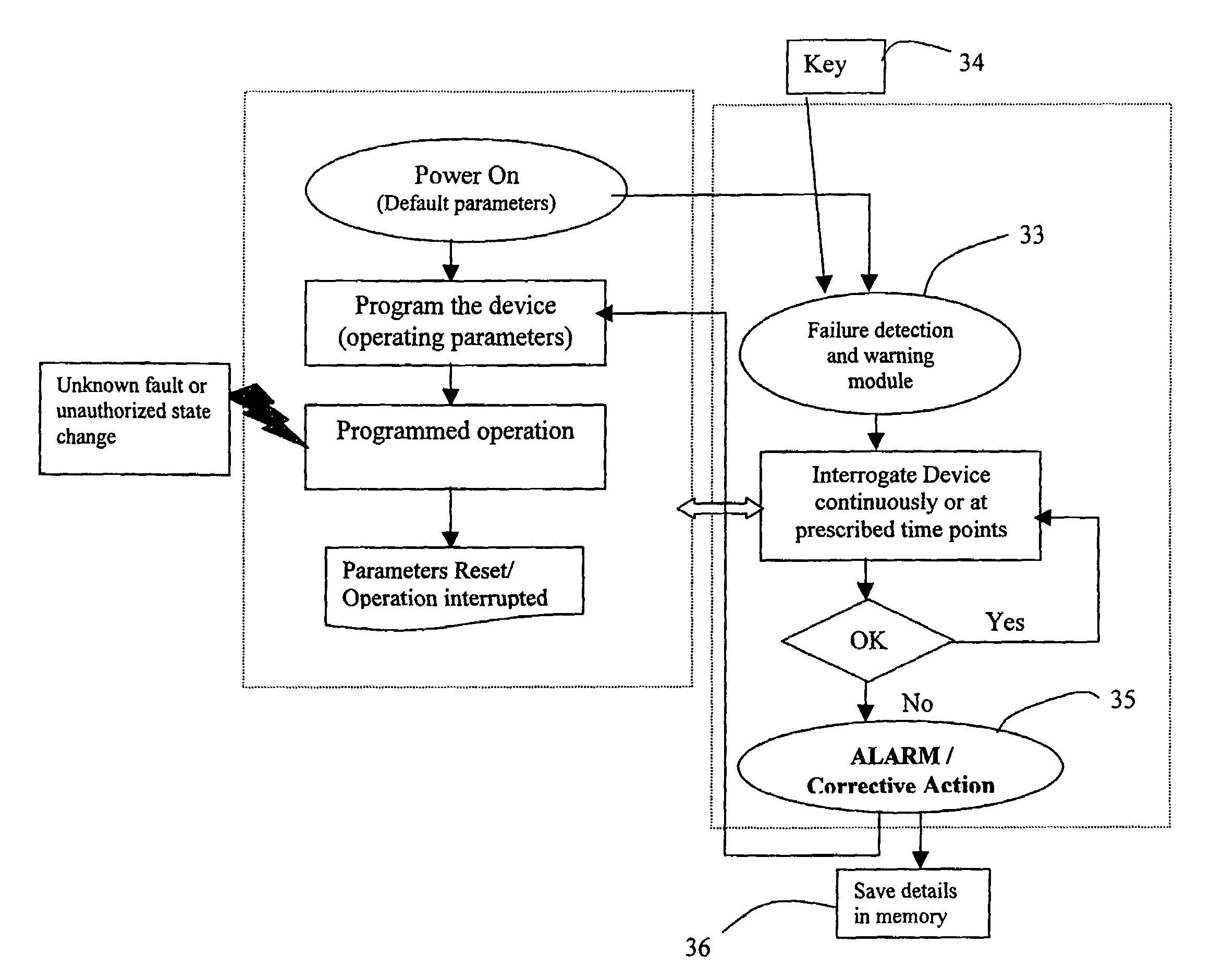
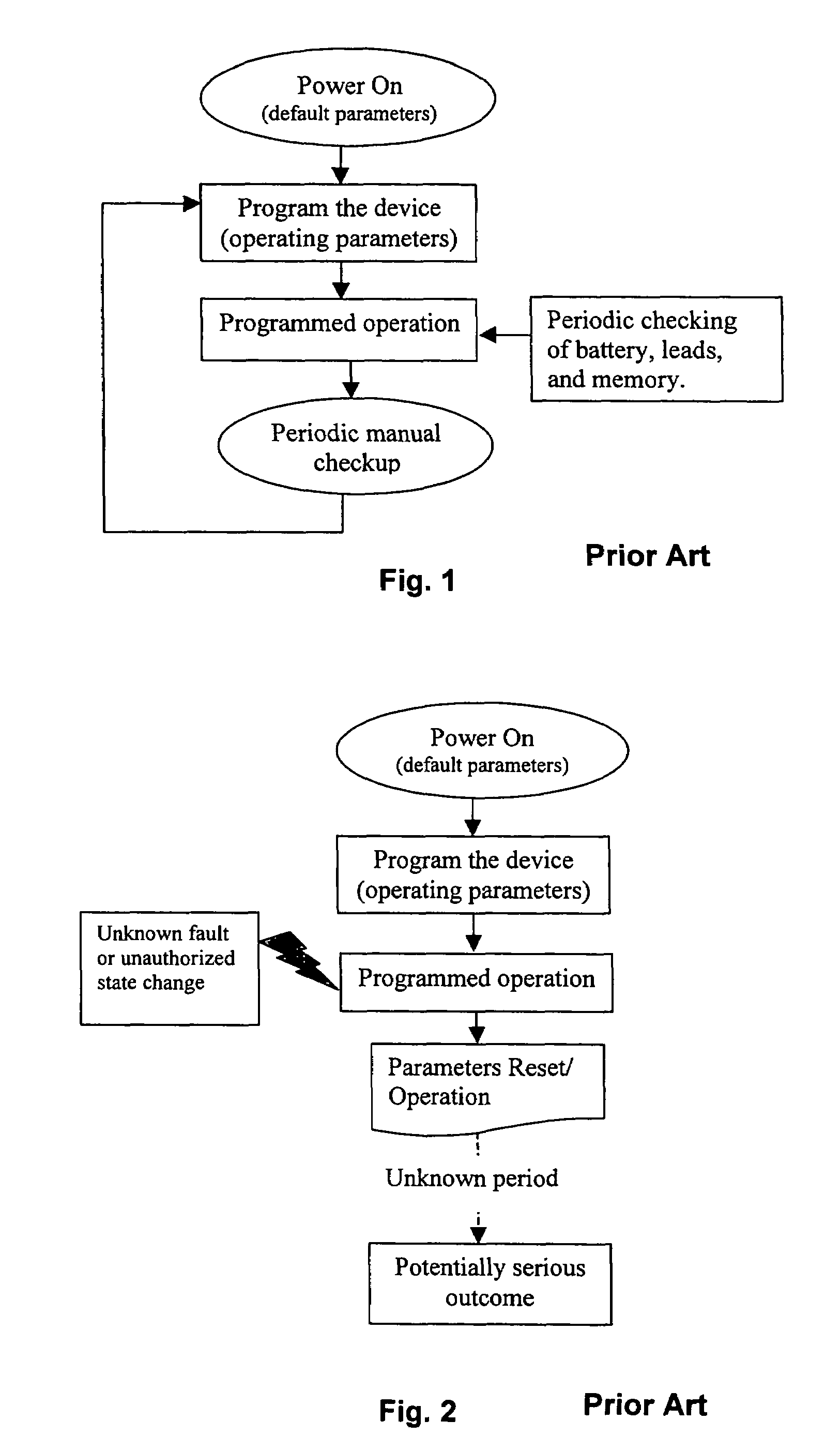
Medical device failure detection and warning system
a warning system and medical device technology, applied in the field of medical devices, can solve the problems of unaddressed problems, unintentional or accidental shut-off, non-user programmed changes in recording/detection or stimulation parameters (e.g., caused), and remain serious, and achieve the effect of reliable performan
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0060]In this example, the FDWS is connected to a medical device via a communication interface in a bi-directional configuration, e.g., via conductors, optical fibers, or telemetry. The FDWS contains a real-time clock and issues a status request to the medical device every ten minutes, which is received via a communications port of the medical device. This action by the FDWS is automatically enabled as soon as the medical device is powered on, and every time the medical device is reset. If not in a failure state, the medical device usually returns an acknowledgment to the FDWS. If, on the other hand, the medical device does not properly acknowledge or respond to the FDWS query within a specified period of time, e.g., one-half second, or the response does not conform to requirements, the FDWS determines that the medical device may be in a fault state. In this case, the FDWS may re-send a query or status request. After “N” successive failures to receive an acknowledgment indicative of...
example 2
[0061]If the FDWS is designed to simply monitor an existing medical device without modifying the medical device to add a communication interface between it and the FDWS, the FDWS would only be able to observe a limited set of information from which it must deduce the state of function of the medical device in order to infer failure. For example, the FDWS may be placed in close proximity to or contiguous with a medical device, such as a nerve stimulator that has been programmed to deliver currents to a nervous structure in an open-loop mode every ten minutes for thirty seconds. In this example, the FDWS can be configured with a clock / timer and one or more sensors to detect the presence of the field associated with electrical currents delivered by the medical device and verify that these stimulations are being delivered on schedule and for the prescribed duration, frequency and intensity. Each time the start of a stimulus train is detected, the FDWS checks the reading of this internal...
example 3
[0062]In this example suppose that, as in the previous example, the FDWS is designed to monitor an existing medical device without a communication interface between the medical device and the FDWS. In this example, however, do not assume anything in particular about the timing of observable outputs of the FDWS. Such may be the case, for instance, in a closed-loop therapeutic medical device that may apply electrical stimulation to tissue in response to a sensed change of state. Such devices include, but are not limited to, ventricular defribrilators acting in response to abnormal heart rhythms, or neural stimulators acting in response to detected neurological events such as epileptic seizures or acute pain. Since cardiac arrhythmias or epileptic seizures are typically aperiodic phenomena, the FDWS system can not be provided in advance with times of therapy delivery. However, in many cases, the subject using the medical device and / or an observer will be aware of the event that is to t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com