CD20 Antibodies and Uses Thereof
a technology of cd20 and antibodies, which is applied in the field of cd20 antibodies, can solve the problems of rituximab-refractory nhl patients that are not active on rituximab, the type i antibodies typically do not have effective pro-apoptotic activity on their own, and many patients do not respond to rituximab, so as to improve the adcc function, improve stability, and increase stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Production of Murine CD20 Antibodies
[0483]An expression plasmid pSRa-CD20 was constructed that contained the entire CD20 coding sequence (CDS) flanked by XbaI and BamHI restriction sites that allowed expression of human CD20 (GI 23110989). 300-19 cells, a pre-B cell line derived from a Balb / c mouse (Reth et al., Nature, 317:353-355 (1985)), was transfected with this expression plasmid to stably express high levels of human CD20 on the cell surface and used for immunization of Balb / c VAF mice. Mice were subcutaneously immunized with approximately 5×106 CD20-expressing 300-19 cells per mouse every 2-3 weeks by standard immunization protocols known to those of skill, for example, such as those used at ImmunoGen, Inc. Immunized mice were boosted with antigen three days before being sacrificed for hybridoma generation. Spleens from mice was collected according to standard animal protocols, such as, for example grinding tissue between two sterile, frosted microscopic slides to obtain a si...
example 2
Binding Characterization by Flow Cytometry
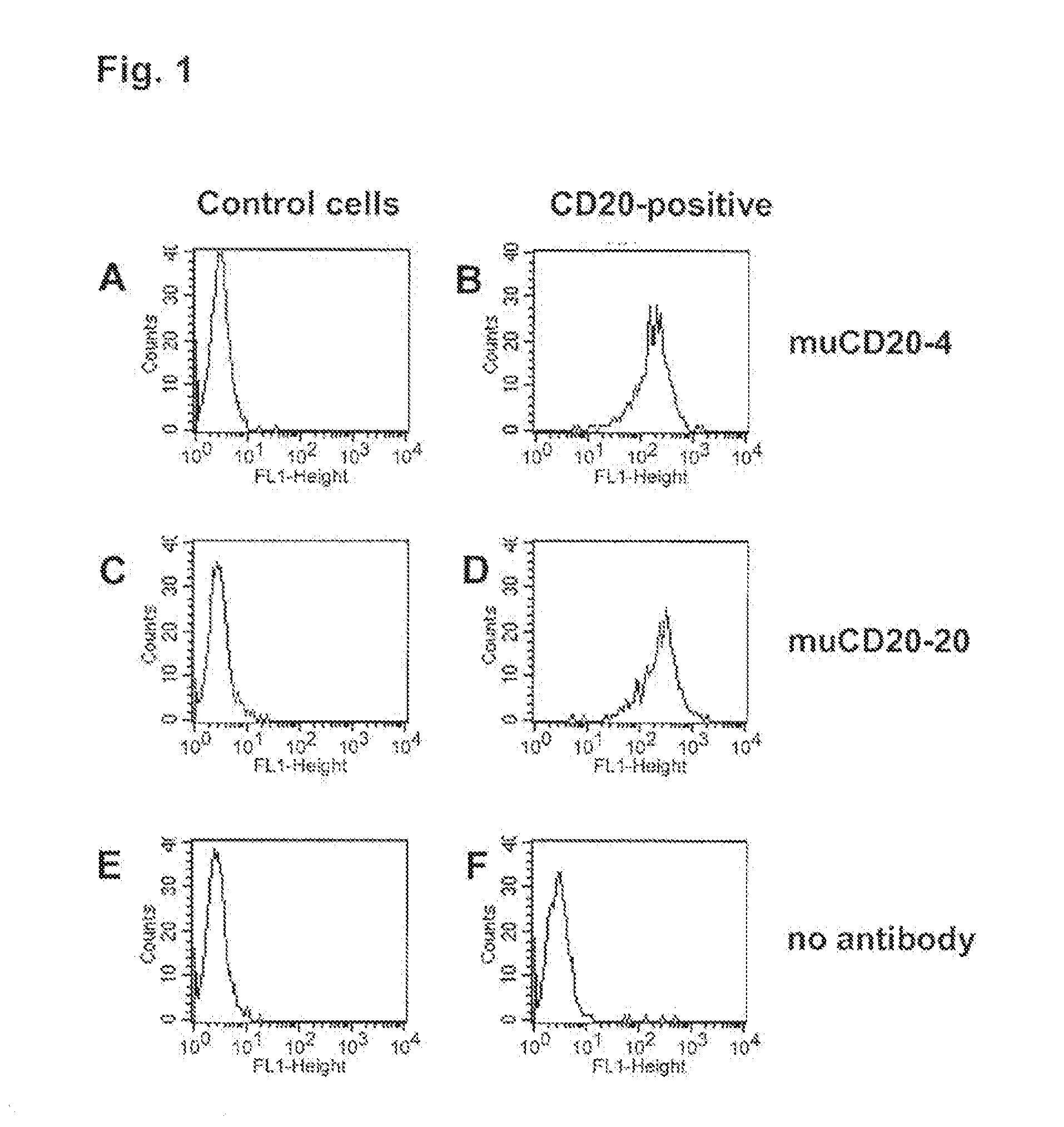
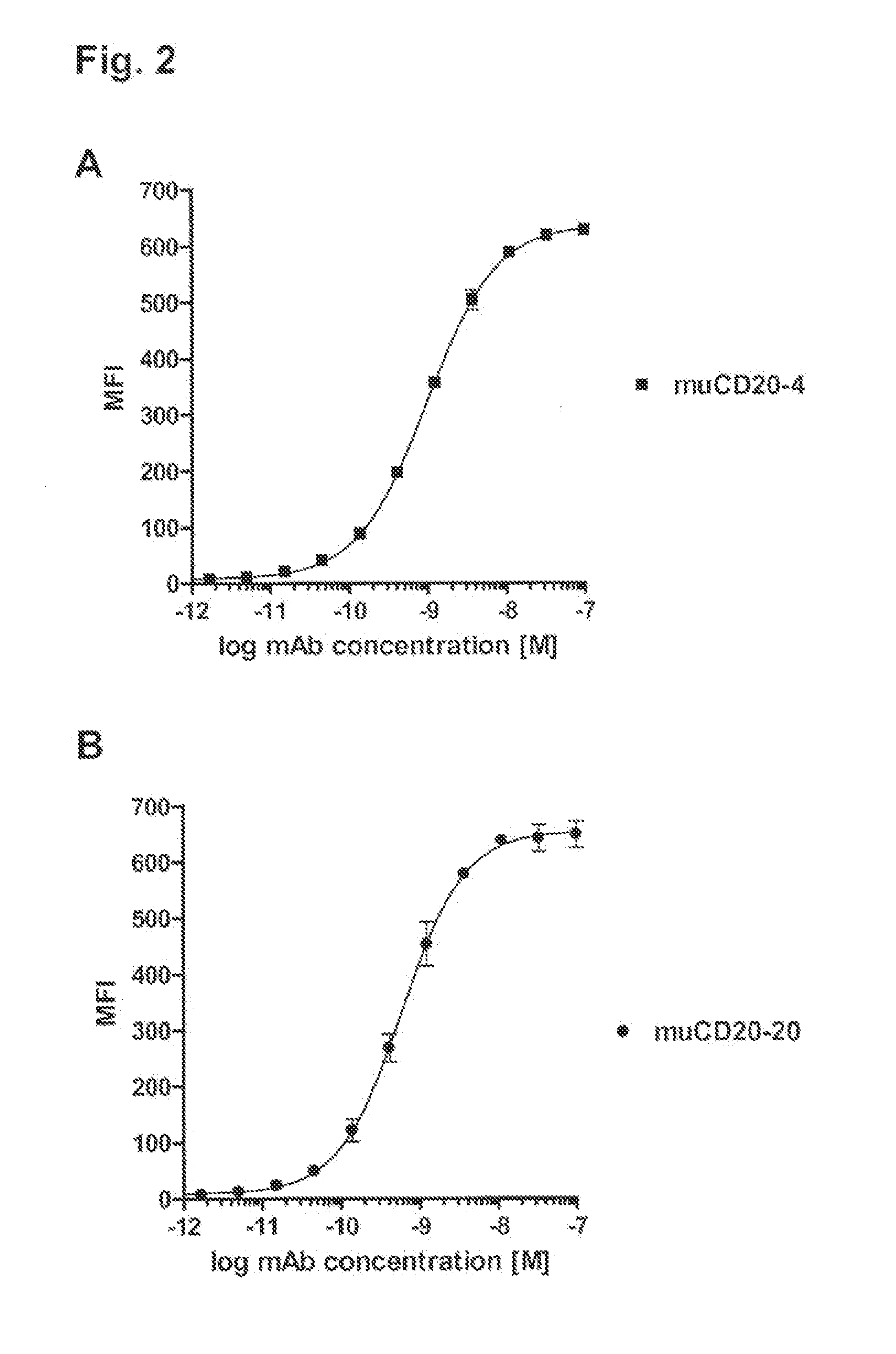
[0490]Binding specificity was tested by flow cytometry using purified antibodies. FACS histograms demonstrating the binding of muCD20-4 and muCD20-20 to CD20-expressing 300-19 cells and the absence of binding to the parental 300-19 cells are shown in FIG. 1. Either muCD20-4 or muCD20-20 antibody was incubated for 3 h with either CD20-expressing 300-19 cells or the non-transfected 300-19 cells (1×105 cells per sample) in 100 μL FACS buffer (RPMI-1640 medium supplemented with 2% normal goat serum). Then, the cells were pelleted, washed, and incubated for 1 h with 100 μL of FITC-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG-antibody (such as is obtainable from, for example Jackson Laboratory, 6 μg / mL in FACS buffer). The cells were pelleted again, washed with FACS buffer and resuspended in 200 μL of PBS containing 1% formaldehyde. Samples were acquired using a FACSCalibur flow cytometer with the HTS multiwell sampler or a FACS array flow cytometer and analyze...
example 3
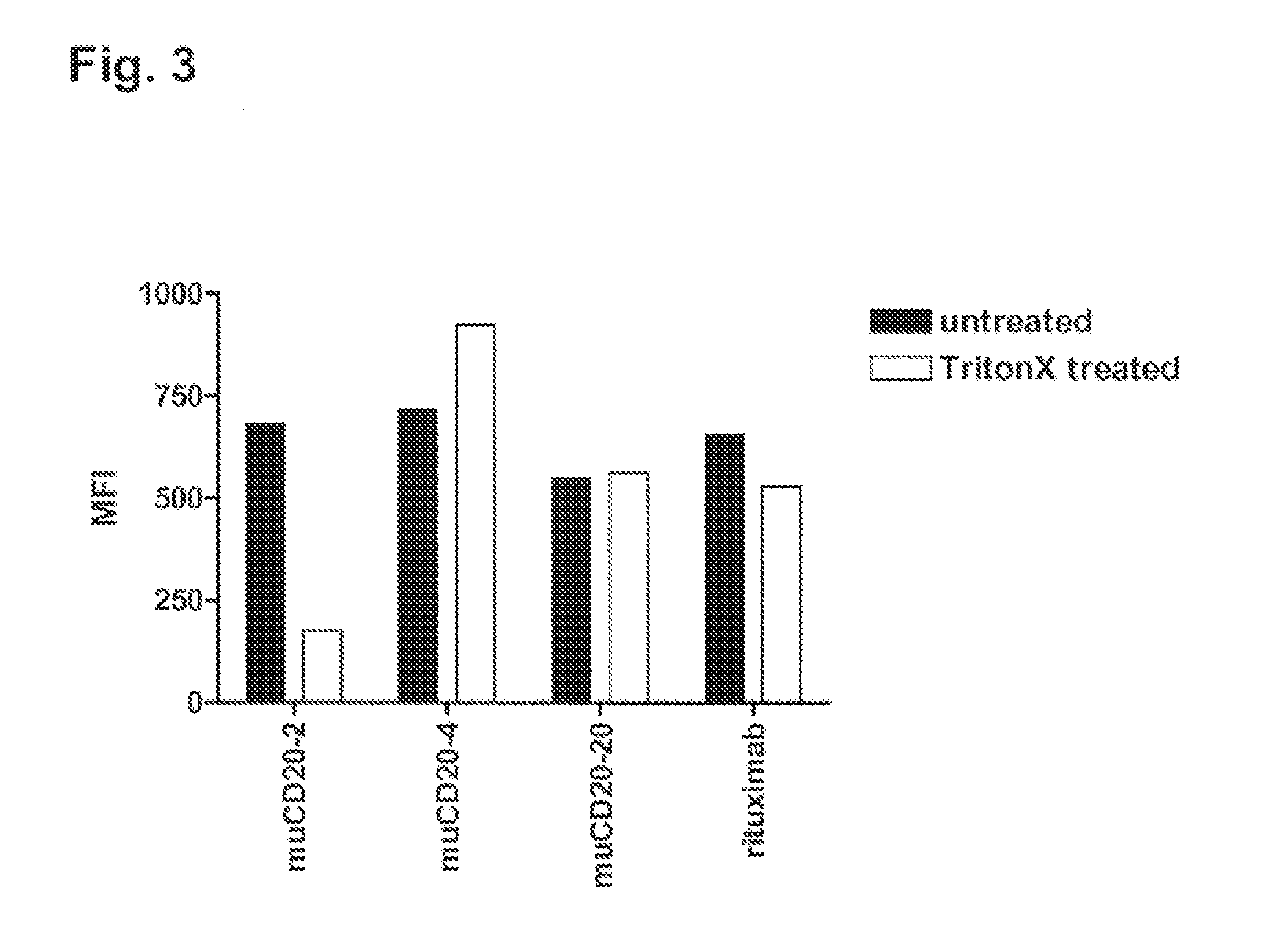
[0493]The reorganization of CD20 into lipid rafts following antibody binding has been correlated with the ability of the antibody to effectively recruit complement factors and elicit CDC activity. As a measure of antibody induced CD20 re-distribution to lipid rafts we employed a flow cytometry based method modified from Cragg et al. (2003), supra). The principle of this assay is based on the TritonX-100 insolubility of lipid raft compartments at low temperatures.
[0494]Cells were harvested by centrifugation, washed and re-suspended in RPMI-1640 with 1% BSA. 0.2 mL of cells at 2.5×106 cells were used for each assay in duplicate. Anti-CD20 antibodies were added at 10 μg / mL and samples were incubated for 15 min at 37° C. Samples were centrifuged, washed twice and re-suspended in 0.2 mL of FACS buffer (1×PBS, 1% BSA, 20 mM Na-azide). Samples were chilled on ice and kept cold from this point on. To detect the fraction of antigen associated with lipid rafts in response to antibod...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com