Enhanced oil recovery process to inject low salinity water and gas in carbonate reservoirs
a technology of carbonate reservoir and oil recovery process, which is applied in the direction of fluid removal, chemistry apparatus and processes, borehole/well accessories, etc., can solve the problems of reducing time, low efficiency, and high cost of full-field low salinity water injection, and achieves enhanced oil recovery process, high carbon dioxide solubility, and improved efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example
Example 1
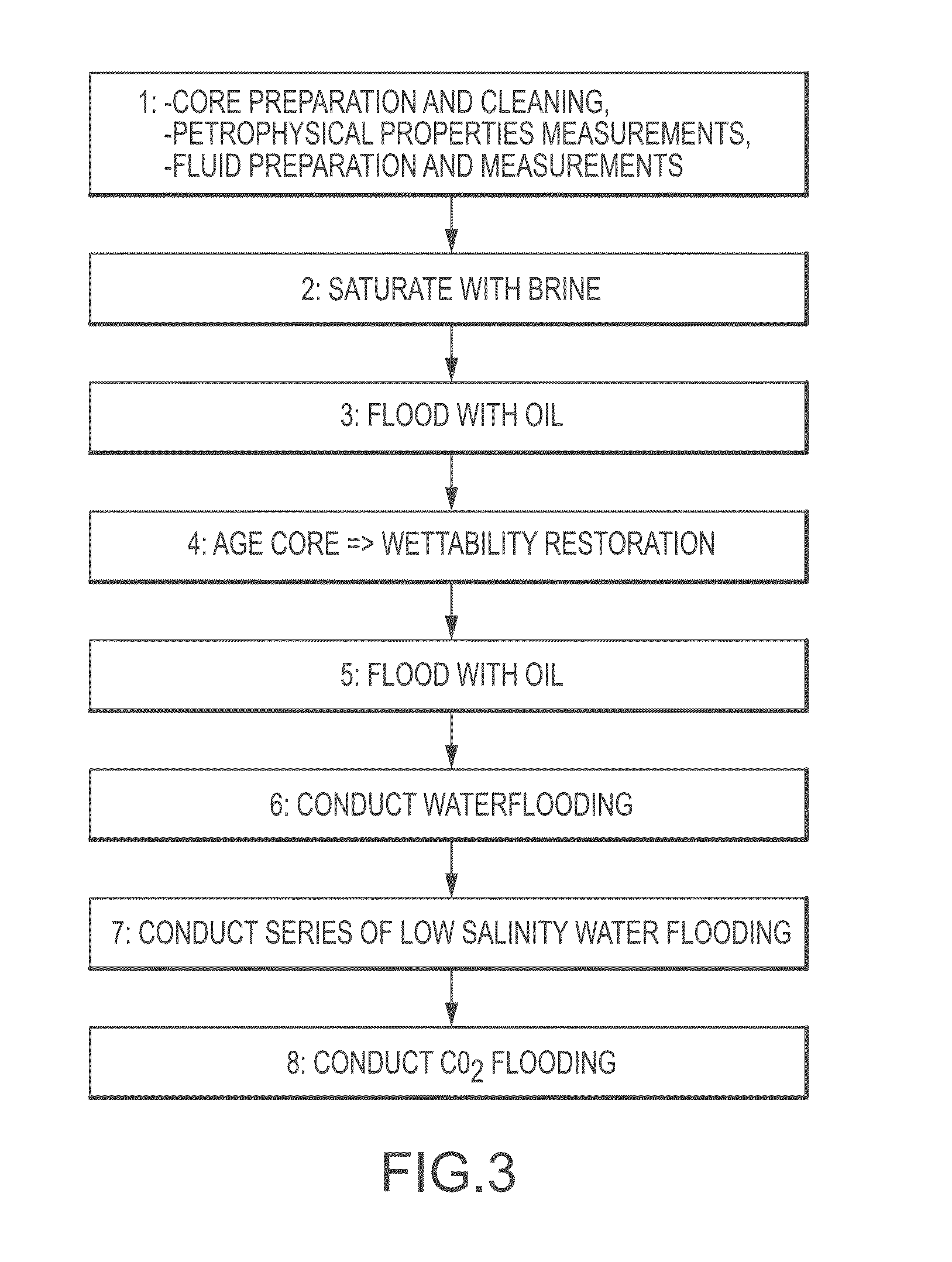
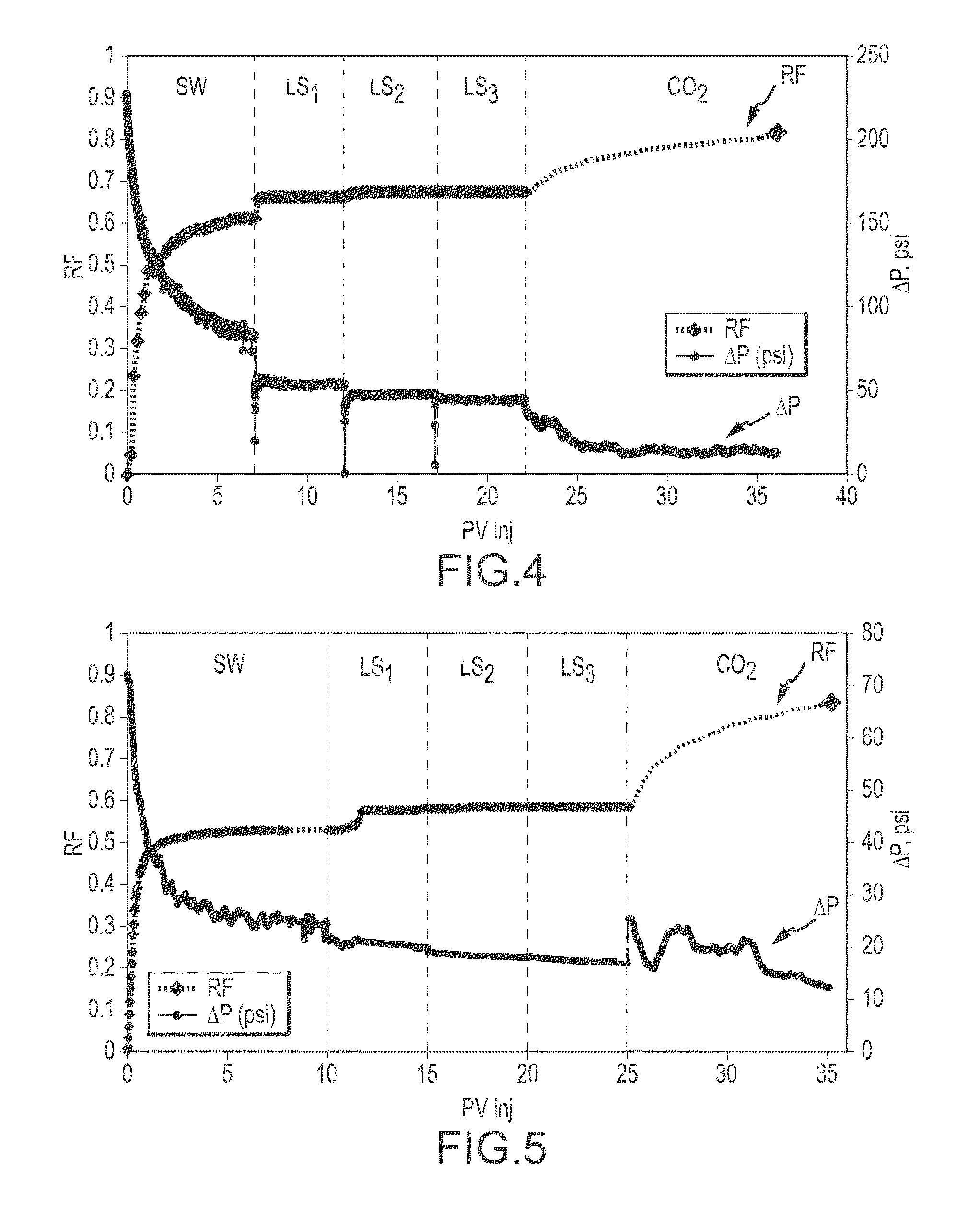
[0054]Two core-flood experiment of seawater flood, followed by three sets of low salinity-water flood, flowed by CO2 flood is performed on Facies 5 (F5) of Reservoir I core samples from a giant carbonate oil field in the Middle East. Facies description and geologic study of the reservoir can be found in Jobe (2013). Cores were prepared, cleaned using toluene and methanol. The petrophysical properties such as permeability and porosity are measured using Core Measurement System (CMS-300). Table 1 lists rock properties of samples used in the two core-flood experiments. The core type for all samples was F5 carbonate core (composite core). The diameter of the samples was about 1.5 inches and the PV was about 29.98 cc for Example 1 and 34.864 cc for Example 2. The miscible CO2 flooding following seawater and low salinity waterflooding (e.g. LS2, LS4, LSx) on composite carbonate cores. Eight weeks of aging applied. The miscible CO2 flooding following seawater and low salinity wate...
example 2
[0063]The core-flood protocol applied to the second core-flood on a second F5 sample from Reservoir I was similar to the first core-flood protocol. About 52.8% oil was recovered during waterflooding, about 5.2% additional oil was recovered during LS2 flooding, and about 0.4% and no additional oil was recovered during LS4 and LS50 flooding cycles, respectively. Finally, about 25% additional oil was recovery during about 10 PV continuous miscible CO2 flooding. FIG. 5 illustrates the oil recovery factor and pressure drop as a function pore volume injected.
example 3
[0064]The interfacial tension (IFT) between brine and oil as well as wettability of core discs with oil was measured at ambient conditions. Drop Shape Analyzer, DSA 100, was used to measure contact angles between solids and fluids and IFT between different fluids. For both IFT and wettability measurements, the effect of salinity of brine was investigated. About 32° API gravity crude oil from Reservoir I was used in both IFT and wettability measurement. Also the Reservoir I formation brine (FB) was used in the IFT and wettability measurements. Pendant drop method was used to determine the IFT, whereas, captive oil droplet contact angle measurement method was applied during the contact angle measurements. Detailed discussion on the IFT and contact angle measurement and additional results can be found in Teklu et al. (2014), Teklu et al., (2015), and Alameri et al. (2014).
[0065]Wettability measurements were performed on crude-aged F5 carbonate, Berea sandstone, and Three Forks core dis...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com