Biological enzyme degumming method for cotton stalk bark fibre
A degumming method and technology of cotton stalk sheath, which is applied in the field of biological enzyme degumming of cotton stalk sheath fiber, can solve the problems of poor spinnability of cotton stalk sheath fiber, long degumming time, and large fiber damage, so as to improve textile performance and reduce emissions and treatment capacity, damage reduction effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
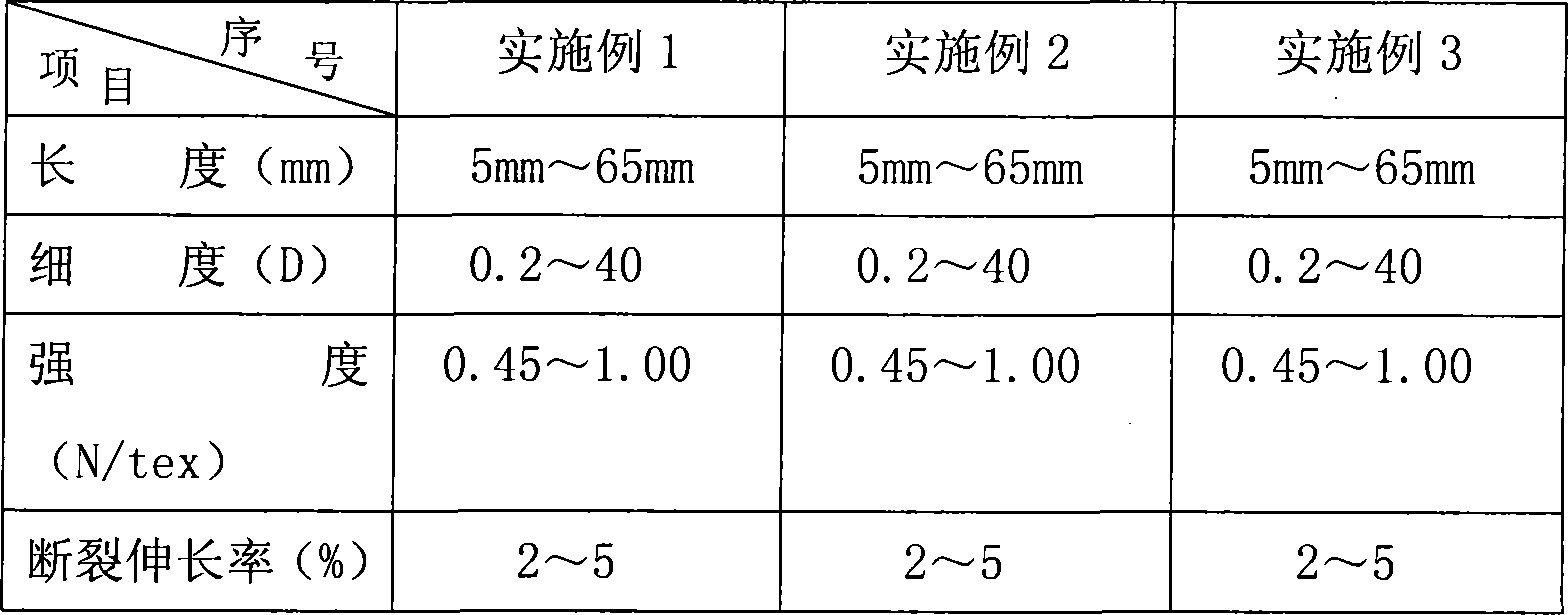
Embodiment 1
[0014] (1) Skin removal: take the dry fine-staple cotton stalk, and separate the cotton stalk skin from the cotton stalk by hand, and try to avoid bringing the hard wood fiber layer in the cotton stalk.
[0015] (2) Acid enzyme solution treatment: put the cotton stalk bark into the acid enzyme solution with a temperature of 50°C and a pH of 5.0 at a bath ratio of 1:3 for 8 hours; the enzyme concentration in the acid enzyme solution is 1%, and the acidity of the enzyme solution Available oxalic acid, glacial acetic acid or sulfuric acid are regulated, and the biological enzyme that enzyme liquid is used is acid pectinase and cellulase, and the weight ratio of acid pectinase and cellulase is 2: 1; Both pectinase and cellulase are commercially available from Ningxia Fengda Gloria Biological Products Co., Ltd.
[0016] (3) Alkaline enzyme solution treatment: put the cotton stalk skin treated by acid enzyme solution into the alkaline enzyme solution with a temperature of 55°C and p...
Embodiment 2
[0019] (1) Skin removal: take the dry coarse cotton stalk, and separate the cotton stalk skin from the cotton stalk by hand, and try to avoid bringing the hard wood fiber layer in the cotton stalk.
[0020] (2) Acidic enzyme solution treatment: put the cotton stalk bark into the acidic enzyme solution with a temperature of 50° C. and a pH of 5.0 at a bath ratio of 1:4 for 2 hours; the enzyme concentration in the acidic enzyme solution is 1.5%, and the acidity of the enzyme solution It can be regulated by oxalic acid, glacial acetic acid or sulfuric acid, and the biological enzymes used in the enzyme solution are acid pectinase and cellulase, and the weight ratio of acid pectinase and cellulase is 2:1.
[0021] (3) Alkaline enzyme solution treatment: put the cotton stalk bark treated with acid enzyme solution into the alkaline enzyme solution with a temperature of 55°C and pH 9.0 at a bath ratio of 1:3 for 2 hours. The degumming can be completed when the enzyme concentration is...
Embodiment 3
[0024] (1) Skin removal: take the dry long-staple cotton stalk, and separate the cotton stalk skin from the cotton stalk by hand, and try to avoid bringing the hard wood fiber layer in the cotton stalk.
[0025] (2) Acidic enzyme solution treatment: put the cotton bark into the acidic enzyme solution with a temperature of 50°C and a pH of 5.0 at a bath ratio of 1:5 for 4 hours; the enzyme concentration in the acidic enzyme solution is 1%, and the acidity of the enzyme solution It can be regulated by oxalic acid, glacial acetic acid or sulfuric acid, and the biological enzymes used in the enzyme solution are acid pectinase and cellulase, and the weight ratio of acid pectinase and cellulase is 2:1.
[0026] (3) Alkaline enzyme solution treatment: put the cotton stalk skin treated by acid enzyme solution into the alkaline enzyme solution with a temperature of 55°C and pH 9.0 at a bath ratio of 1:5 for 1 hour. The degumming can be completed when the enzyme concentration is 0.5%. ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com