Human face tracing method
A face position and frame image technology, applied in the field of face tracking, can solve the problems of matrix inversion, difficult inversion operation, poor robustness, etc., and achieve the effect of improving robustness, improving tracking ability, and reducing the amount of calculation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
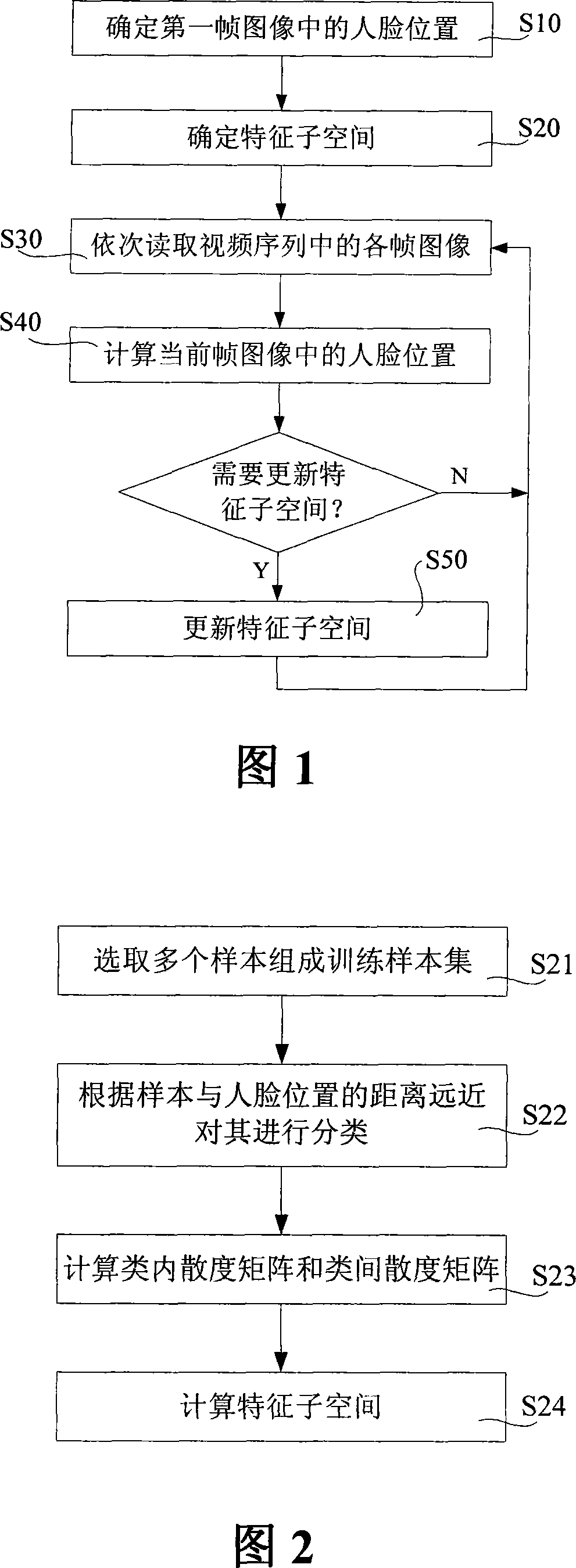
[0019] In the example below, a rotatable rectangle is used X t = ( x t , y t , s x t , s y t , θ t ) To represent the face position in the tth frame image, where x t and y t Respectively represent the horizontal and vertical coordinates of the center of the face, s x t Indicates the width of the face, s y t Indicates the height of the face, θ t Indicates the rotation angle of the face. However, it should be clear that according to the present invention, the position of a human face can also be represented by using more or less feature quantities.
[0020] Fig. 1 shows the main steps of face tracki...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com