Methods for treating a mammal before, during and after cardiac arrest
A technology for mammals, cardiac arrest, applied in mammals during and after, to treat the field before cardiac arrest, which can solve problems such as affecting the blood flow of organs, damage to cardiac function, and long duration of vasoconstriction effect.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0089] Embodiment 1: Levosimendan is used for the treatment of suffering from post-cardiac arrest resuscitation
[0090] Uses for myocardial dysfunction in mammals
[0091] All animals received humane care and guidelines for the care and use of laboratory animals in accordance with the Principles of Laboratory Animal Care formulated by the National Society for Research in Medicine, which were issued by the Prepared by the Institute of Laboratory Animal Resources and published by the National Institutes of Health (NIH Publication 86-32, revised 1985).
[0092]Method: Male Sprague-Dawley rats weighing 500-550 g were fasted overnight and allowed to drink water freely. Animals were anesthetized by intraperitoneal injection of pentobarbital (45 mg / kg). Additional doses (10 mg / kg) were administered approximately every hour, or as needed to maintain anesthesia, in addition, non-anesthetics were administered 30 minutes prior to induction of cardiac arrest. Acc...
Embodiment 2
[0100] Example 2: Dobutamine and Levosimendan
[0101] Comparison in Treatment of Rats with Postresuscitated Myocardial Failure
[0102] Dobutamine is widely used in the treatment of myocardial systolic failure after resuscitation from prolonged cardiac arrest. However, dobutamine has the potential to increase the severity of ischemic myocardial injury. Levosimendan, an additional inotrope, has the benefit of improving myocardial contractility without increasing the severity of ischemic injury. Therefore, an experiment was performed to determine whether administration of levosimendan, when resuscitated from cardiac arrest, reduces postresuscitated myocardial ischemic injury and improves outcome compared with dobutamine and placebo.
[0103] Animal preparation: Fifteen male Sprague-Dawley rats weighing 450 and 550 g were fasted overnight with free access to water. Subsequent intraperitoneal injection of 45 mg kg -1 pentobarbital to anesthetize...
Embodiment 3
[0114] Example 3: Dobutamine and levosimendan for treatment
[0115] Comparison in Postresuscitated Myocardial Failure in Rats
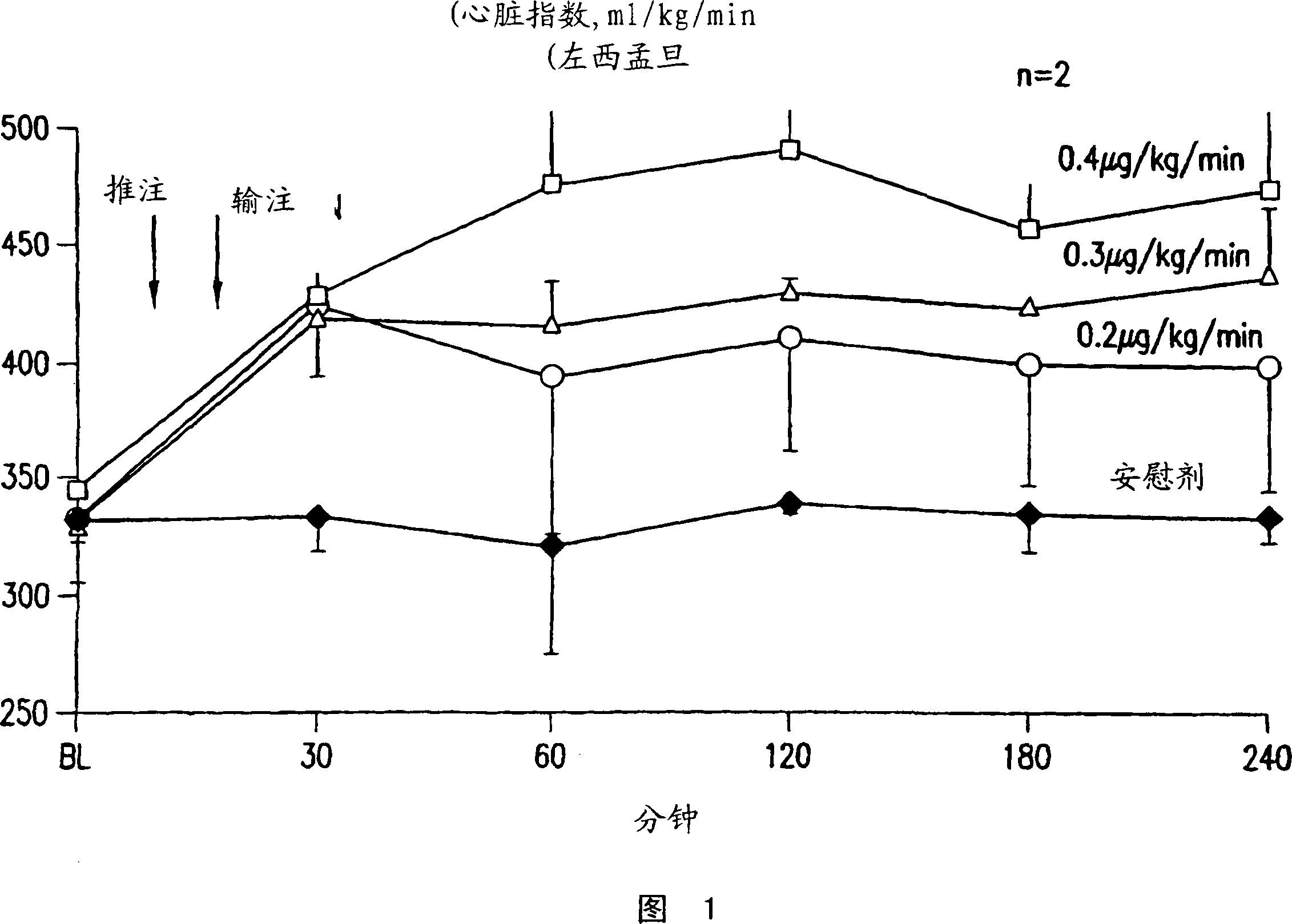
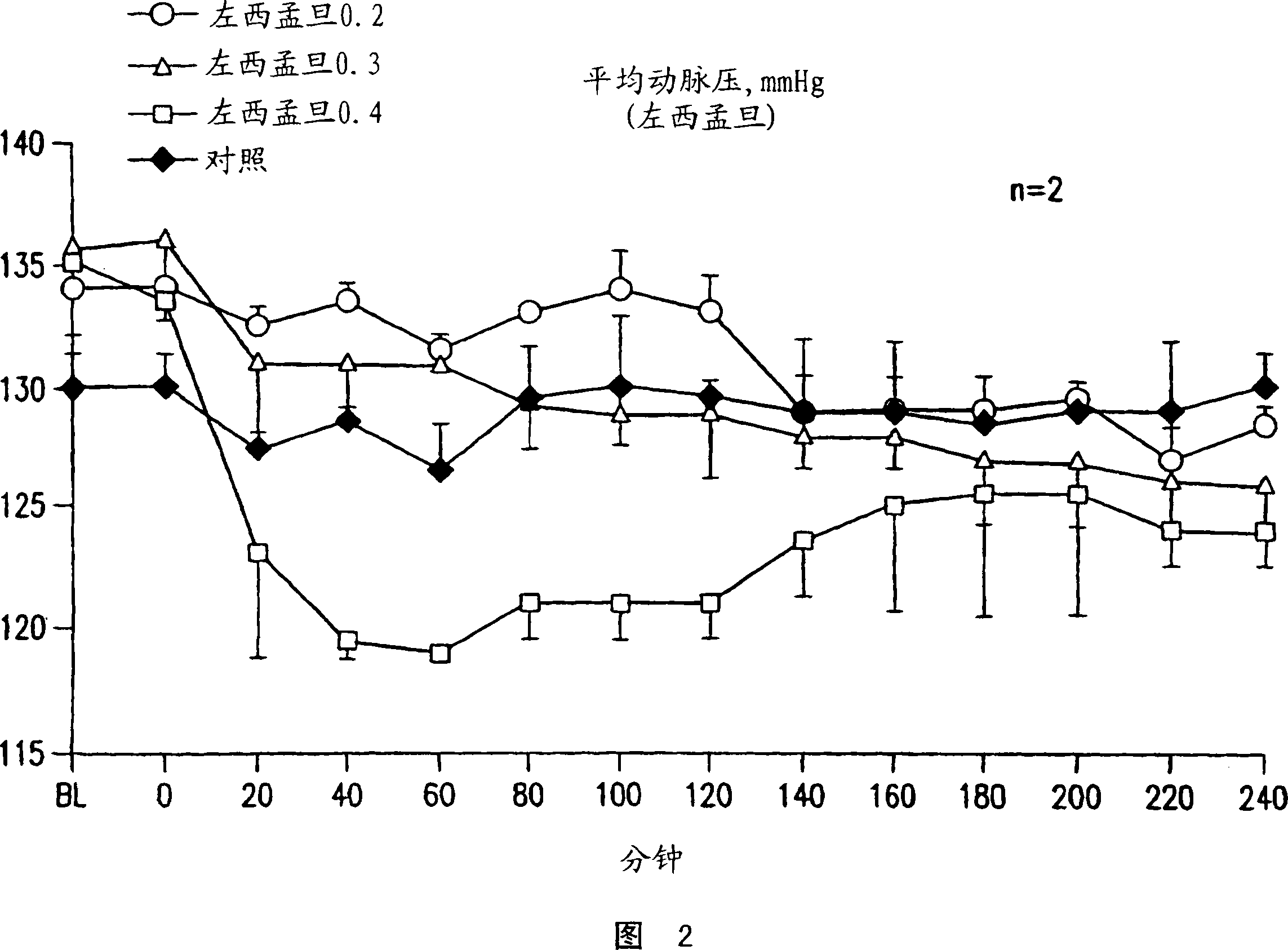
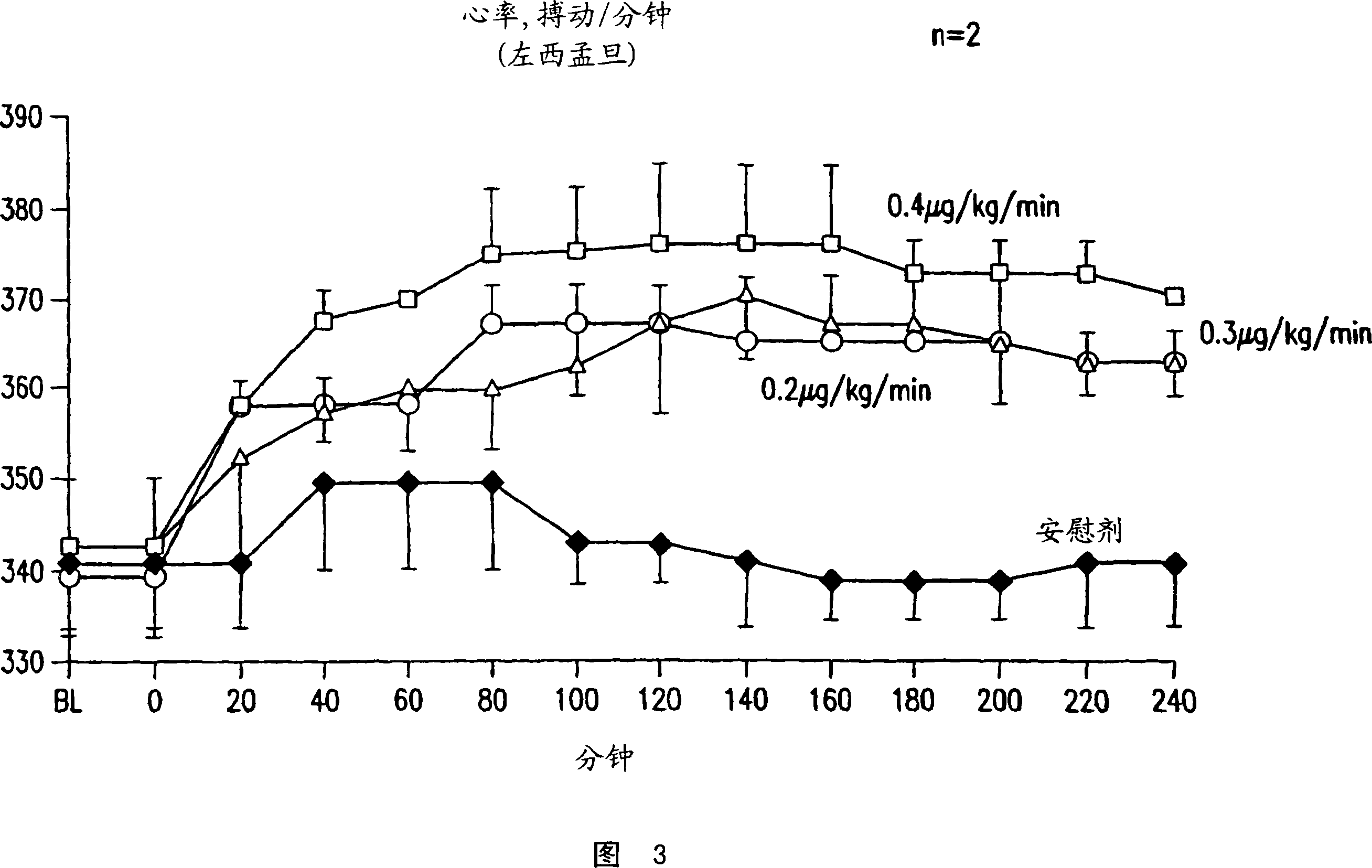
[0116] Experimental preparation: This experiment was carried out in the commonly used pig model of cardiac arrest and cardiac resuscitation. (21, 22). Briefly, 15 male domesticated pigs weighing 35 and 40 kg were fasted overnight with free access to water. Intramuscular injection of ketamine (anesthetic) (20mg / kg -1 ) to start anesthesia, ear intravenous injection of sodium pentobarbital (30mg / kg -1 ) to complete the anesthesia. Anesthesia was maintained by injecting additional doses of sodium pentobarbital (8 mg / kg) every hour. A cuffed endotracheal tube is inserted into the trachea. Mechanically ventilate the animal 15 mL kg with the aid of a volume-controlled ventilation device (Model MA-1, Puritan-Bennett, Carlsbad, CA) -1 , the maximum airflow is 40L min -1 , FiO 2 is 0.2. End-tidal PCO was detected with an infrared analyzer (Model 01R...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com