Growth method of dendritic crystal structure that provides directional heat transfer
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0063]The above and other detailed contents, features and effects with respect to the growth method of dendritic crystal structure that provides directional heat transfer of the present invention will be clearly presented in the following preferred embodiments and accompanying drawings.
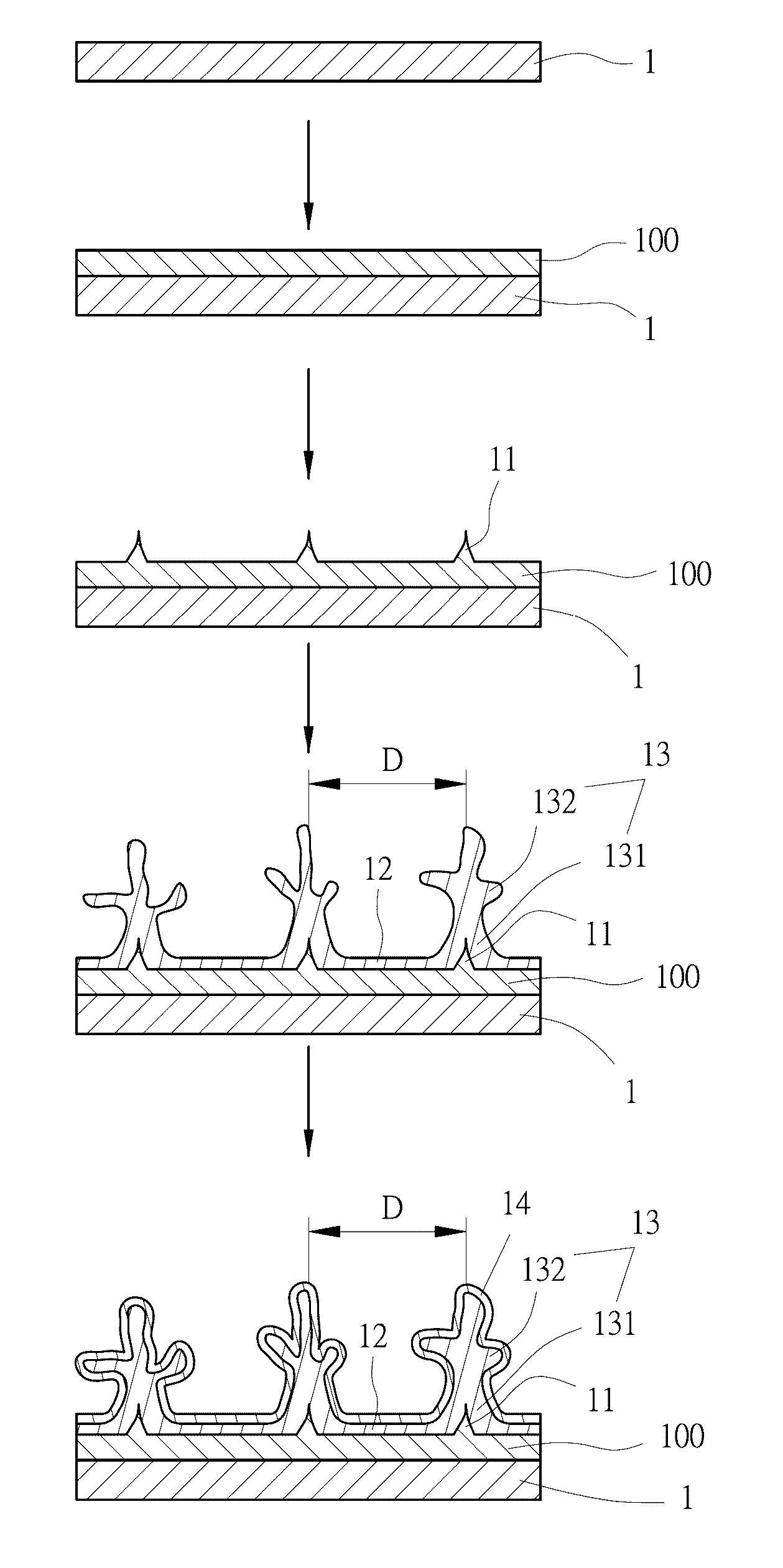
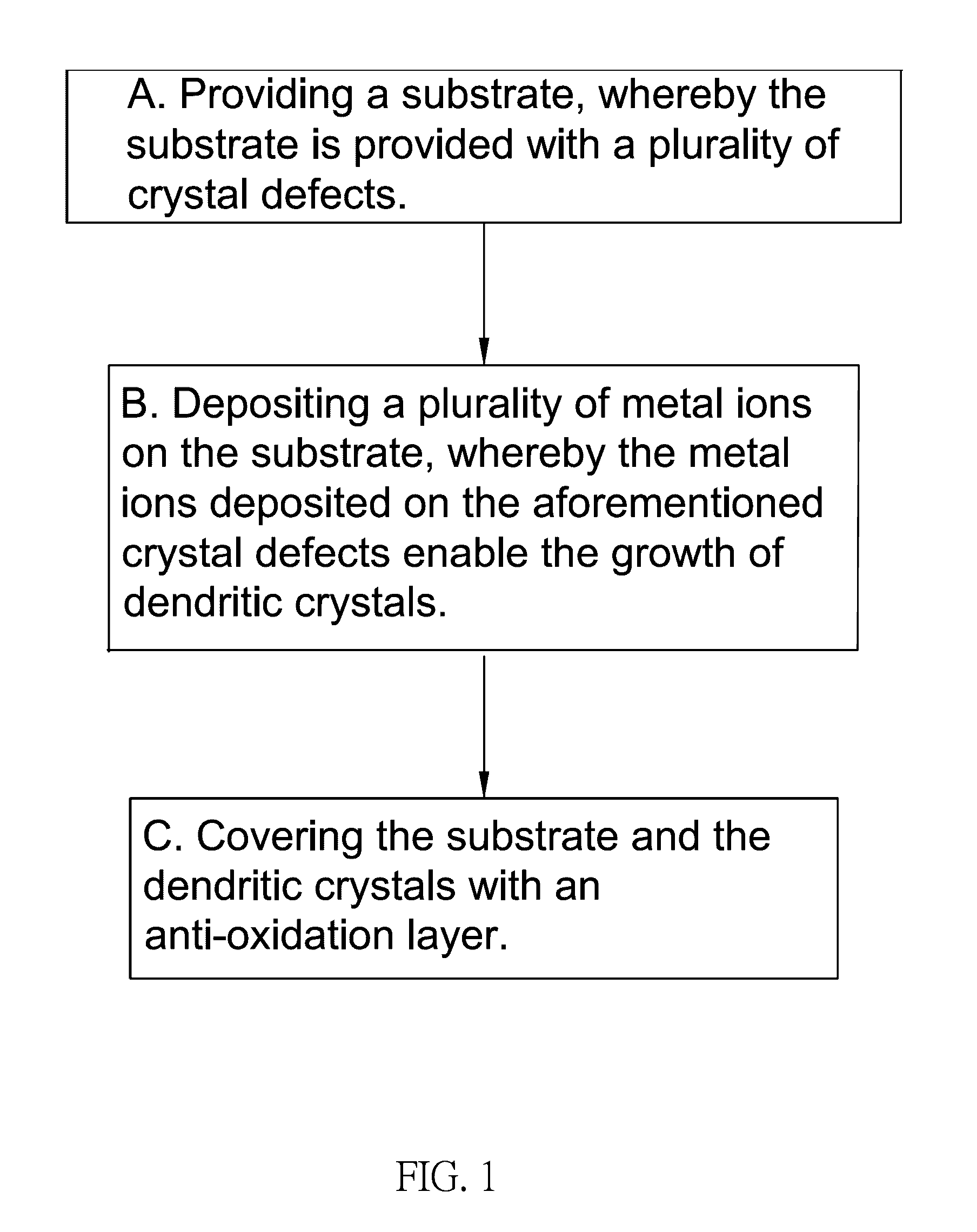
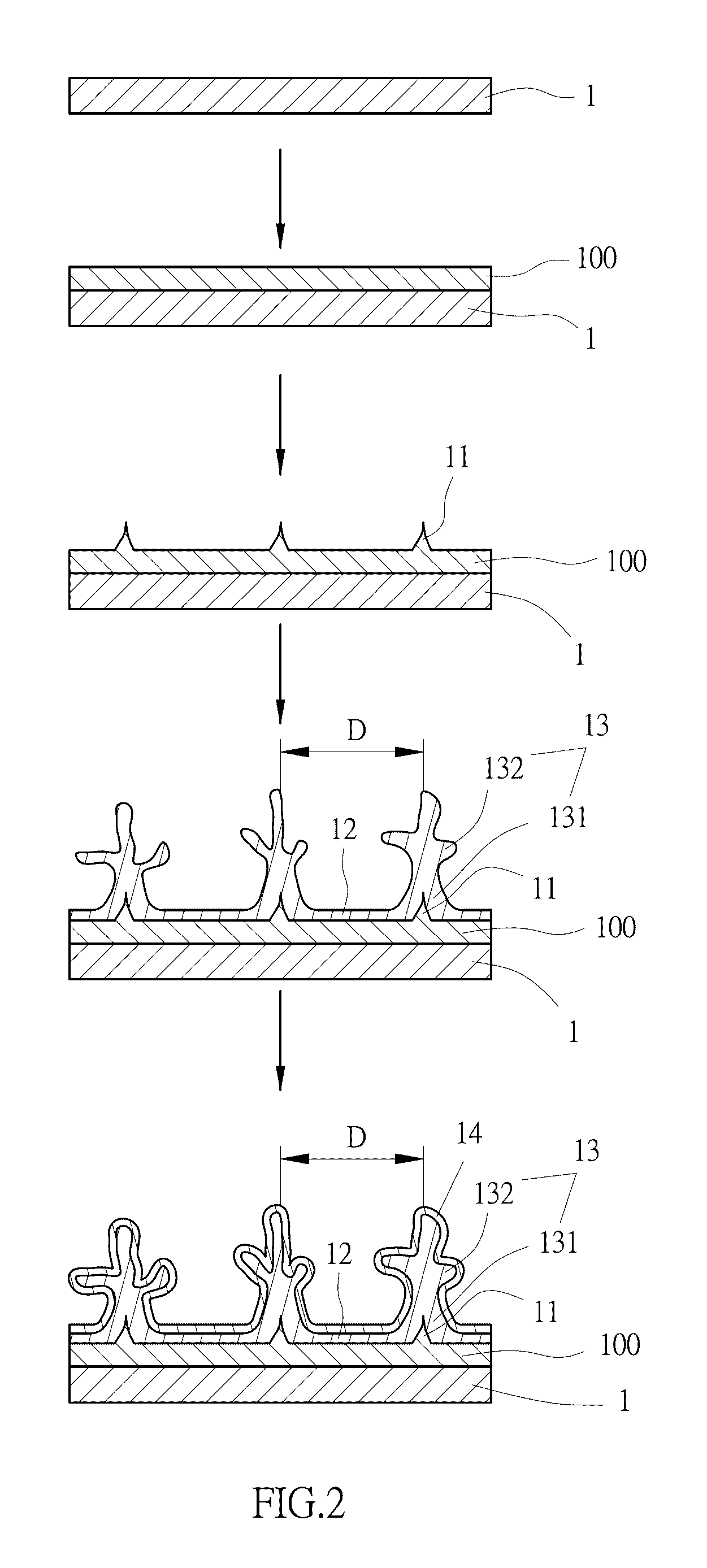
[0064]Referring first to FIG. 1 and FIG. 2, which show a step flow diagram and a preparation flow diagram, respectively, of an embodiment of a growth method of dendritic crystal structure that provides directional heat transfer of the present invention, comprising the following steps: A. Providing a substrate (1), whereby a substrate (1) is provided with a plurality of crystal defects (11) separated at intervals. The definition of the crystal defects (11) in the present invention is hereby described as not only including forms whereby there is damage to the regular crystal structure such as general point defects and line defects, but also includes whisker type defects. It is preferred that the substra...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com