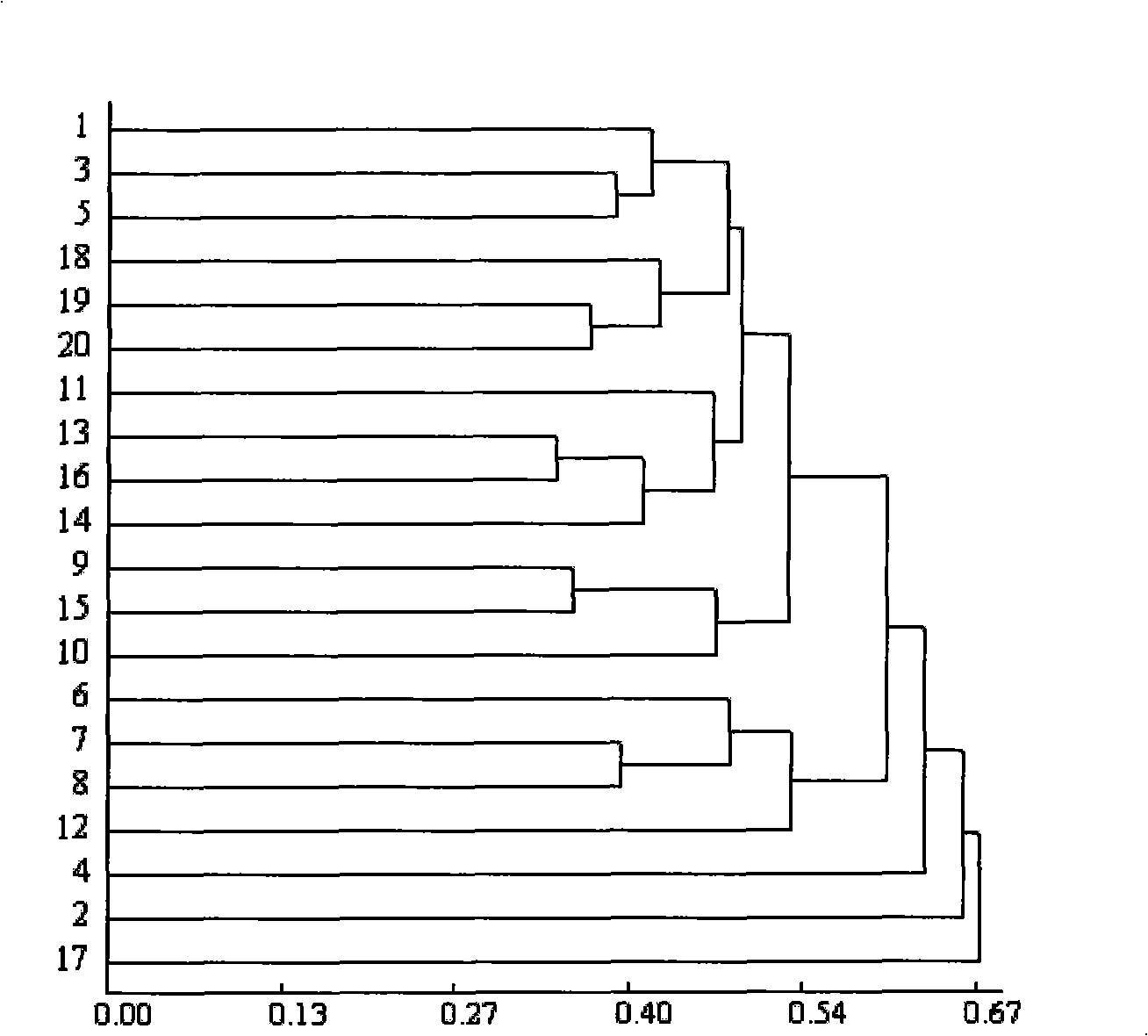
[0031] Cultivation of materials: Take 20 parts of non-heading Chinese cabbage from the Germplasm Resources Shanghai Branch of the State Key Laboratory as test materials (Table 1), select plump seeds, and sow them on a mixture of peat, vermiculite and organic fertilizer (volume ratio 4: 1). 4:1) in the mixed substrate, pour water thoroughly and drill a 0.5 cm deep hole, sow the seeds into the hole, and then cover with 0.5 cm thick peat. Seal it tightly with a black film and place it on a seedbed at about 30°C for 3-4 days. After germination and unearthed, transfer it to an artificial climate room with a day temperature of 25°C and a night temperature of 18°C for 2 weeks. Leaves were used for DNA extraction.
[0032] DNA extraction: The CTAB method is used to extract DNA, and the specific operation steps are as follows:
[0033] 1. Leaf cleaning: select 3-5 young leaves, about 2g (grams), and wash them with pure water;
[0034] 2. Grinding leaves: freeze, add liquid nitrogen...
Embodiment 2
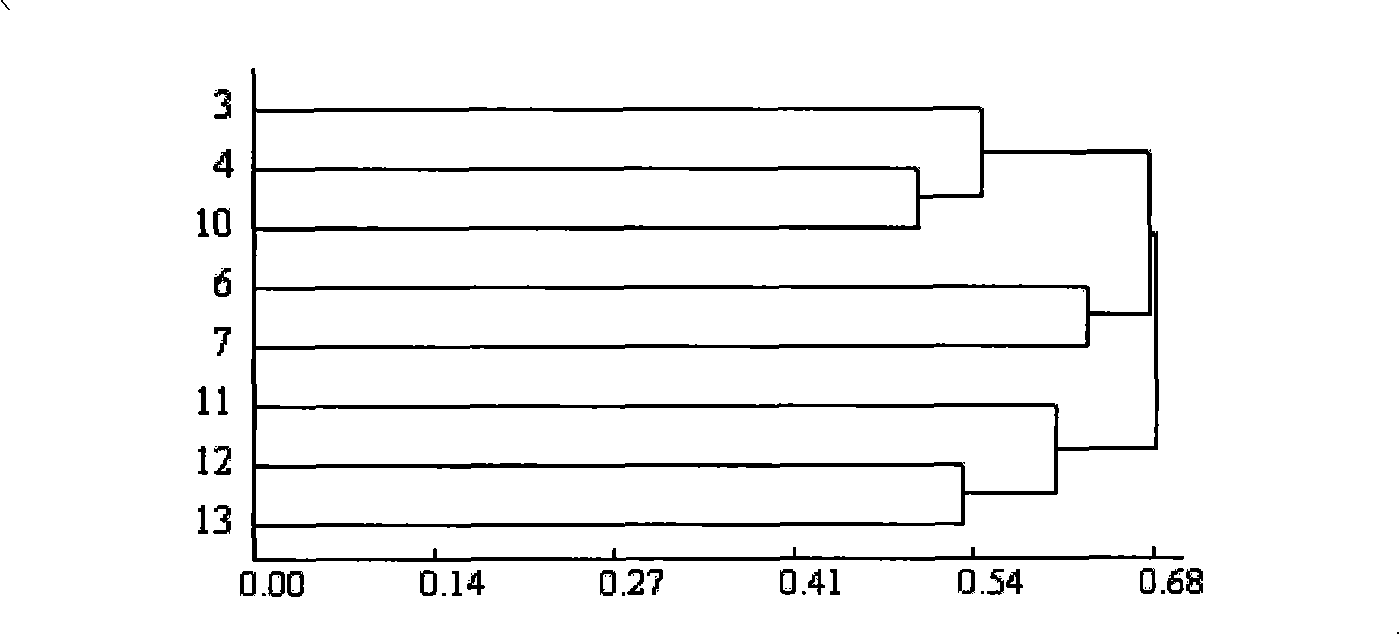
[0076] Cultivation of materials: 8 parts of non-heading Chinese cabbage with different disease resistance and strength from the Shanghai branch of the State Key Laboratory of Germplasm Resources were used as test materials (Table 2). Fertilizer (volume ratio 4: 4: 1) mixed substrate, after watering thoroughly, drill 0.5cm deep holes, sow seeds into the holes, and then cover with 0.5cm thick peat. Seal it tightly with a black film and place it on a seedbed at about 30°C for 3-4 days. After the seeds germinate and unearth, transfer them to an artificial climate room with a day temperature of 25°C and a night temperature of 18°C for 2 weeks, and cut true leaves at the two-leaf stage. Leaves were used for DNA extraction.
[0077] DNA extraction: The CTAB method is used to extract DNA, and the specific operation steps are as follows:
[0078] 1. Leaf cleaning: select 3-5 young leaves, about 2g, and wash them with pure water;
[0079] 2. Grinding leaves: freeze, add liquid nitro...
Embodiment 3
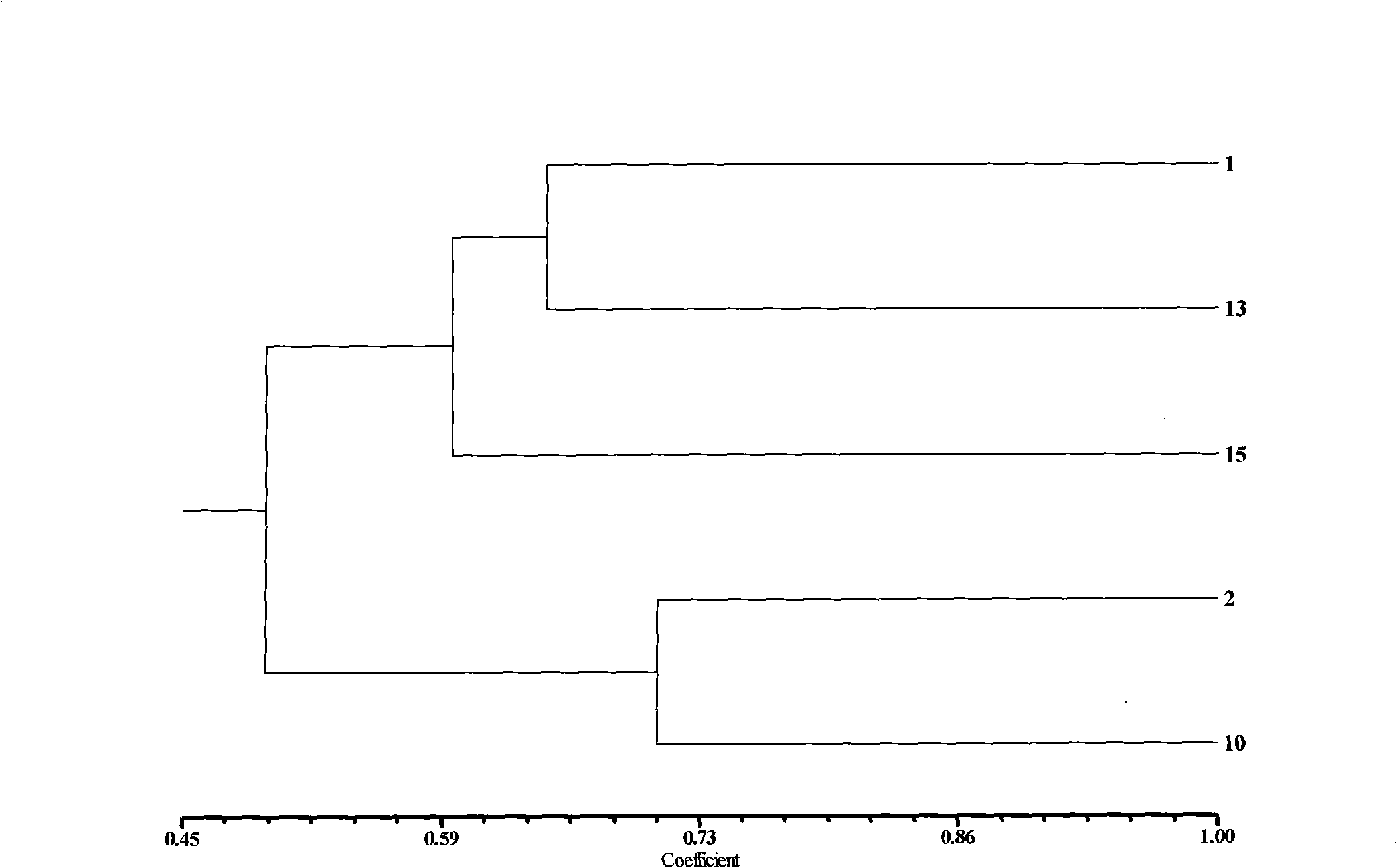
[0117] Cultivation of materials: Take 5 parts of non-heading Chinese cabbage from the Germplasm Resources Shanghai Branch of the State Key Laboratory as test materials (Table 3), select plump seeds, and sow them on a mixture of peat, vermiculite and organic fertilizer (volume ratio 4: 1). 4:1) in the mixed matrix, after pouring water thoroughly, drill a 0.5cm deep hole, sow the seeds into the hole, and then cover with 0.5cm thick peat. Seal it tightly with a black film and place it on a seedbed at about 30°C for 3-4 days. After the seeds germinate and unearth, transfer them to an artificial climate room with a day temperature of 25°C and a night temperature of 18°C for 2 weeks, and cut true leaves at the two-leaf stage. Leaves were used for DNA extraction.
[0118] DNA extraction: The CTAB method is used to extract DNA, and the specific operation steps are as follows:
[0119] 1. Leaf cleaning: select 3-5 young leaves, about 2g, and wash them with pure water;
[0120] 2. G...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com