High penetration composition and uses thereof
a composition and composition technology, applied in the field of pharmaceutical compositions, can solve the problems of limited penetration ability, adverse reactions, and inability to effectively treat the condition, and achieve the effects of reducing potential suffering, faster rate, and effective or much faster treatmen
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
on of a HPP from a Parent Drug
[0150]In certain embodiments, a parent compound having the following Structure P:
F-L1-H Structure P
reacts with a compound having the following structure Q:
to obtain a HPP of Structure L:
[0151]including stereoisomers and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof, wherein:
[0152]F, L1-4 and T are defined as supra; and
[0153]W is selected from the group consisting of OH, halogen, alkoxycarbonyl and substituted aryloxycarbonyloxy. (Scheme 1)
Preparation of N-acetyl-p-aminophenyl dimethylaminobutyrate.HCl
[0154]15.1 g (0.1 mol) of acetaminophen was dissolved in 200 ml of acetone and 200 ml of 10% NaHCO3. 18.6 g (0.1 mol) of dimethylaminobutyryl chloride hydrochloride was added into the mixture was stirred for 3 hours at RT. The solvents were evaporated off. 500 ml of ethyl acetate was added into the reaction mixture and the mixture was washed with 5% NaHCO3 (1×200 ml) and water (3×100 ml). The organic solution was dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate. Sodium sul...
example 2
-Aminophenol Derivatives Showed Higher Aqueous Solubility Comparing to their Parent Drugs
[0158]HPPs of 4-aminophenol derivatives had higher aqueous solubility comparing to their parent drugs (Table 1).
TABLE 1Solubility of HPPs and parent drugsHPP(g / L)Parent Drug(g / L)N-Acetyl-p-aminophenyl>400N-Acetyl-p-aminophenoldimethylaminobutyrate•HCl(acetaminophen)4-acetamidophenyl salicylyl>4004-acetamidophenyldimethylaminobutyrate•HClsalicylate (acetaminosalol)
example 3
-Aminophenol Derivatives Showed Higher In Vitro Penetration Rates Across Human Skin Comparing to their Parent Drugs
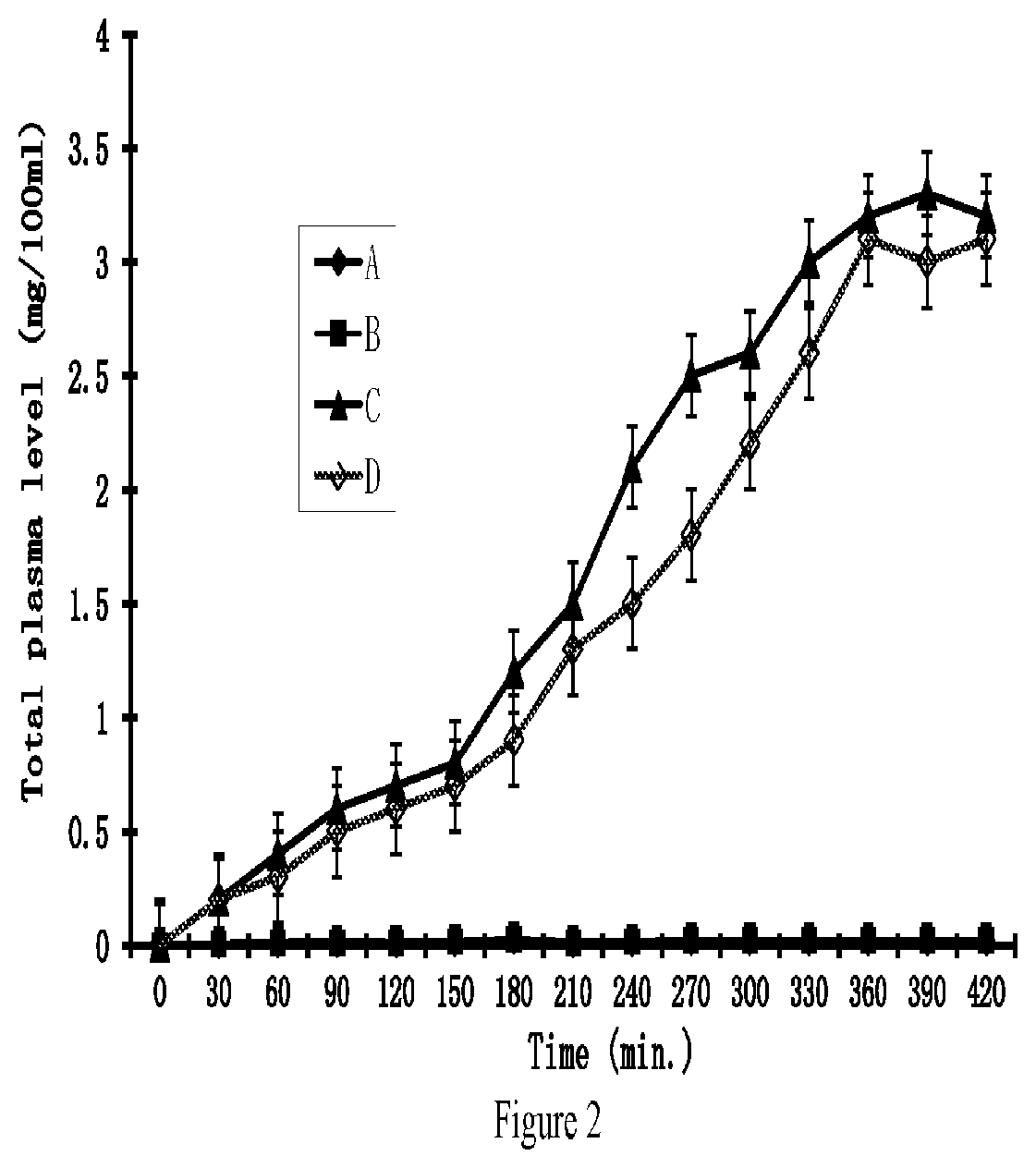
[0159]The penetration rates of HPPs of 4-aminophenol derivatives and their parent drugs through human skin were measured in vitro by modified Franz cells. The Franz cells had two chambers, the top sample chamber and the bottom receptor chamber. The human skin tissue (360-400 pm thick) that separated the top and the receptor chambers was isolated from the anterior or posterior thigh areas.
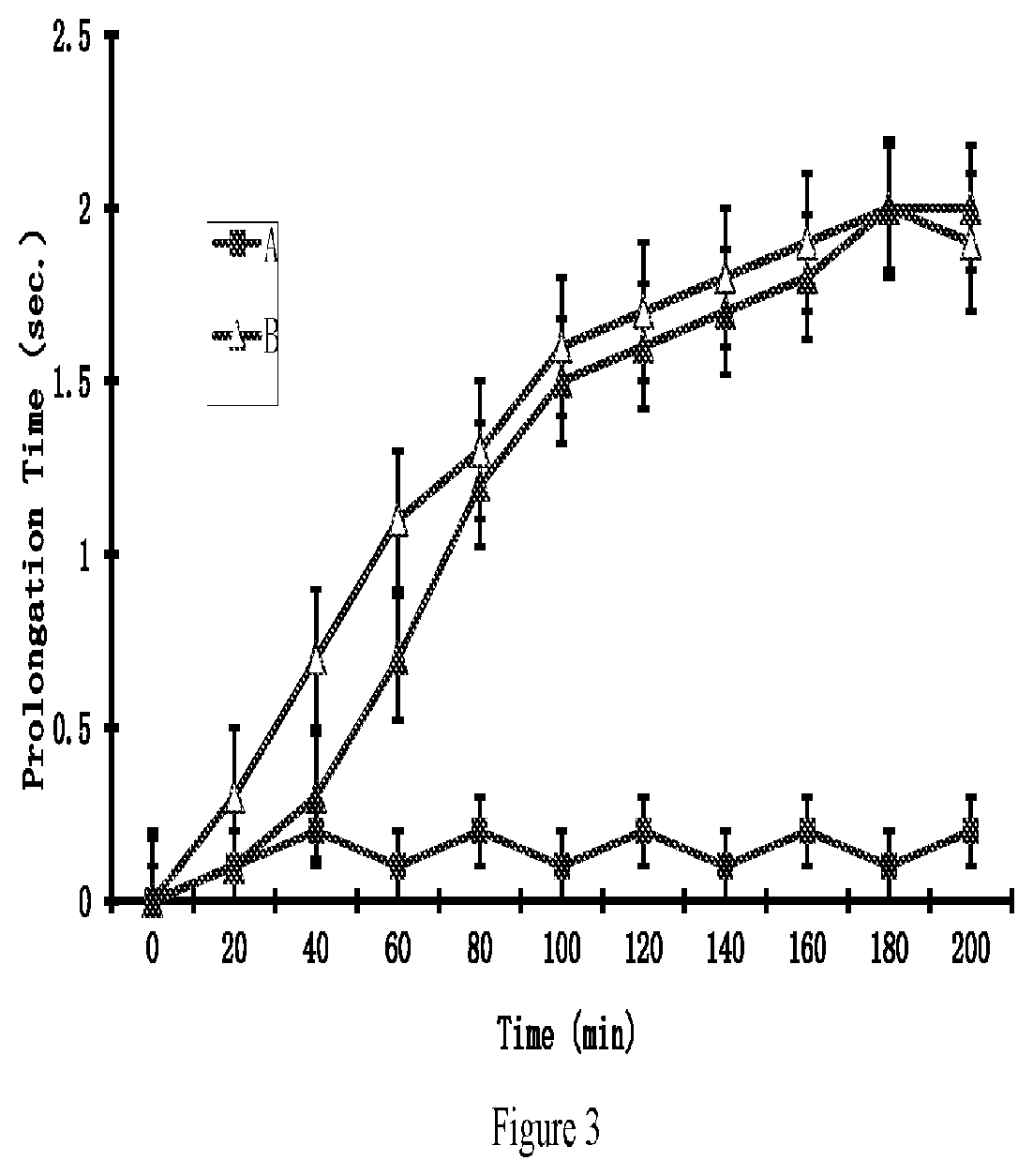
[0160]The compound tested (2 mL, 20% in 0.2 M phosphate buffer, pH. 7.4) were added to the sample chamber of a Franz cell. The receptor chamber contained 10 ml of 2% bovine serum albumin in saline which was stirred at 600 rpm. The amount of the tested compound penetrating the skin was determined by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) method. The results were shown in FIG. 1. The apparent flux values of the tested compounds were calculated from the slopes in FIG. 1 and summariz...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| lipophilic | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| chemical structure | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| structure | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com