Wide temperature ultra-low loss MnZn soft magnetic ferrite material and preparing method thereof
A soft ferrite, ultra-low technology, applied in the direction of magnetism of inorganic materials
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
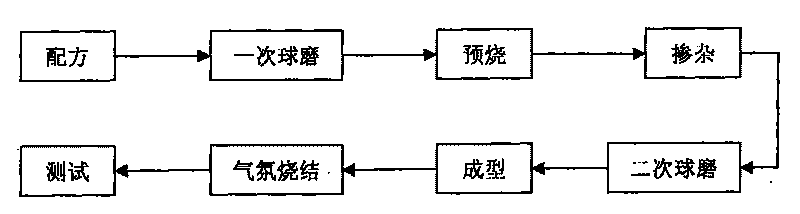
[0020] The loss of ferrite mainly includes hysteresis loss, eddy current loss and residual loss. When the frequency is lower than 500kHz, hysteresis loss and eddy current loss dominate the total loss, and the remaining loss is negligible. In a wide temperature range, hysteresis loss dominates at low temperature, while eddy current loss dominates at high temperature. Therefore, reducing the hysteresis loss at low temperature and the eddy current loss at high temperature as much as possible is the key to the preparation of wide temperature ultra-low loss ferrite materials. The hysteresis loss is mainly related to the initial permeability of the material, the greater the initial permeability, the lower the hysteresis loss. For MnZn ferrite, the most effective way to increase the initial permeability is to reduce the magnetocrystalline anisotropy constant. Fe 2+ and Co 2+ Has a positive magnetocrystalline anisotropy constant, so an appropriate amount of Fe 2+ and Co 2+ It ca...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Curie point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| electrical resistivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com