Method for producing proteins in transformed Pichia
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Fed Batch Fermentation without Co-feeding
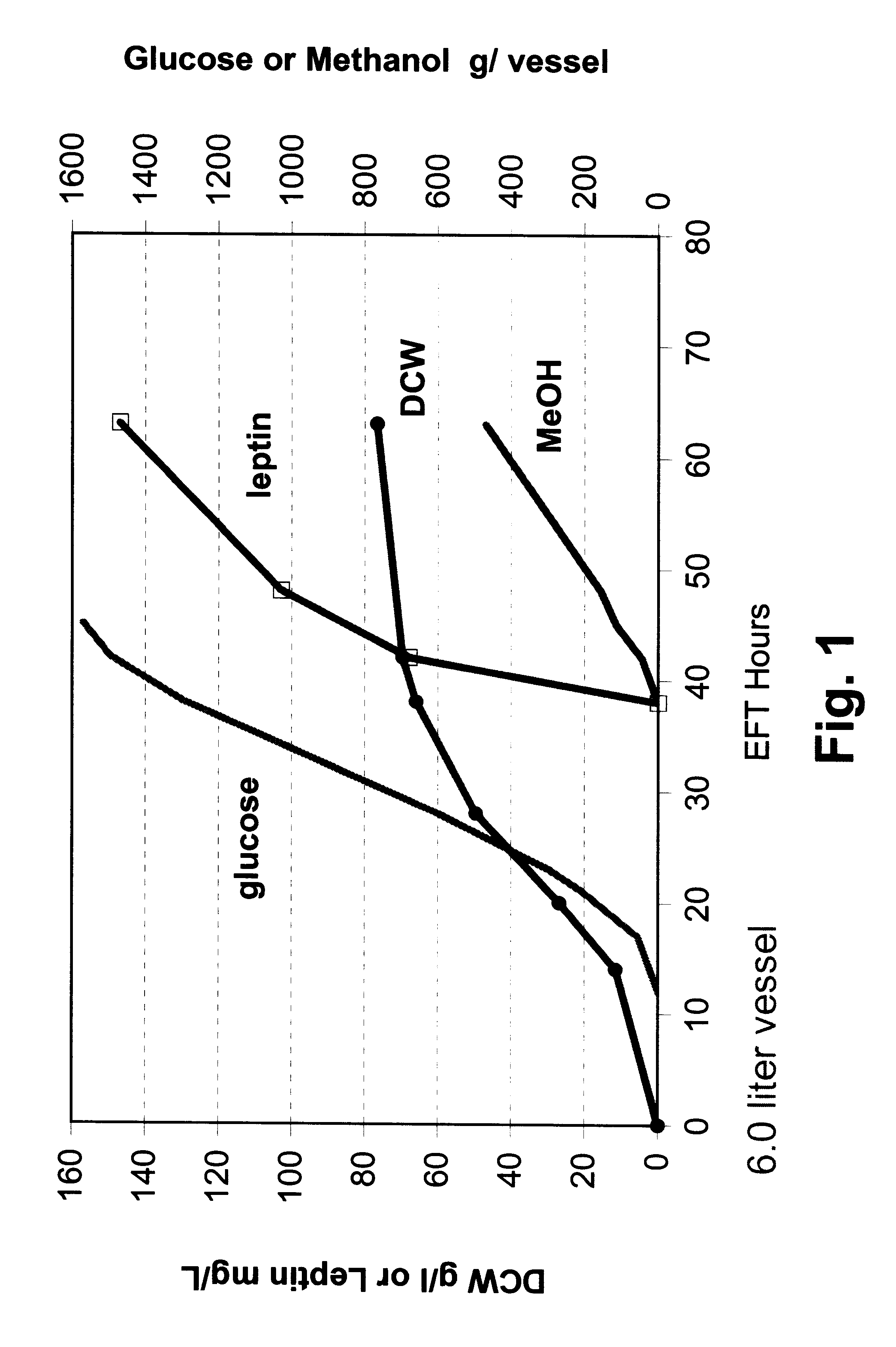
In this example, P. methanolica PMAD16-OBNEE was grown in a fed batch fermentation in a non co-feeding mode. The fermentation was run in a 6.0 liter vessel with a 3.0 liter starting volume. The fermentation was started in a batch mode on 2.5% glucose using a 250 ml inoculum from a 16 hour shake flask culture grown in YEPD broth (Difco Laboratories, Inc.). The fermentation culture was grown at 30.degree. C. with pH controlled at 5.0 by the addition of 5 N NH.sub.4 OH. Dissolved oxygen was maintained above 30% through the use of an agitation speed increase / oxygen sparging cascade. At approximately 12 hours into the run, a glucose feed ("feed 1") was initiated and supplied to the fermentor using stepped rate increases for the next 33 hours (45 hours elapsed fermentation time (EFT)). At 38 hours EFT, a slow feed of 100% methanol was introduced to the fermentation culture. The glucose feed was stopped at 45 hours EFT with 1500 grams of glucose fee...
example 2
Fed Batch Fermentation with Co-feeding
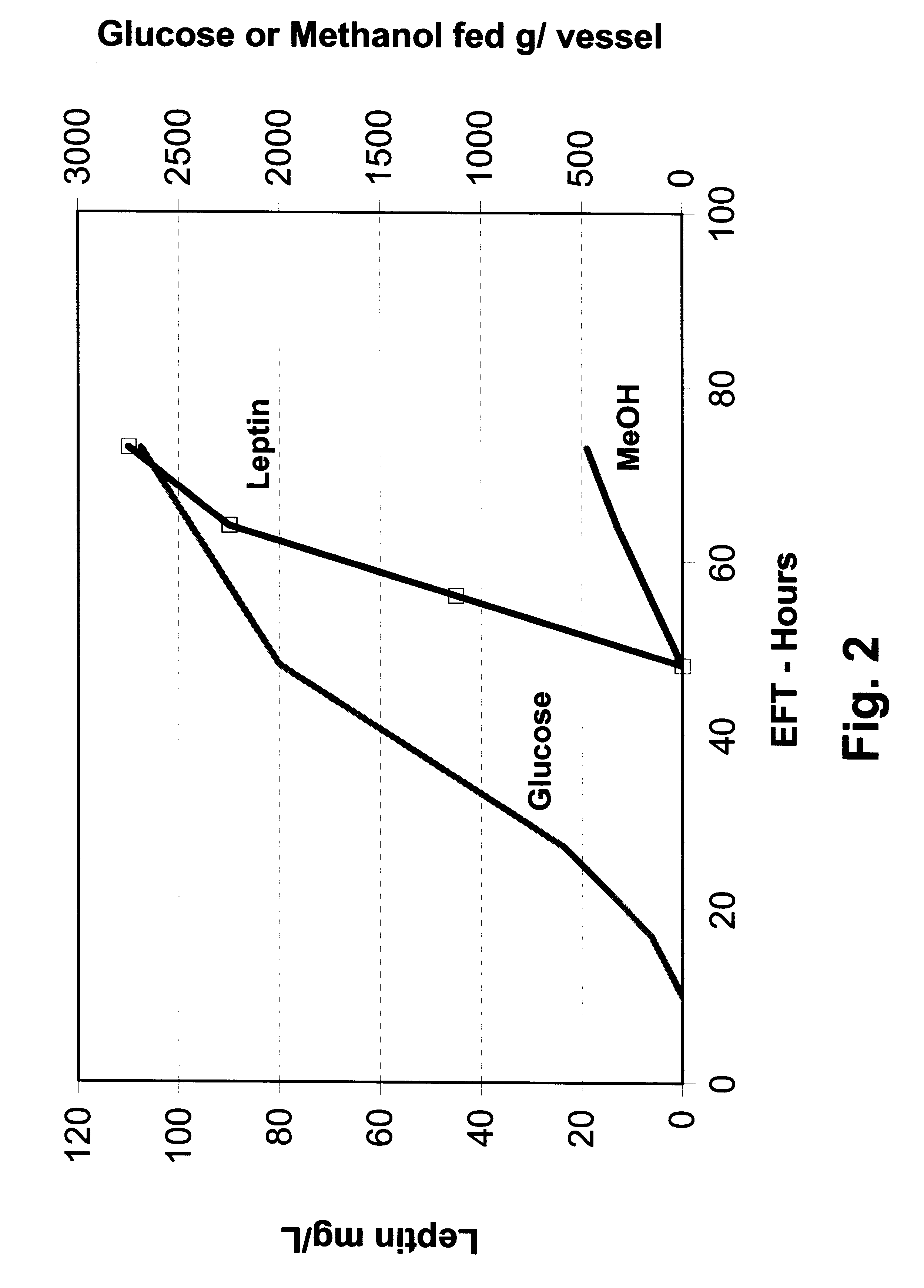
In this example, P. methanolica PMAD16-OBNEE was grown in a fed batch fermentation with glucose-methanol feeding. The fermentation was started in a batch mode on 2.5% glucose using a 250 ml inoculum from a 16 hour shake flask culture grown in YEPD broth (Difco). The fermentation was run in a 6.0 liter vessel with a 3.0 liter starting volume. The fermentation was performed at 30.degree. C. with pH controlled at 5.0 by the addition of 5 N NH.sub.4 OH. Dissolved oxygen was maintained above 30% through the use of an agitation speed increase / oxygen sparging cascade. At 10 hours into the run, a glucose feed ("feed 1") was initiated and supplied to the fermentor using stepped rate increases for the next 18 hours (28 hours EFT). The glucose feed rate was then held constant for the next 20 hours. At 48 EFT hours, the glucose feed rate was lowered by 50% and the methanol feed was started. A total of 475 grams of 100% methanol and 2690 grams of feed 1 were...
example 3
Fed Batch Fermentation with Co-feeding and Additional Nitrogen
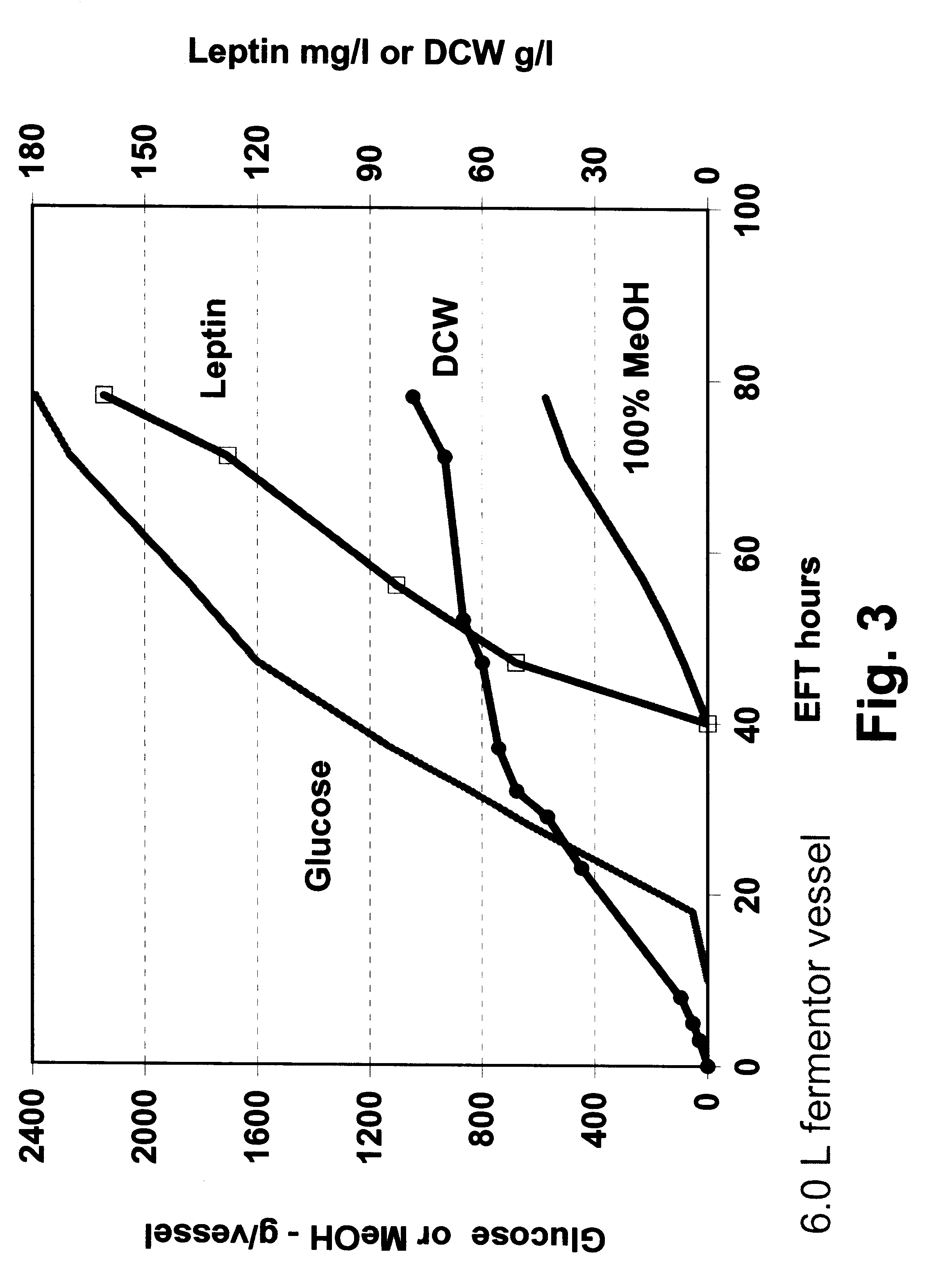
In this example, P. methanolica PMADI6-OBNEE was grown in a fed batch fermentation in a glucose methanol co-feeding mode. The fermentation was started in a batch mode on 2.5% glucose using a 250 ml inoculum from a 16 hour shake flask culture grown in YEPD broth (Difco). The illustrative minimal medium was supplemented with additional nitrogen by adding casamino acids (5.0 grams / liter) and ammonium sulfate (10.0 grams / liter). The fermentation was run in a 6.0 liter vessel with a 3.0 liter starting volume. The fermentation was performed at 30.degree. C. with pH controlled at 4.0 by the addition of 5 N NH.sub.4 OH. Dissolved oxygen was maintained above 30% through the use of an agitation speed increase / oxygen sparging cascade. At approximately 10 hours into the run, a glucose feed ("feed 1") was initiated and supplied to the fermentor using stepped rate increases for the next 30 hours (40 hours EFT). At 40 hours EFT, a slow ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com