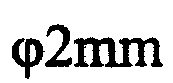Biomedical degradation-absorption-controllable macromolecule metal composite implantation material and use thereof
A polymer material, biomedical technology, applied in the field of biomedical composite materials and metal implant materials, can solve the problems of degradation time and strength, rigidity mismatch, poor processing stability and storage stability, and poor degradation controllability, etc. To achieve the effect of being beneficial to healing, easy to control the degradation rate, and improve the strength
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0018] Use some 99.95% pure magnesium filaments (after polishing, the wire diameter is 0.5mm), ultrasonically clean them in acetone and alcohol for 5 minutes, dry them in a vacuum oven, put them into a customized mold, and add molten poly Lactic acid (PLA), the volume ratio of pure magnesium wire is about 30%, processed into a test sample (30mm×20mm×3mm) after cooling, soaked in the simulated plasma solution prepared according to Table 1 and corroded completely after about 6 months degradation.
[0019] Since the corrosion rate of pure magnesium materials can be adjusted by factors such as impurity content, grain size and heat treatment, the degradation rate of polylactic acid can also be controlled according to the molecular weight of polylactic acid and the thickness of the coating, so according to the above process The medical Controllable Degradation The degradation rate of pure magnesium-polylactic acid composites can be optimized and adjusted from both pure magnesium and...
Embodiment 2
[0023] After polishing 12 as-cast AZ31B magnesium alloy 2mm rods, they were ultrasonically cleaned in acetone and alcohol for 5 minutes, dried in a vacuum oven, and then made into composite materials with polyglycolic acid (PGA). AZ31B magnesium alloy rods The proportion is about 30%, and a test sample (40mm×30mm×6mm) is made, soaked in 0.9% NaCl solution for about 9 months and then completely corroded and degraded.
[0024] Since the corrosion rate of the AZ31B magnesium alloy material can be adjusted by factors such as impurity content, grain size and heat treatment, the degradation rate of polyglycolic acid can also be controlled according to the molecular weight and the thickness of the coating, so the medical can be prepared according to the above process. Controlled degradation The degradation rate of magnesium alloy materials can be optimized and adjusted from two aspects of alloy matrix and surface polyglycolic acid and their ratio.
Embodiment 3
[0026] Ultrasonic cleaning of high-purity magnesium (99.99%) chips in acetone and alcohol for 5 minutes, drying in a vacuum oven, and then compounding with a copolymer of polylactic acid and polyglycolic acid (PLGA), the proportion of magnesium chips is about 40%, A test sample (35mm×20mm×3mm) was made, and it was completely corroded and degraded after soaking in 0.9% NaCl solution for about 4 months.
[0027]Since the corrosion rate of pure magnesium materials can be adjusted by factors such as impurity content, grain size and heat treatment, the degradation rate of the copolymer of polylactic acid and polyglycolic acid can also be controlled according to the ratio of the two and the thickness of the coating, so The degradation rate of the medical controllable degradable magnesium alloy material prepared by the above process can be optimized and adjusted from the two aspects of alloy matrix and surface polylactic acid and polyglycolic acid.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| elastic modulus | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com