Input current limited power supply and audio power amplifier for high power reproduction of nondeterministic signals
a technology of input current and limited power supply, applied in power management, high-level techniques, wireless communication, etc., can solve the problems of low-voltage battery, audio fidelity, and audio power
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
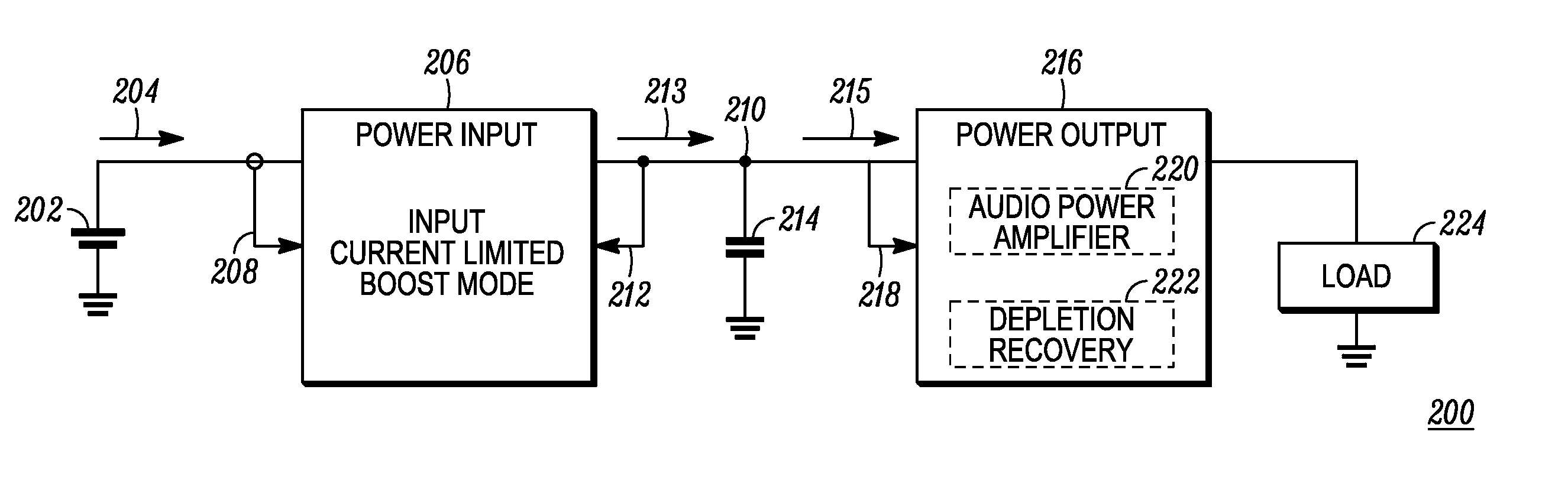
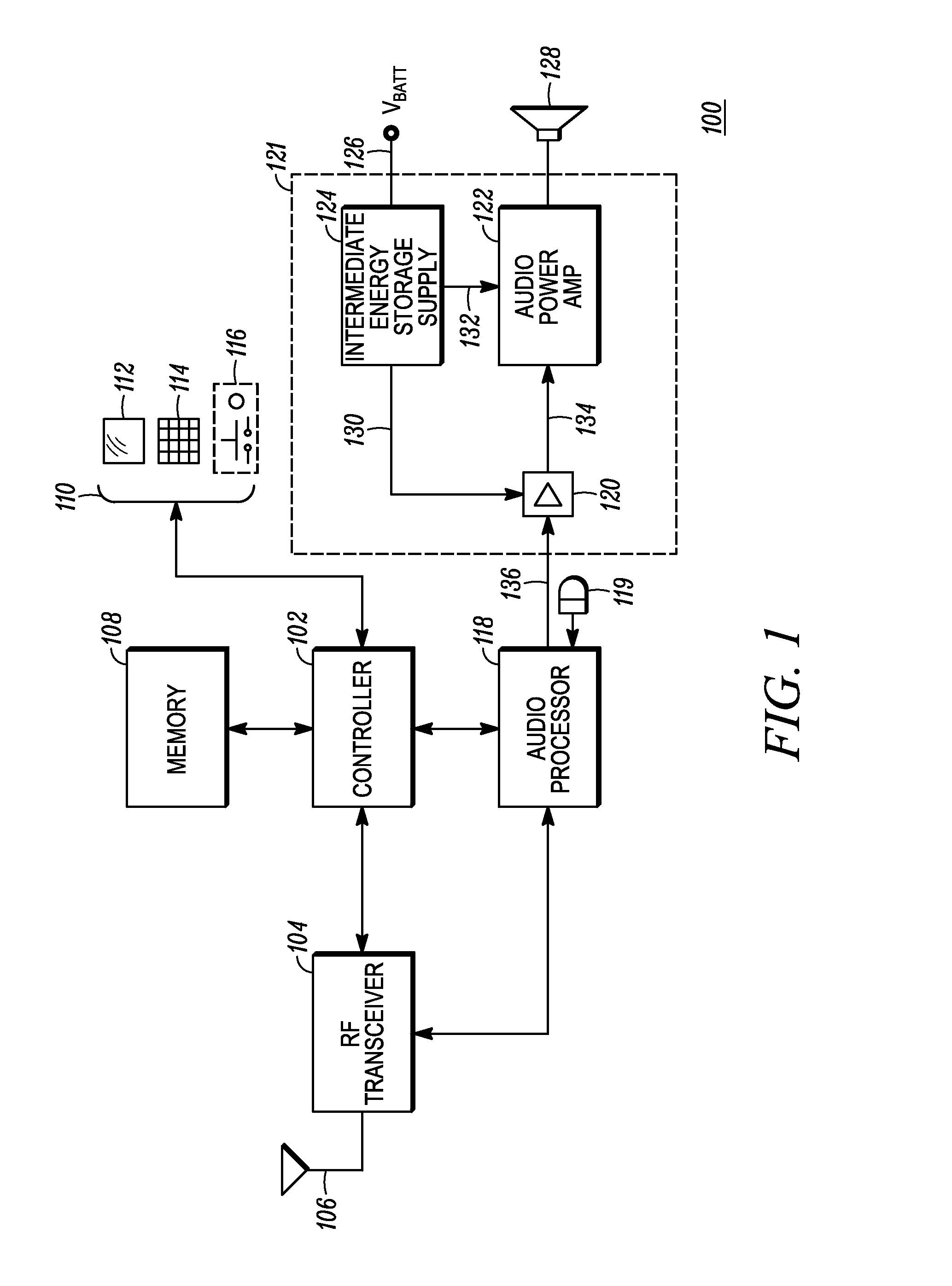
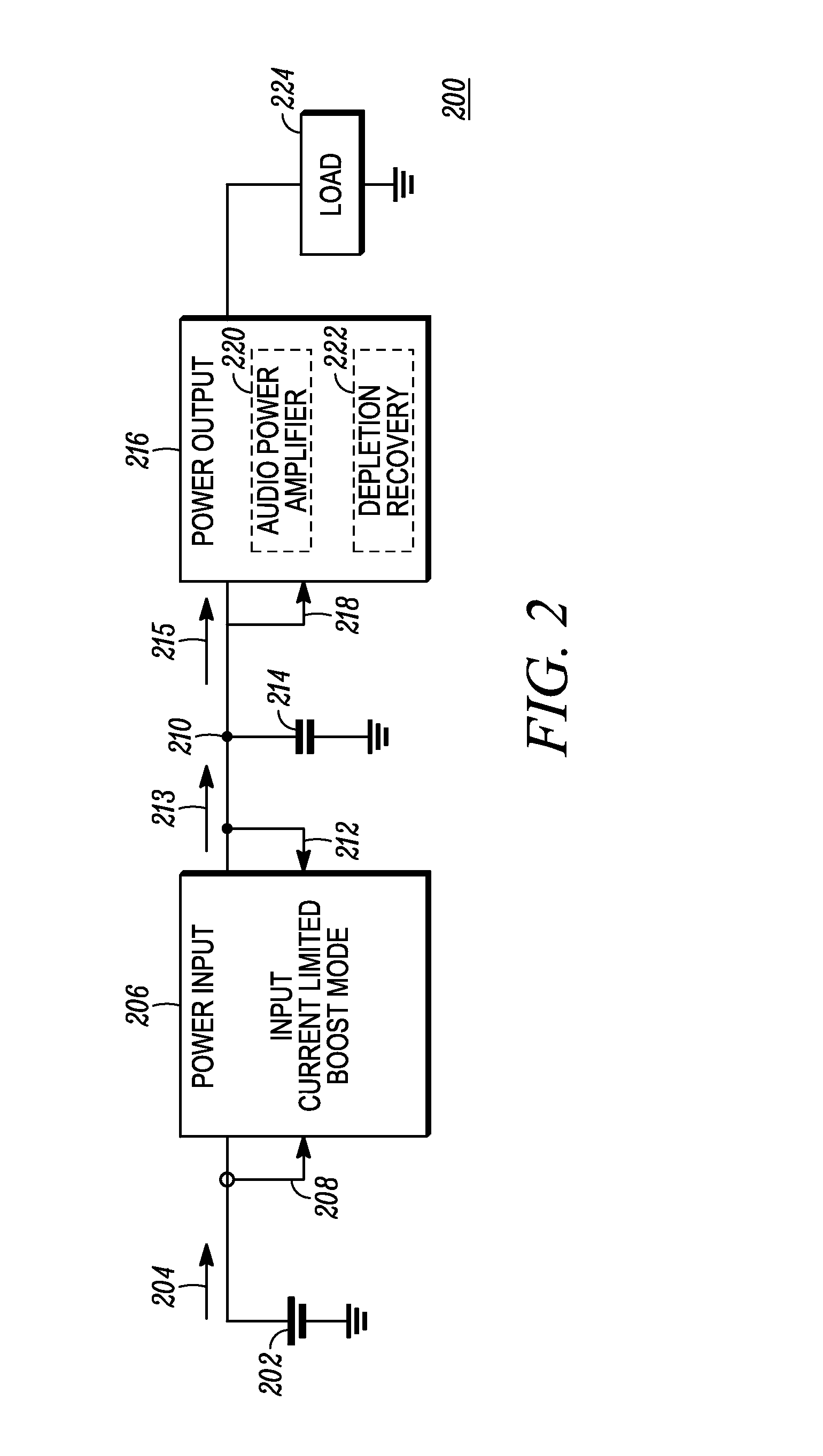
[0015]Some embodiments as disclosed herein include a method for powering an audio power amplifier includes boosting a voltage level of a battery to a boost voltage level across a boost capacitor at an output of a boost stage without exceeding a preselected input current limit. The boost voltage level is higher than the voltage level of the battery and higher than a supply voltage required for the audio power amplifier to output a predefined maximum peak power into a load. The method further includes deriving the supply voltage from the boost voltage and providing the supply voltage to the audio power amplifier to power the audio power amplifier. The audio power amplifier amplifies an input signal to produce an amplified signal. The method further includes comparing a state of charge indication parameter to a depletion threshold, wherein the state of charge indication parameter is dependent on the boost voltage, and, when the state of charge indication parameter is below the depletio...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com