Methods and Compositions for Preparing Biological Specimens for Microscopic Analysis
a technology of biological specimens and compositions, applied in the direction of optical elements, instruments, separation processes, etc., can solve the problems of prohibitively inefficient and damaging mechanical sectioning and reconstruction, incompatible with immunostaining/molecular phenotyping, etc., and achieve the effect of increasing the optical clarity of the specimen
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
or Imaging Whole Tissue
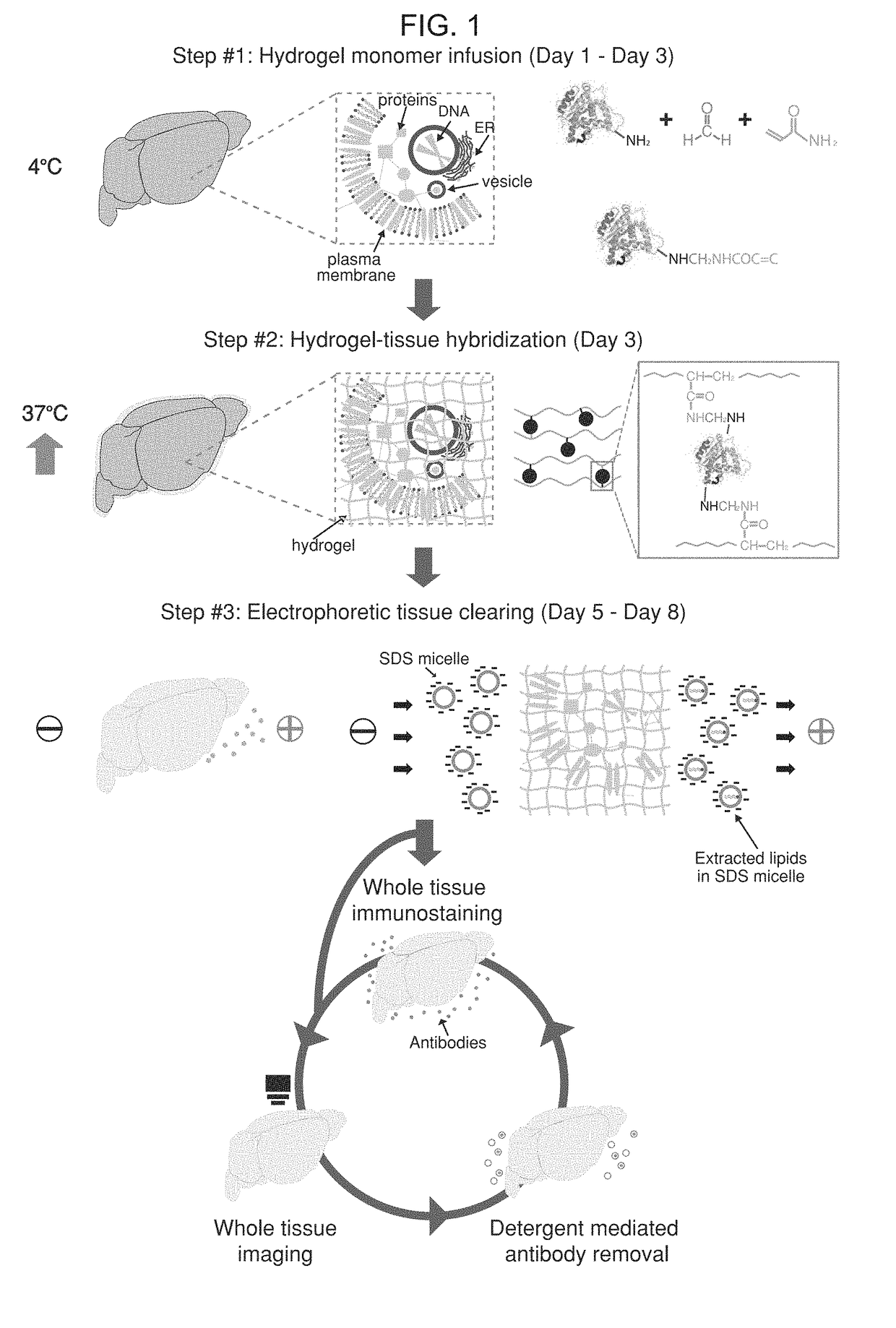
[0158]A process was developed to image whole tissue (including whole organs / organisms) for precise three-dimensional (3-D) imaging, immunohistology, clinical diagnostics, and functionalization. By embedding a tissue in nano-porous hydrogel that physically supports the ultrastructure of the tissue and then electrophoretically removing only membrane lipids, the whole tissue becomes highly transparent and permeable to macro-molecules. This technology preserves proteins, small peptides, small molecules, and nucleic acids in the tissue in their three-dimensional distribution, secured by the fine hydrogel mesh. By bypassing destructive sectioning of the tissue, subcellular structures may be analyzed. In addition, tissue can be iteratively stained, unstained, and restained with other reagents for comprehensive analysis. An illustration of the process, termed “CLARITY,” is provided in FIG. 1. Panel a: tissue is crosslinked using formaldehyde (red) in the presence of h...
example 2
nd Systems for CLARITY Process
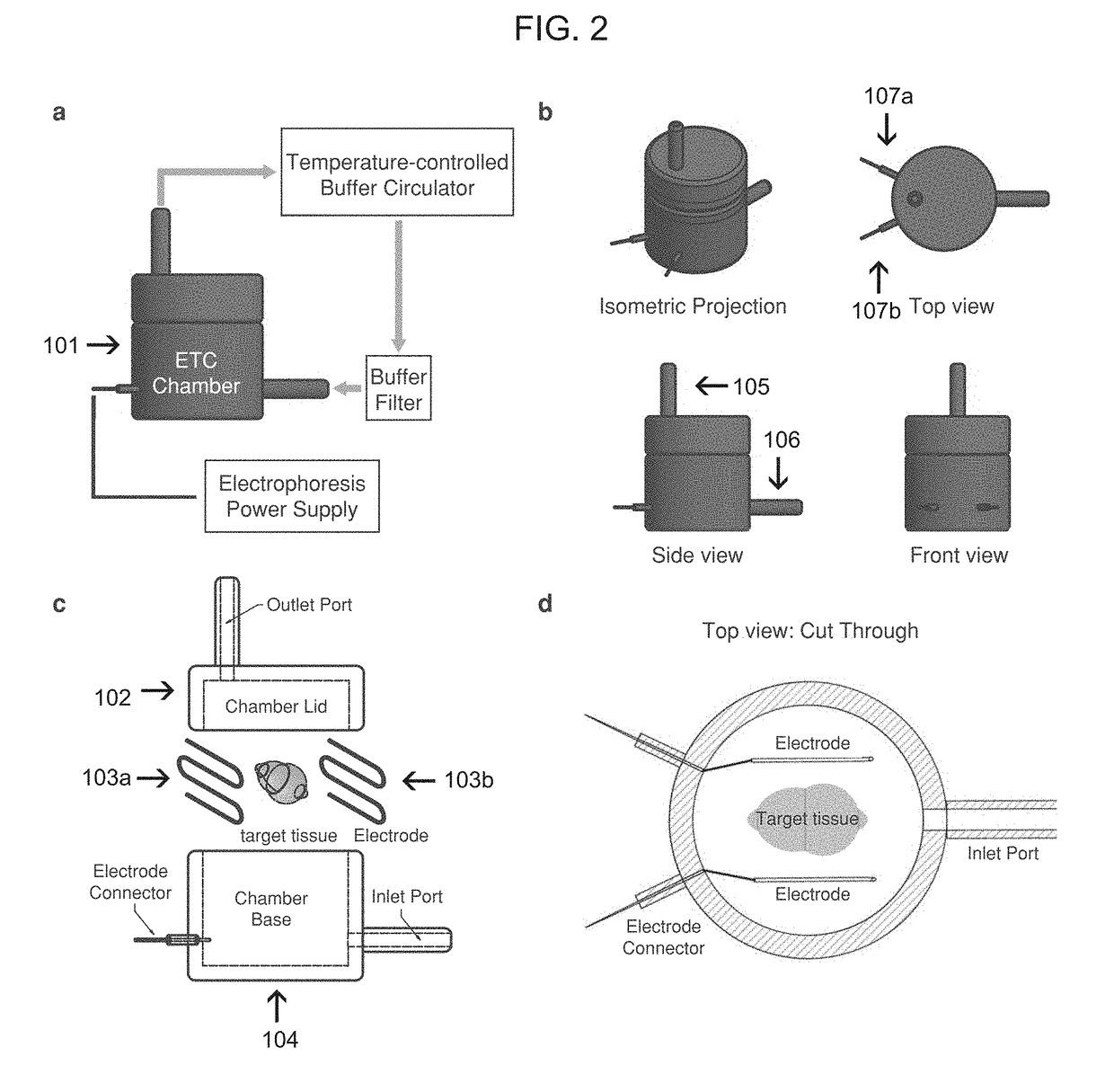
[0159]An electrophoretic tissue clearing (FTC) chamber and associated components (including a temperature-controlled buffer circulator, buffer filter, and electrophoresis power supply) were developed to carry out portions of the CLARITY process described in Example 1. Illustrations of the devices and systems are provided in FIG. 2. Panel a: ETC setup consists of the custom ETC chamber, a temperature-controlled buffer circulator (RE415, Lauda, Germany), a buffer filter (Cat. No. 4422K61, McMaster, Robbinsville, N.J.), and a power supply (Cat. no. 164-5052, Biorad, Hercules, Calif.). The sample is electrophoresed by applying 20-60V to the electrodes. Buffer solution is circulated through the chamber to maintain temperature and the composition of the buffer solution constant throughout the clearing process. Panels b-d: ETC chamber design. Panel b shows various views of a representative device showing a cylindrical plastic housing, inlet / outlet ports (Cat. ...
example 3
f Intact Adult Mouse Brain Samples
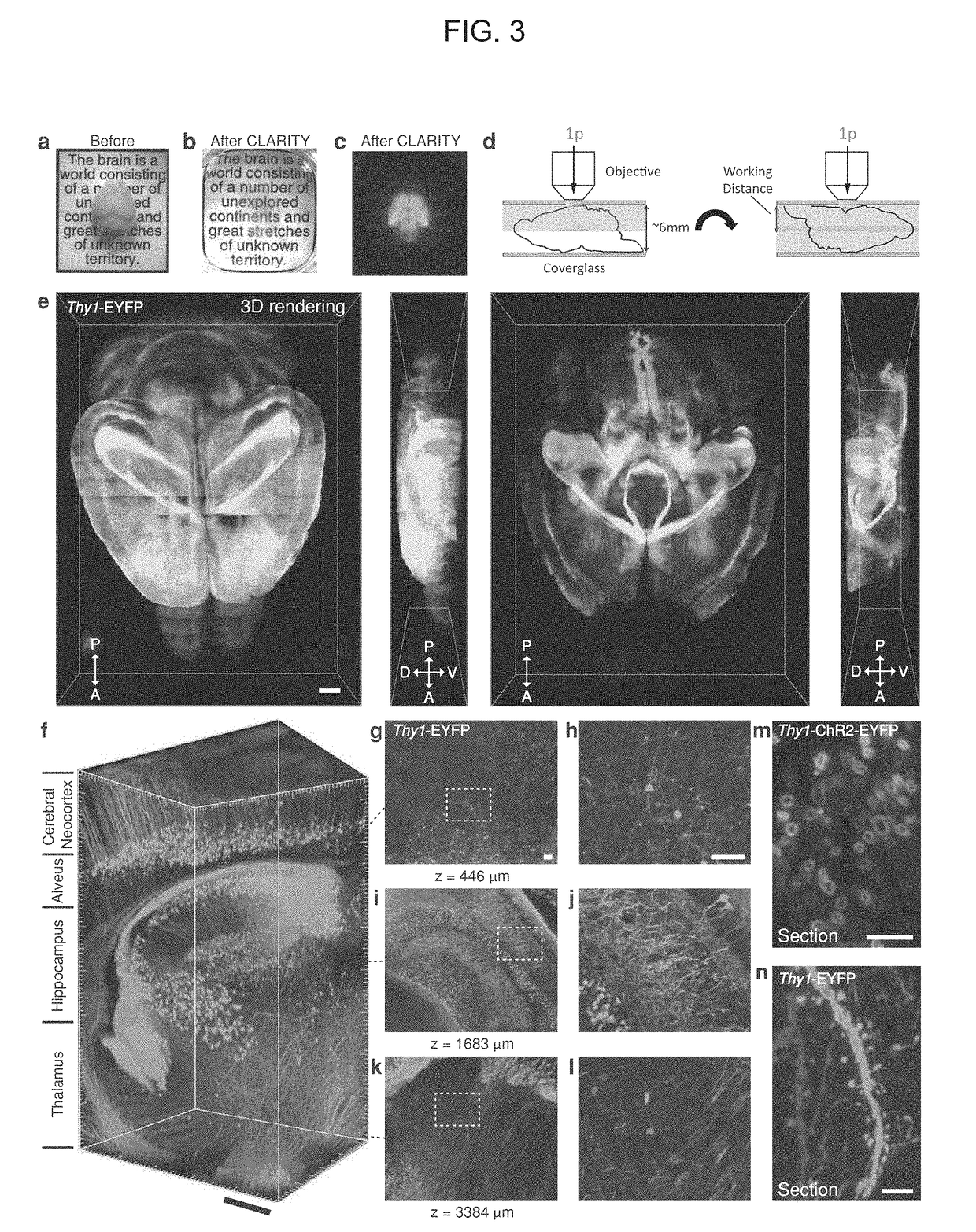
[0160]Intact adult mouse brain samples were subjected to the CLARITY process and imaged. FIG. 3 shows the results. Panels a-d: images of whole mouse brains (three months old) with a Ramon y Cajal quote in the background. Panel a: before CLARITY. Panel b: after CLARITY: Thy1-EYFP H line brain after hydrogel-tissue hybridization, ETC, and refractive index (RI) matching with FocusClear™. Panel c: fluorescent image of the same brain shown in Panel b. Panel d: mounting of the whole cleared mouse brain for imaging. The brain is enclosed between two coverglasses. The dorsal half of the brain is first imaged using single photon (1P) excitation microscopy, and then the brain is inverted and the ventral half is imaged. Panel e: 3D reconstruction of the intact CLARITY-processed mouse brain (three months old) that was imaged using a 10× water immersion objective (numerical aperture (NA)=0.3, working distance=3.6 mm) and 514 nm excitation. Left, reconstruction o...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| voltage | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| depths | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com