Decimation of baseband DTV signals prior to channel equalization in digital television signal receivers
a technology of digital television signal and channel equalization, applied in the direction of amplitude demodulation, line-faulst/interference reduction, television system, etc., can solve the problems of quantization noise, pronounced phase errors, and unsuitable qam dtv signal receiving vsb dtv signal, etc., to reduce the cost of the dtv receiver
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
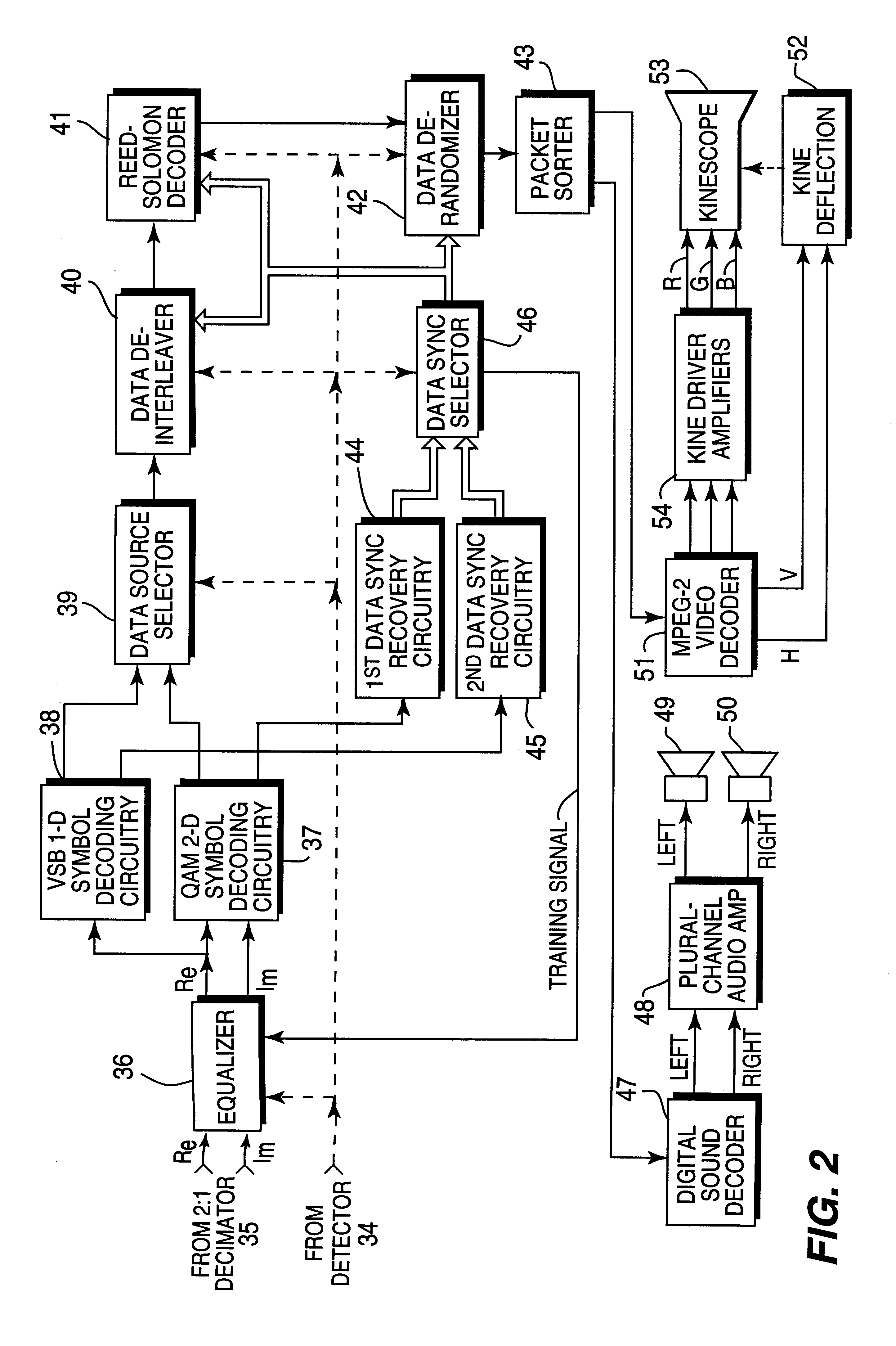
FIG. 1 shows a tuner 5 comprising elements 11-21 that selects one of channels at different locations in the frequency band for DTV signals and performs plural frequency conversion of the selected channel to a final intermediate-frequency signal in a final intermediate-frequency band. FIG. 1 shows a broadcast receiving antenna 6 arranged to capture the DTV signals for the tuner 5. Alternatively, the tuner 5 can be connected for receiving DTV signals from a narrowcast receiving antenna or from a cablecast transmission system.
More particularly, in the tuner 5 shown in FIG. 1, a channel selector 10 designed for operation by a human being determines the frequency of first local oscillations that a frequency synthesizer 11, which functions as a first local oscillator, furnishes to a first mixer 12 for heterodyning with DTV signals received from the antenna 6 or an alternative source of such signals. The first mixer 12 upconverts the received signals in the selected channel to prescribed f...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com