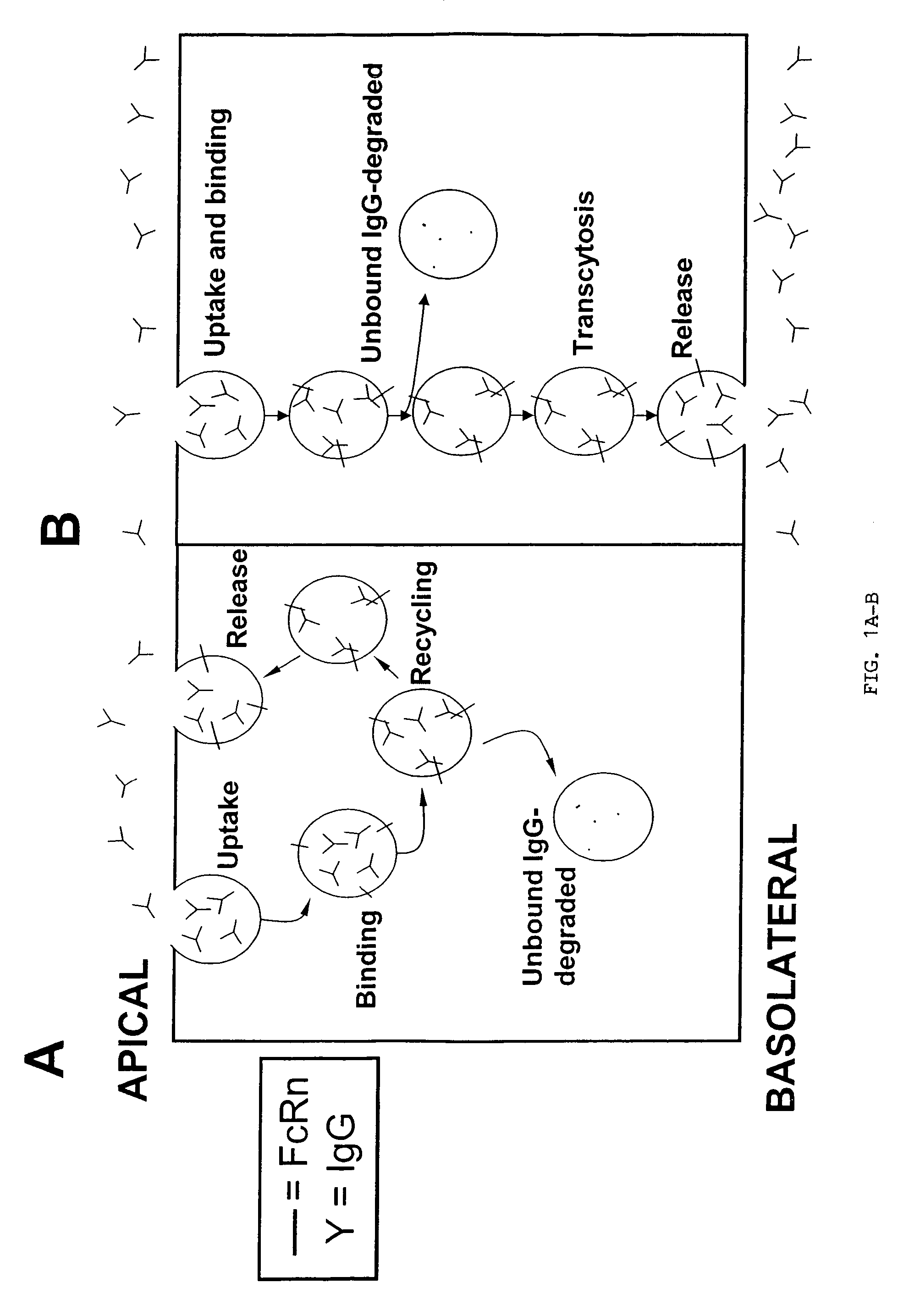
Immunoglobulin molecules with improved characteristics
a technology of immunoglobulin and characteristics, applied in the field of immunology and molecular biology, to achieve the effect of increasing the serum half life of an igg1
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Materials & Methods
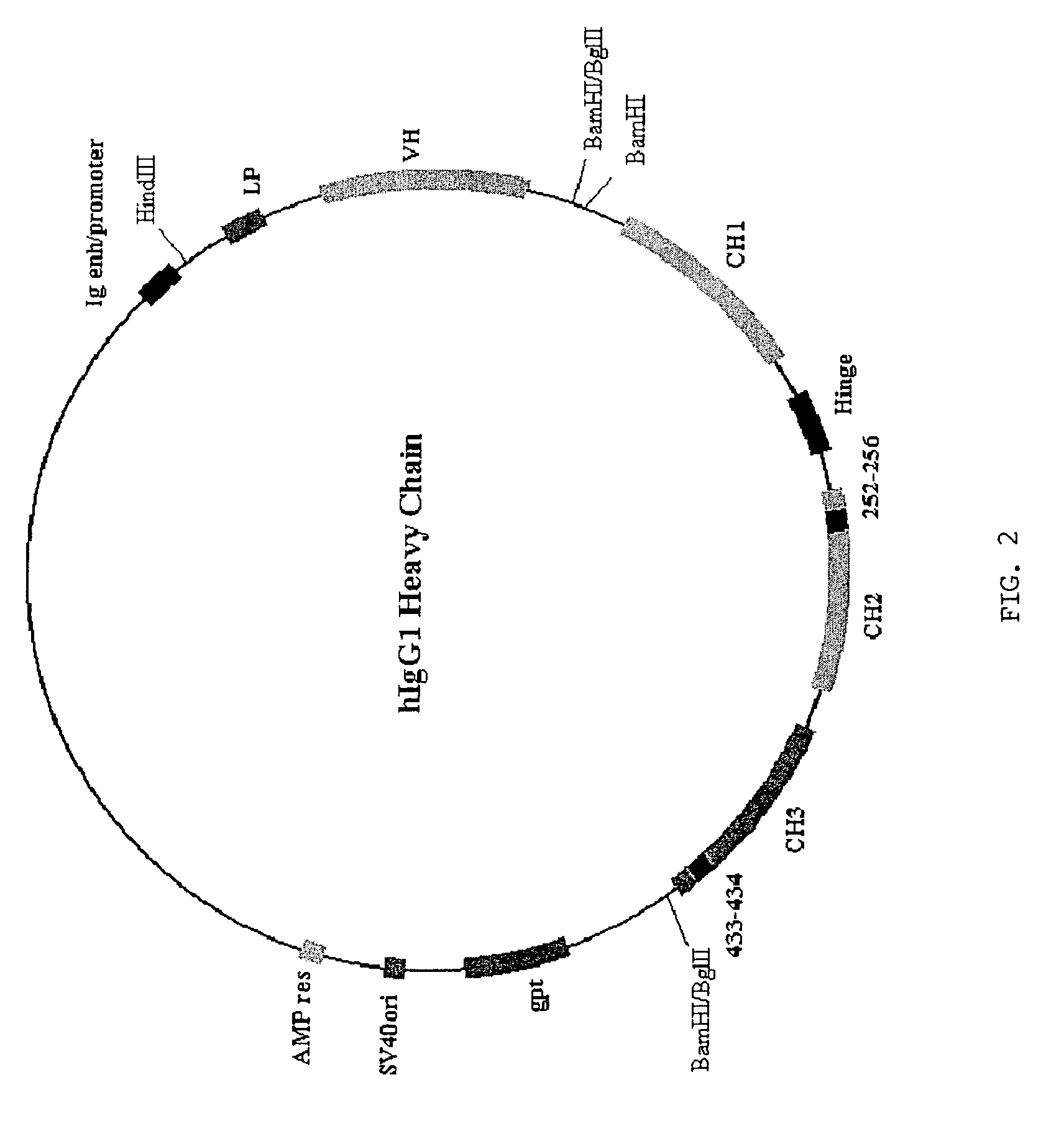
[0086]Site directed mutagenesis. The human IgG1 constant regions were mutated using the PCR with mutagenic oligonucleotides and splicing by overlap extension (Horton et al., 1989). Restriction sites encompassing the mutated sequence in the constant region gene were used for recloning the mutated regions as smaller subfragments of the entire constant region gene. Following recloning, constant region genes were sequenced to ensure insertion of the desired mutation without second site mutations. Mutated genes were recloned into the final expression construct (FIG. 2) using standard methods of molecular biology.
[0087]Transfection for expression of antibodies. NSO cells expressing a human anti-lysozyme specific light chain (HuLys5: Foote and Winter, 1992) were transfected by electroporation with heavy chain expression constructs (FIG. 2) encoding an anti-lysozyme heavy chain with mutations in the Fc region as described. Transfectants were selected in medium containing ...
example 2
Results
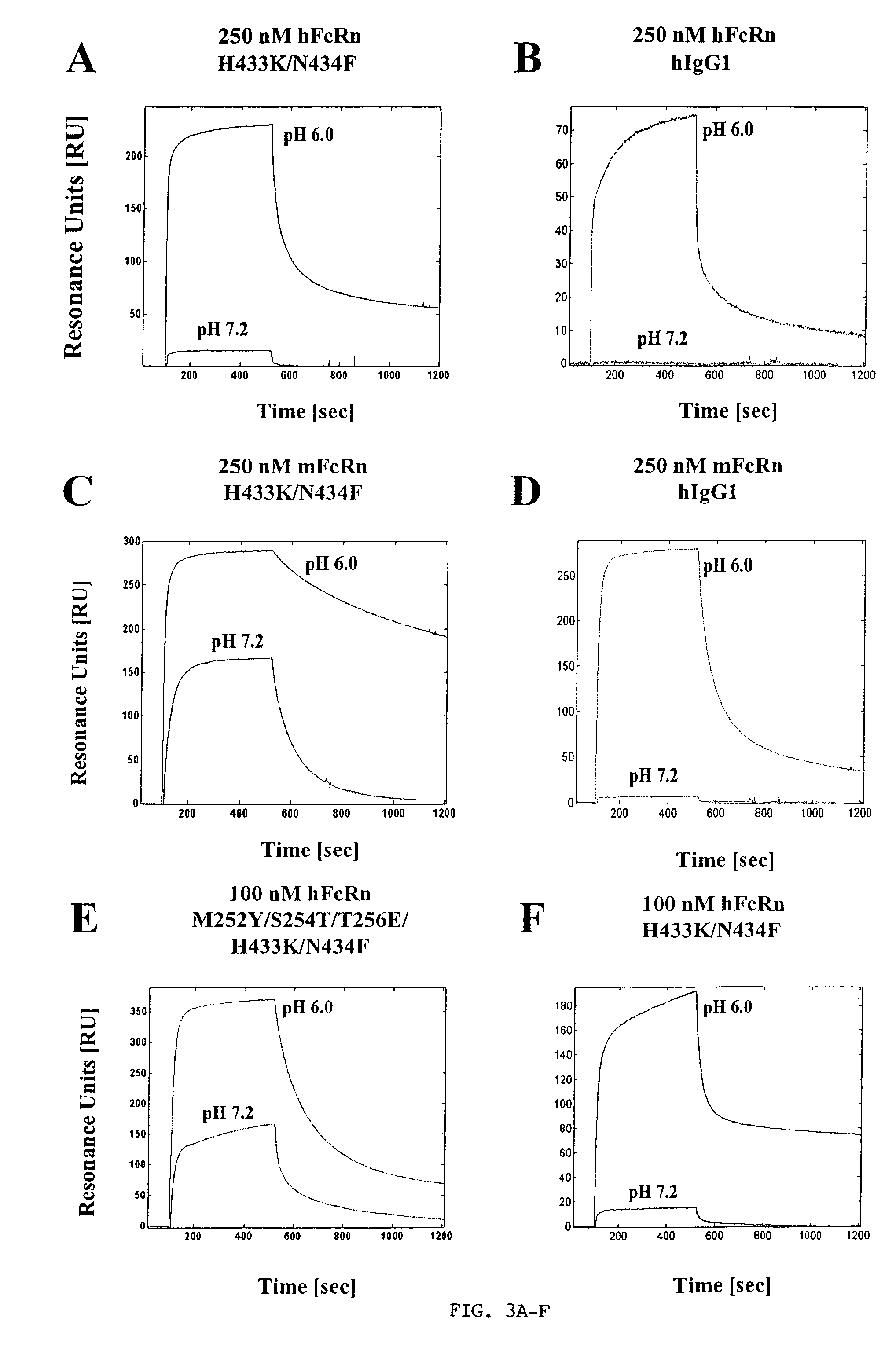
[0093]Analyses of the interactions of human FcRn with wild-type human IgG1 and human IgG1 mutants containing Lys433, Phe434 and His436 (mutated to corresponding mouse IgG1 residue at position 436) or Lys433, Phe434 and Tyr436 (wild-type residue at position 436) indicates that the mutant with the wild-type Tyr436 has an approximately two-fold higher affinity than the mutant containing His436 (Table I). In addition, both mutants have substantially higher affinities for human FcRn than the corresponding wild-type human IgG1. These affinities are further improved when mutations of Met252 to Tyr, Ser254 to Thr and Thr256 to Glu are added to the position 433, 434 (and 436) mutations. Higher affinity for binding to human FcRn is retained for the human IgG1 variant containing the wild-type residue Tyr, rather than histidine, at position 436 (Table II). Taken together, the data therefore indicate that Tyr436 is preferred over His436 for the interaction of human IgG1 with human FcRn.
[0...
example 3
Methods & Results
[0100]Labeling of antibodies. Antibodies were labeled using lodogen or biotinylated in 0.1 M carbonate buffer (pH 8.5) using 9 μg EZ-link Sulfo-NHS biotin (Pierce) per milligram of antibody as described (Firan et al., 2001). Prior to use in studies, all labeled antibodies were compared with their unlabeled counterparts using surface plasmon resonance to ensure that labeling had not altered their binding characteristics.
[0101]Placental transport assays. Essentially the same methods as those described previously were used (Firan et al., 2001). Three mgs of each of wild-type IgG1 or human IgG1 mutant containing Lys433 and Phe434 with the wild-type residue Tyr at position 436 (labeled with either biotin or 125I) were added to the maternal compartment of the ex vivo placental model and transport to the fetal compartment analyzed by sample collection at the indicated times. Following collection, samples were centrifuged at 1500 g for 10 minutes and pellets discarded. The ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| flow rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentrations | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com