Variable damping force damper
a damper and variable technology, applied in the direction of shock absorbers, mechanical equipment, transportation and packaging, etc., can solve the problems of reducing the mechanical strength of the piston main body, affecting the smoothness of the telescopic, so as to reduce the number of assembly steps, prevent the deformation of the electric coil, and reduce the number of components
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first modified embodiment
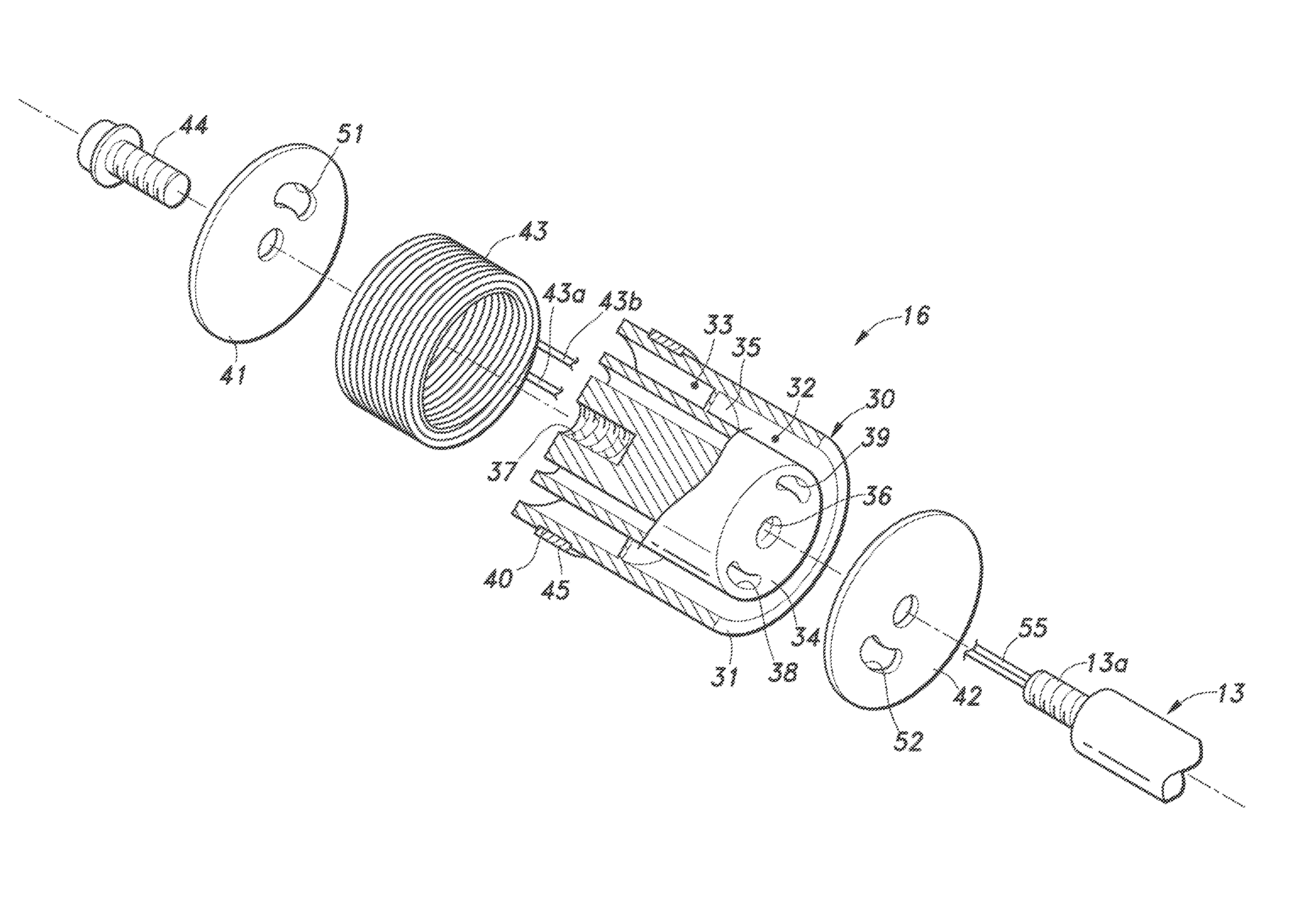
[0027]As shown in FIG. 6, in the piston 16 according to the first modified embodiment, the hollow cylindrical outer yoke 31 and the columnar inner yoke 34 are separately formed of a ferromagnetic material, and these yokes 31 and 34 are connected with each other by a hollow cylindrical connection member 61 made of a non-magnetic material (such as austenitic stainless steel or aluminum alloy). The connection member 61 is inserted between the outer yoke 31 and the inner yoke 34 and is secured to these yokes 31 and 34 by means of press-fitting, welding, adhesion or the like. In the first modified embodiment, a connection member made of a ferromagnetic material as shown in the exemplary embodiment is not included, and thus, the magnetic flux generated by the electromagnetic coil 43 acts upon the valve plates 41, 42 without leaking out in the middle, as shown by broken lines in FIG. 6. Further, the connection member 61 has a much larger axial size than the connection member in the exempla...
second modified embodiment
[0028]As shown in FIG. 7, in the piston 16 according to the second modified embodiment, the outer yoke 31 and the inner yoke 34 are connected with each other by the connection member 35 as in the exemplary embodiment, but the connection member 61 made of a non-magnetic material is securely fitted in a part of the first gap 32 on the side of the contraction-side valve plate 42. The mode of operation in the second modified embodiment is substantially the same as that in the foregoing exemplary embodiment, but owing to the combination of the connection member 35 and the connection member 61, relative displacement between the outer yoke 31 and the inner yoke 34 can be restrained more effectively.
third modified embodiment
[0029]As shown in FIG. 8, in the piston 16 according to the third modified embodiment, the outer yoke 31 and the inner yoke 34 are connected with each other by the connection member 35 as in the exemplary embodiment, but connection members 61, 62 each made of a non-magnetic material are securely fitted in a part of the first gap 32 close to the compression-side valve plate 42 and a part of the second gap 33 close to the expansion-side valve plate 41, respectively. The mode of operation in the third modified embodiment is substantially the same as that in the second modified embodiment, but relative displacement between the outer yoke 31 and the inner yoke 34 can be restrained even more effectively.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com