Transplantation of human neural cells for treatment of neurodegenerative conditions
A neural stem cell and symptom technology, applied in nervous system cells, animal cells, nervous system diseases, etc., can solve problems such as unmaintainable survival rate, regulatory and economic obstacles, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
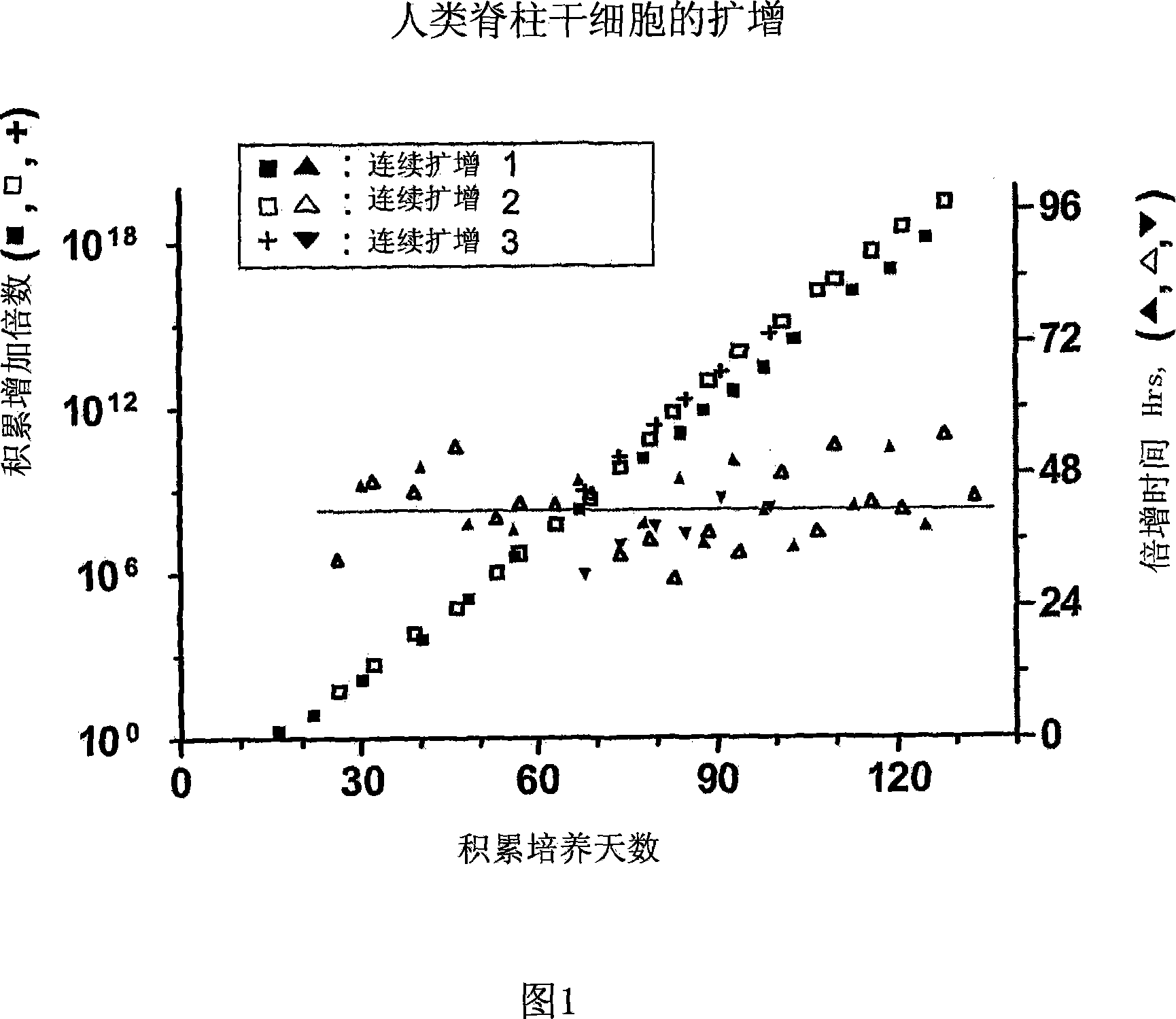
[0147] Example 1. Expansion of human spinal cord neural stem / progenitor cells
[0148] Spinal cords were obtained from at least one donor at a gestational age of approximately 7-8.5 weeks. Use mechanically developed Ca-free ++ and Mg ++ A single contiguous tissue of the spinal cord was dissociated in phosphate-buffered saline. The resulting cell suspension is then seeded into tissue culture plates precoated with poly-L-ornithine or poly-D-lysine and human fibronectin or other extracellular matrix proteins. Tissue culture treated plates or flasks were incubated with 100 μg / ml poly-D-lysine for 1 hour at room temperature. They were then washed three times with water and dried. They were then incubated with 25 mg / ml for 5 minutes at room temperature. Sometimes, 10 mg / ml fibronectin is used for 1 hour at room temperature. Sometimes, 1 mg / ml fibronectin was used for 18 hours at 37°C. Medium consisting of N2 (DMEM / F12 plus insulin, transferrin, selenium, putrescine and proges...
Embodiment 2
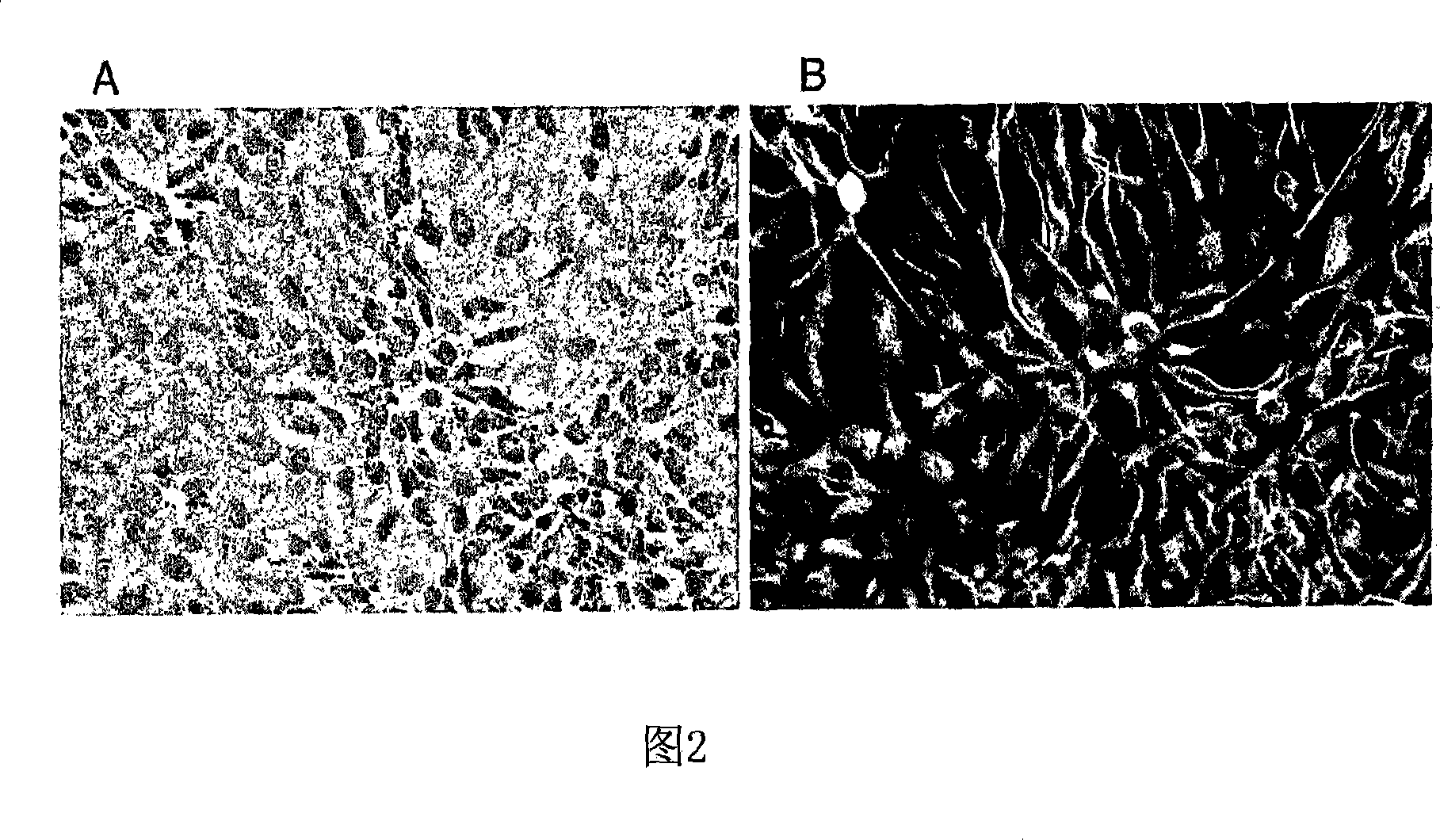
[0150] Example 2. Differentiation of Human Spinal Cord Neural Stem / Progenitor Cells
[0151] At any time during the expansion of NSCs, cultures can be differentiated by extracting mitogens, such as bFGF, from the culture. Differentiation of NSCs occurs approximately 1-3 days after removal of the mitogen and exhibits a distinct heterogeneous cell morphology. By approximately 4-7 days of differentiation, non-specific antigens such as MAP2c, tau, and type III β-tubulin can be visualized by immunostaining. By approximately 12-14 days, elongated fascicled axons and clear polarization of subcellular protein trafficking are evident throughout the culture. By approximately day 28, synaptic proteins, such as synapsin and synaptophysin, are localized to axon terminals and appear as punctate staining. Another feeder layer of astrocytes can be provided to further promote long-term maturation of neurons. As shown in Figure 3, differentiation of human spinal NSCs produces mixed cultures ...
Embodiment 3
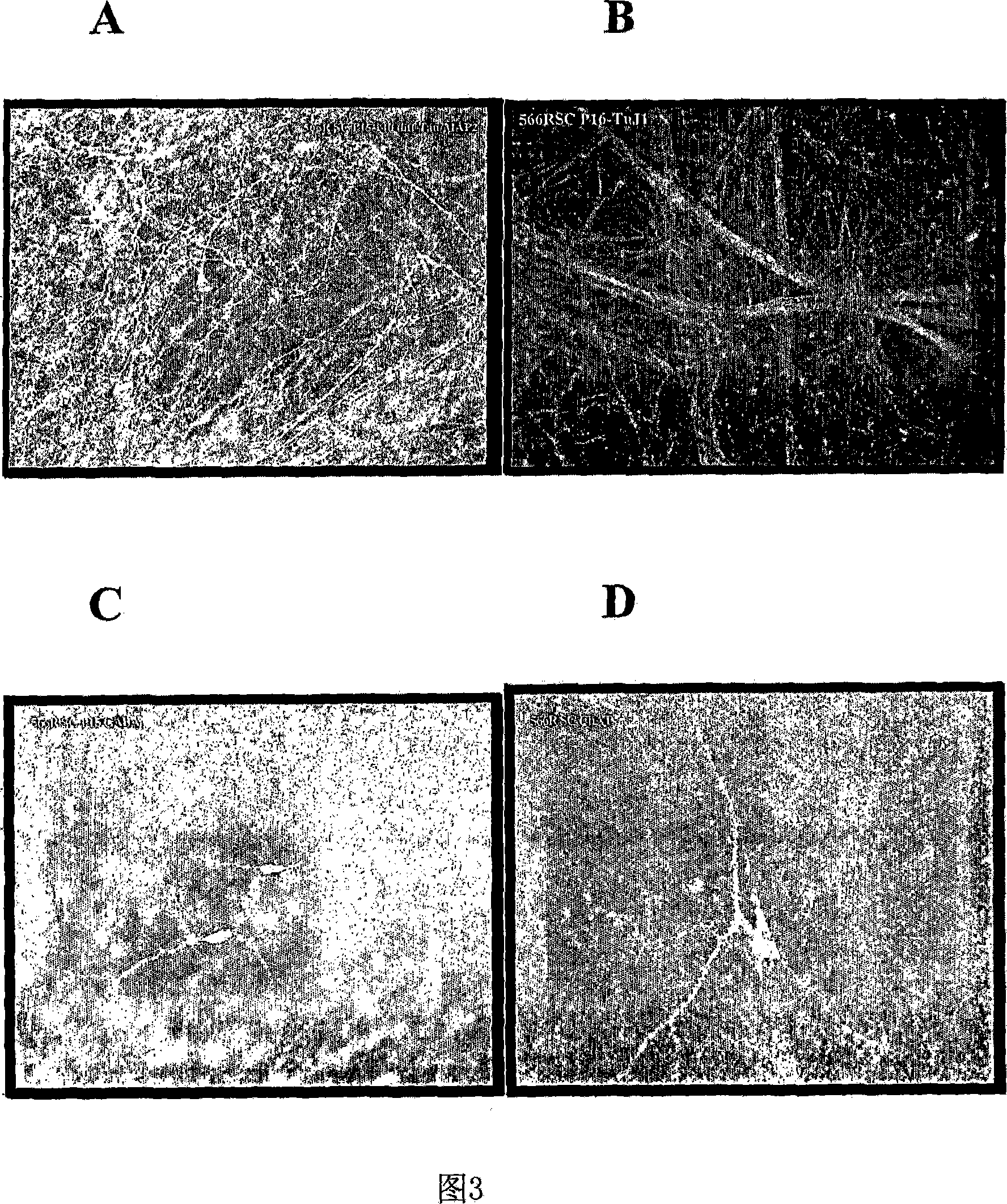
[0152] Example 3. Expansion of human midbrain neural stem / progenitor cells
[0153] Obtain one midbrain tissue at a fetal age of 7-8.5 weeks. NSCs from midbrain tissue were obtained as described in Example 1. Cells were serially passaged through a 160-day pure culture period, and the resulting expansion is shown in FIG. 4 . Throughout the expansion period, NSCs stably maintained their pluripotent and neurogenic potential as well as their differentiation potential to give rise to dopaminergic neurons. Dopaminergic neurons were assessed by neuronal expression of tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) and dopamine transporter (DAT).
[0154] DAT expression is a hallmark of dopaminergic neurons. DAT expression in neurons can be assessed by measuring its effect in transporting radioisotope-labeled dopamine across the synaptic membrane of differentiated neurons in culture. The effect of DAT in cultures from differentiated human midbrain NSCs and monoclonal derived human midbrain NSCs was asses...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com