Electrode material, paste for electrodes, and lithium ion battery
a lithium ion battery and electrode technology, applied in the field of electrode electrode paste, electrode electrode paste, and electrode electrode electrode electrode electrode electrode electrode electrode electrode electrode electrode electrode electrode electrode electrode electrode electrode electrode electrode electrode electrode electrode electrode electrode electrode electrode electrode electrode electrode electrode electrode electrode electrode electrode electrode electrode electrode electrode electrode electrode electrode electrode electrode electrode electrode electrode electrode electrode electrode electrode electrode electrode electrode electrode electrode electrode electrode electrode electrode electrode electrode electrode electrode electrode electrode electrode electrode electrode electrode electrode electrode electrode electrode electrode electrode electrode electrode electrode electrode electrode electrode electrode electrode electrode electrode electrode electrode electrod
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
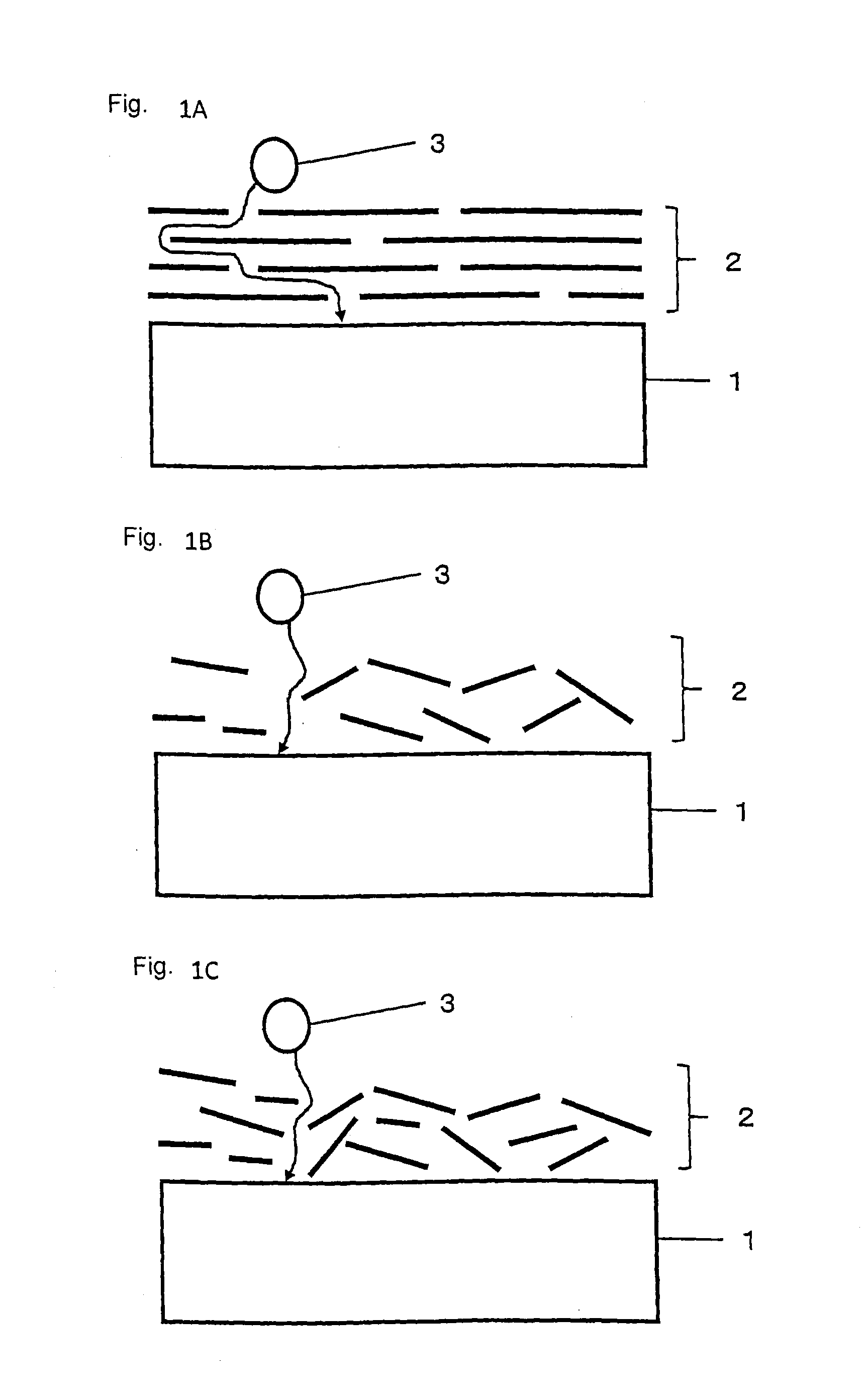
Image
Examples
example 1
[0149]4 mol of lithium acetate (LiCH3COO), 2 mol of iron (II) sulfate (FeSO4), and 2 mol of phosphoric acid (H3PO4) were mixed with 2 L (liters) of water so that the total amount reached 4 L, thereby preparing a homogeneous slurry-form mixture. Next, the mixture was accommodated in a pressure-resistant airtight container having a capacity of 8 L, and was hydrothermally synthesized for 1 hour at 200° C. Next, the obtained sediment was washed using water, thereby obtaining a cake-form precursor of an electrode active material.
[0150]Next, an aqueous solution obtained by dissolving 1.5 g of polyvinyl pyrrolidone and 0.15 g of carboxymethyl cellulose in 100 g of water and 100 g of the precursor of the electrode active material (in terms of the solid content) were mixed so as to produce a slurry, and a dispersion treatment was carried out on the slurry using a binary fluid-type wet jet crusher so that the average particle diameter (D50) of the primary particles of precursor particles of t...
example 2
[0153]An electrode material was obtained in the same manner as in Example 1 except for the fact that the amount of carboxymethyl cellulose added to produce the slurry was changed to 0.375 g and the firing temperature of the granulated body in the non-oxidative atmosphere was set to 720° C. Regarding the content of the organic compound in the slurry of Example 2, the amount of carboxymethyl cellulose (organic compound ii) was 25 parts by mass with respect to 100 parts by mass of polyvinyl pyrrolidone (organic compound i).
example 3
[0154]An electrode material was obtained in the same manner as in Example 1 except for the fact that the amount of carboxymethyl cellulose added to produce the slurry was changed to 0.75 g and the firing temperature of the granulated body in the non-oxidative atmosphere was set to 740° C. Regarding the content of the organic compound in the slurry of Example 3, the amount of carboxymethyl cellulose (organic compound ii) was 50 parts by mass with respect to 100 parts by mass of polyvinyl pyrrolidone (organic compound i).
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com