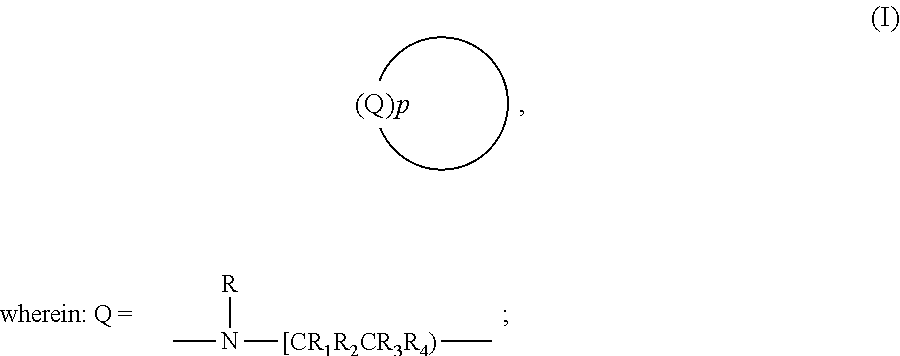
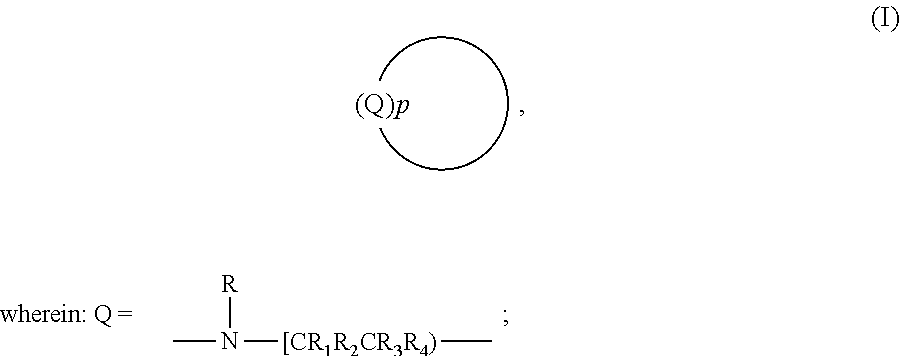
Freeness of paper products
a paper product and free technology, applied in the field of new refining process of paper pulp, to achieve the effect of improving the refining effect of these fibers, improving refining properties, and increasing tensile strength properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
experiment 1
[0092] Treatment of softwood pulp with hydrogen peroxide with and without [Mn2(μ-O)3(Me3TACN)2](CH3COO)2 at pH 11.0 (Me3-TACN=1,4,7-Trimethyl-1,4,7-triazacyclononane).
[0093][Mn2(μ-O)3(Me3TACN)2](CH3COO)2 (as 3.5% aqueous solution) was obtained as disclosed elsewhere (WO2006 / 125517).
[0094]Softwood pulp with a starting ISO-brightness of 49.9 was treated as follows: To a polyethylene (PE) bottle containing 250 g of oven-dry pulp at 10% consistency, was added 10 kg / odtp H2O2 (odtp=oven-dry ton pulp—equals to 29.4 mM H2O2) and 7.2 kg / odtp NaOH (equals to 18 mM NaOH). Depending on the experiments 0.04 kg / odtp [Mn2(μ-O)3(Me3TACN)2](CH3COO)2 (equals to 6.5 μM [Mn2(μ-O)3(Me3TACN)2](CH3COO)2)was added and 1.0 kg / odtp DTPA (Diethylenetriaminepenta-acetic acid, pentasodium salt)—(ex Akzo Nobel; trade name Dissolvine D50; purity is 50%). The initial pH-value was pH 11.0 (measured at 20° C.).
[0095]Note 1: This softwood pulp has been delignified in a O2-delignification step, and partly further ble...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperatures | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com