Method for casting Mg-Al-Zn based magnesium alloy with high strength and high tenacity
A high-strength technology for casting magnesium alloys, which is applied in the field of casting magnesium alloys, can solve problems such as low yield, and achieve the effects of low preparation cost, fine grains, and simple and stable heat treatment process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0042] The basic operation steps of the present embodiment 1 alloy are as follows:
[0043] I), alloy composition:
[0044] The alloy of Example 1 is prepared from commercially available high-purity raw materials. Its chemical composition was analyzed using inductively coupled plasma-atomic emission spectroscopy (ICP-AES) technique. The chemical composition of the alloy of Example 1 is shown in the table below.
[0045]
Alloy grade
Element content (weight percent wt%)
Magnesium (Mg)
Aluminum (Al)
Zinc (Zn)
Manganese (Mn)
Carbon (C)
Example 1
balance margin
5.39
5.23
0.34
0.0089
[0046] II), alloy smelting and casting molding:
[0047] The smelting work of Example 1 is carried out in a pit furnace, and the crucible is made of carbon steel; the casting of the alloy is completed in a metal mold. Among them, the manufacturers of RJ-2 covering / refining agent, RJ-1 washing flux and magnesite modificatio...
Embodiment 2
[0067] The difference from Example 1 is:
[0068] The basic operation steps of the alloy in this embodiment are as follows:
[0069] I), alloy composition:
[0070]
Alloy grade
Element content (weight percent wt%)
Magnesium (Mg)
Aluminum (Al)
Zinc (Zn)
Manganese (Mn)
Carbon (C)
Example 2
balance margin
5.25
6.75
0.36
0.013
[0071] II), alloy smelting and casting molding:
[0072] It is the same as the smelting and casting molding part in embodiment 1.
[0073] III), heat treatment of castings:
[0074] The specific conditions of the T61 heat treatment in Example 2 are the same as the heat treatment in Example 1.
[0075] IV), microstructure characterization
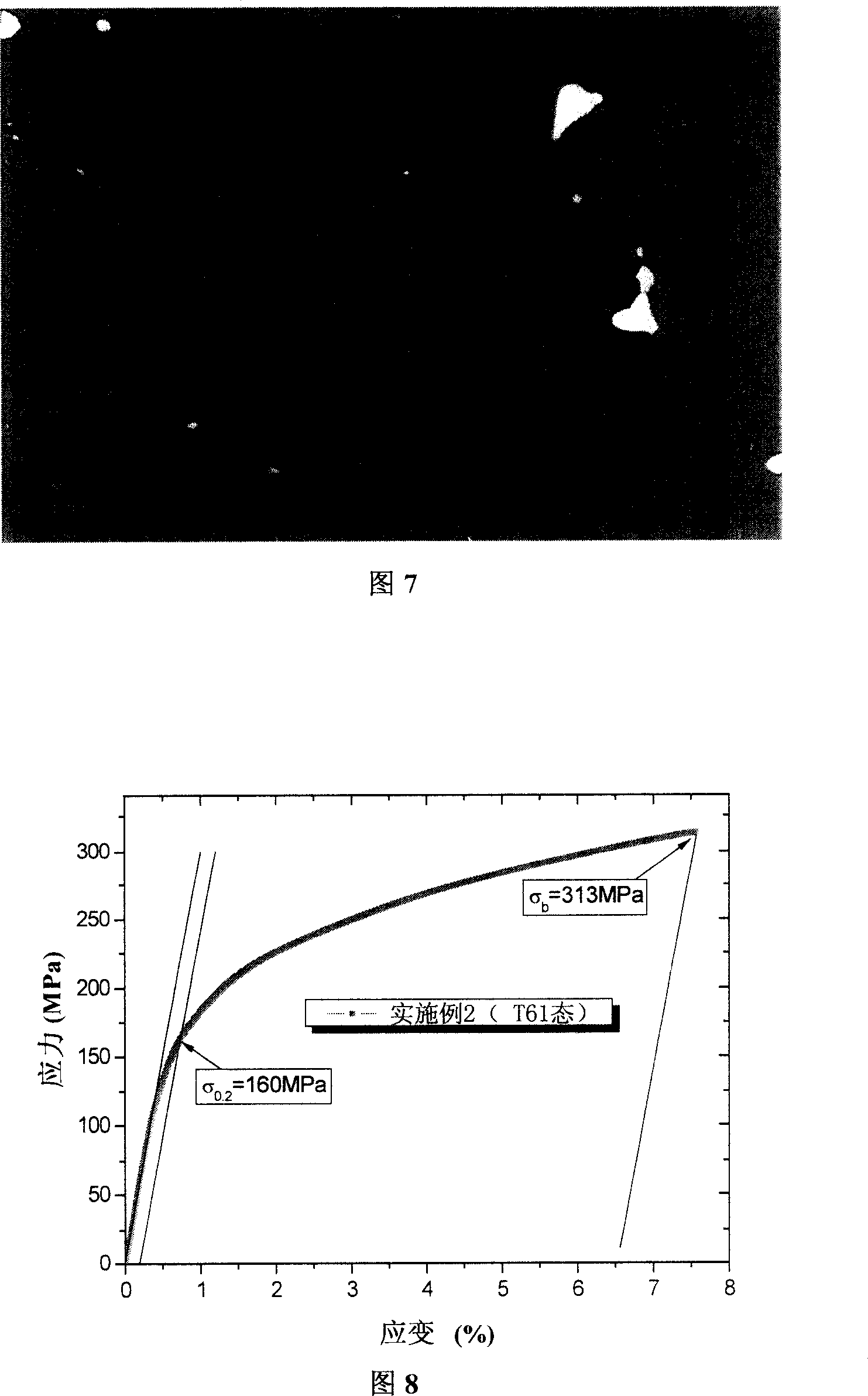
[0076] The sample preparation and characterization means for microstructure observation are the same as in Example 1. Accompanying drawing 6 is the backscatter scanning electron microscope picture of the alloy of Example 2 in the as-cast st...
Embodiment 3
[0082] The difference from Example 1 is:
[0083] The basic operation steps of the alloy in this embodiment are as follows:
[0084] I), alloy composition:
[0085]
Alloy grade
Element content (weight percent wt%)
Magnesium (Mg)
Aluminum (Al)
Zinc (Zn)
Manganese (Mn)
Carbon (C)
Example 3
balance margin
5.83
5.02
0.35
0.010
[0086] II), alloy smelting and casting molding:
[0087] It is the same as the smelting and casting molding part in embodiment 1.
[0088] III), heat treatment of castings:
[0089] Accompanying drawing 9 is the cooling curve of embodiment 3 alloys. It can be seen from the figure that the alloy of Example 3 has two temperature inflection points (375°C and 354°C) near the solidus line. According to the aforementioned heat treatment principles, two heat treatments, T61 and T62, were performed on the alloy of Example 3.
[0090] The T61 heat treatment is partly the same as the h...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com