Zinc, manganese silicate gree luminous fluorescent powder and its preparing method
A technology of zinc-manganese silicate and fluorescent powder, applied in luminescent materials, chemical instruments and methods, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of uneven particle size distribution and components of precipitated products, unsuitable for industrialized large-scale production, and expensive raw materials , achieve the effect of cheap production requirements, short afterglow time, lustful purity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
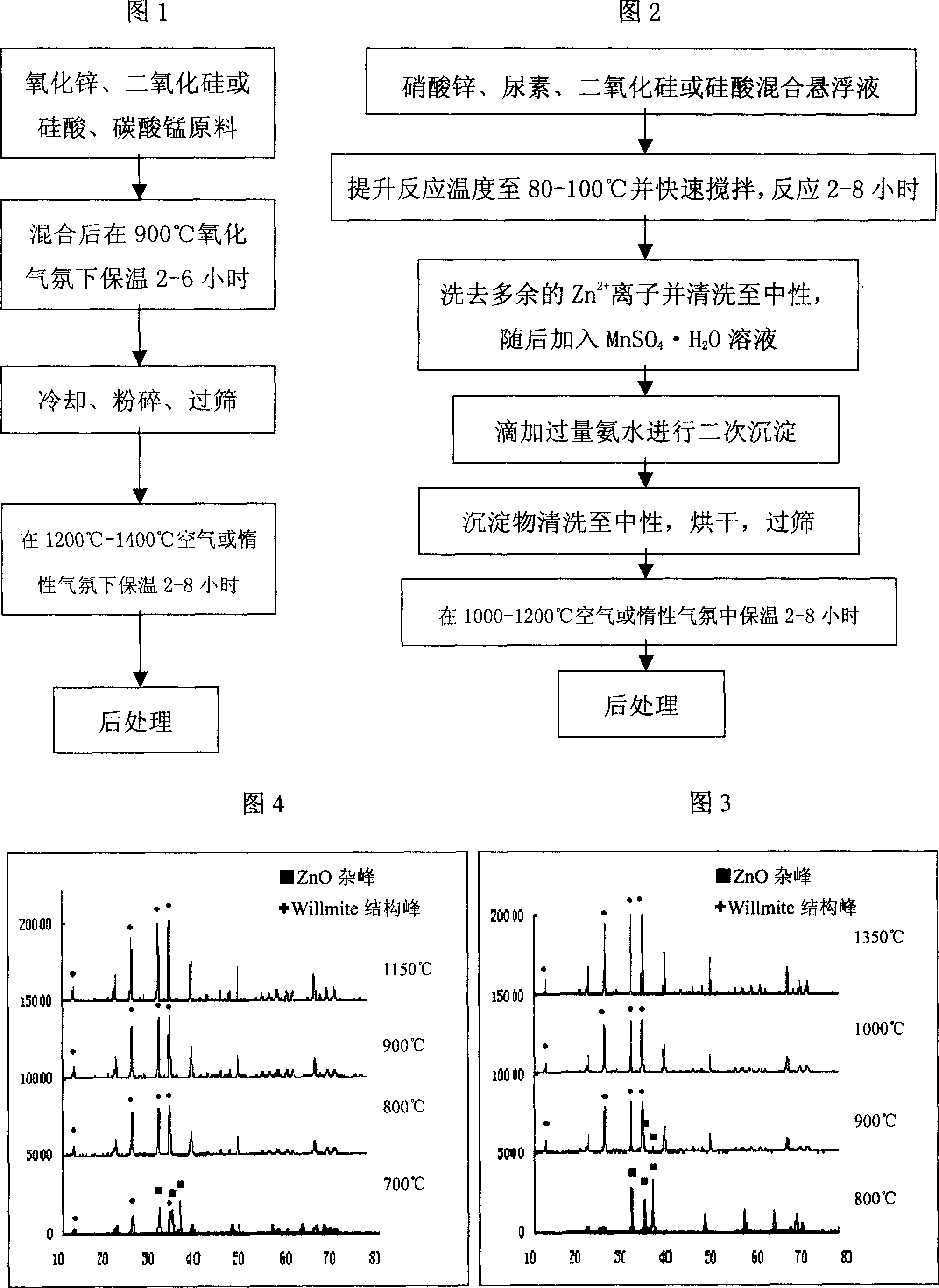
[0045] Embodiment 1: prepare Zn with the method of the present invention 2-x mn x SiO 4 Phosphor powder (the holding temperature is 700°C, 800°C, 900°C and 1150°C respectively).
[0046] Adopt wet chemistry method of the present invention to prepare Zn 2-x mn x SiO 4 Phosphor,
[0047] ① Prepare a uniformly dispersed suspension containing basic zinc carbonate and silicon dioxide: dissolve a certain stoichiometric amount of zinc nitrate and urea in deionized water, and the molar ratio of urea to zinc nitrate is 4:1. Then add the silicic acid slurry and stir well to form a suspension system containing silicon raw materials. The temperature of the system was raised to 95°C, and the reaction was carried out for 3 hours with rapid stirring, and finally a suspension containing basic zinc carbonate and silicon dioxide was generated. Wash the unreacted Zn present in the suspension system with deionized water 2+ ions and make the system neutral.
[0048] ②Add an appropriate am...
Embodiment 2
[0055] Embodiment 2: prepare Zn with wet chemistry method of the present invention 2-x mn x SiO 4 Phosphor.
[0056] Prepare 8 fluorescent powder samples according to the method of Example 1, wherein the molar ratio of urea to zinc nitrate in step ① is 3:1, then add silicic acid slurry and fully stir to form a suspension system of silicon-containing raw materials. The temperature of the system is raised to 100°C; the insulation condition of step ③ is 1150°C for 4 hours, and the Mn 2+ The mole percentages are 0.005, 0.01, 0.02, 0.03, 0.04, 0.05, 0.08, 0.1, respectively.
[0057] Sample serial number
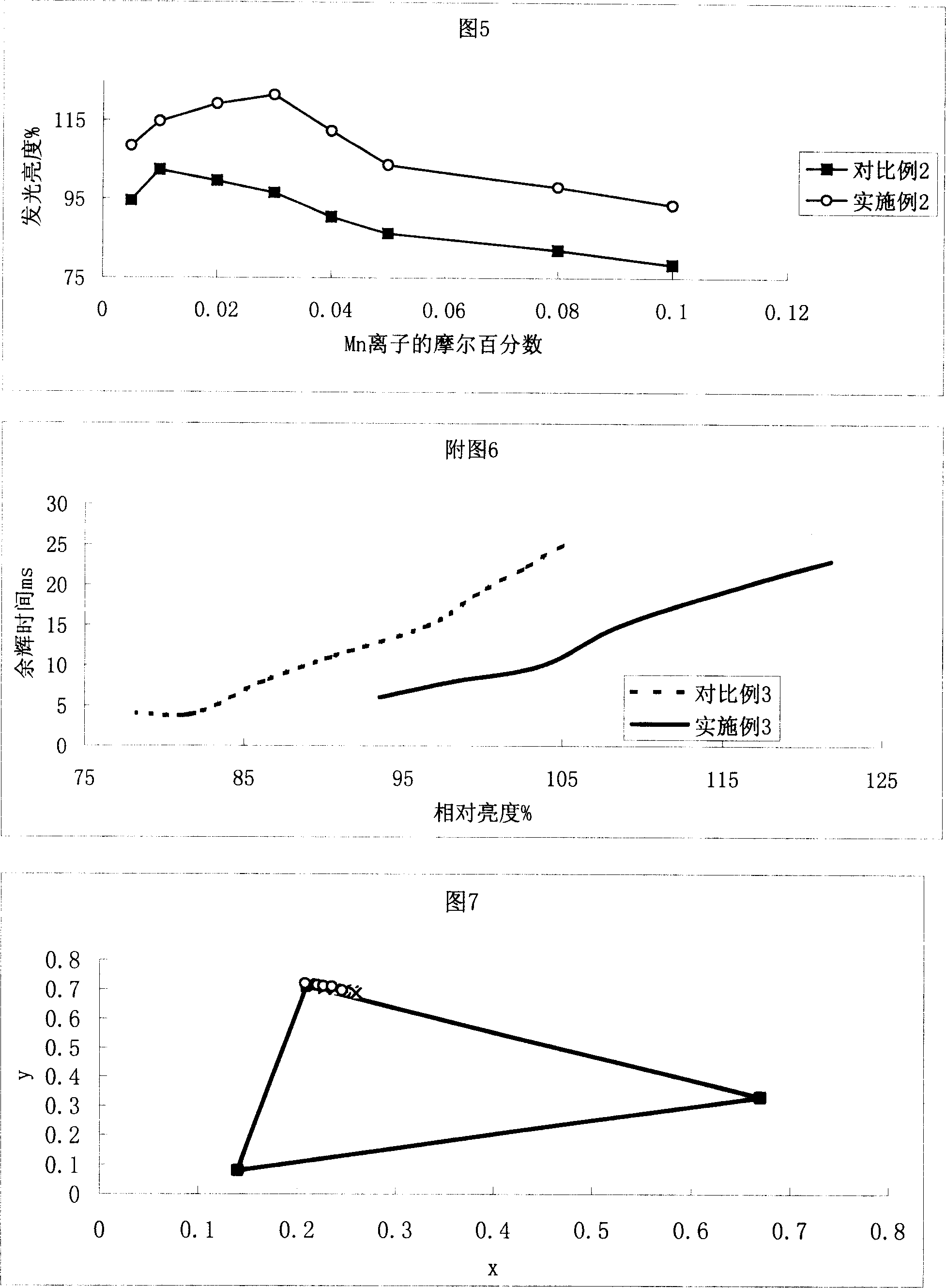
[0058] Accompanying drawing 5 is according to the method for comparative example 2 and embodiment 2, in the same Mn 2+ The difference in luminance of the prepared phosphors under concentration conditions. It can be found from the figure that the brightness of the samples prepared by the method of the present invention is generally higher than that of the samples pr...
Embodiment 3
[0061] Embodiment 3: prepare Zn with wet chemistry method of the present invention 2-x mn x SiO 4 Phosphor.
[0062] Prepare 8 fluorescent powder samples according to the method of Example 1, wherein the insulation condition of step ③ is 1150 ° C for 6 hours, Mn 2+ The mole percentages are 0.057, 0.07, 0.092, respectively.
[0063] Table 1 shows the values of brightness and afterglow time of phosphors prepared according to the high-temperature solid-phase method and the method of the present invention.
[0064] brightness
[0065] Accompanying drawing 6 is the prepared Zn of high temperature solid phase method and the inventive method 2-x mn x SiO 4 The afterglow time variation curve of phosphor powder. Under the same luminance condition, the sample prepared by the method of the invention has a shorter afterglow time.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com