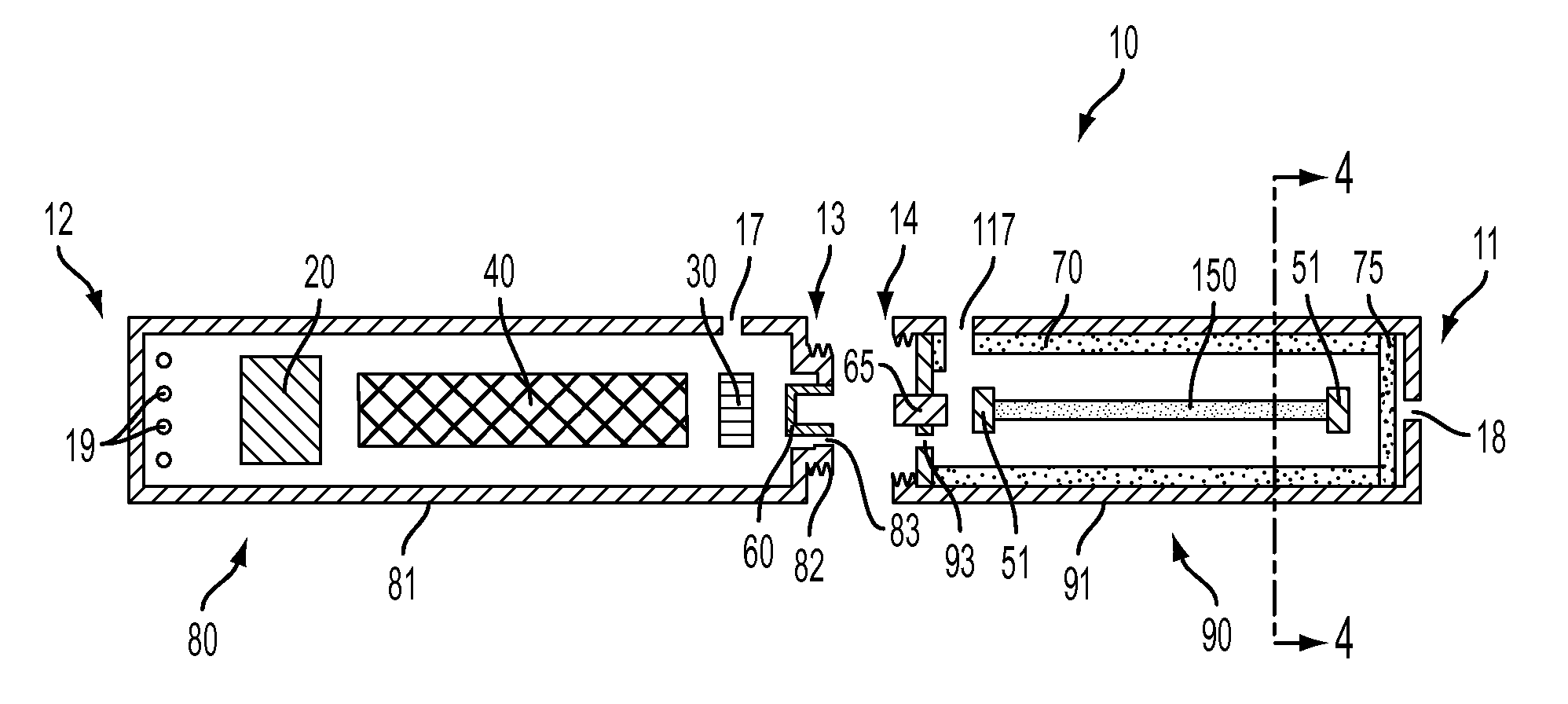
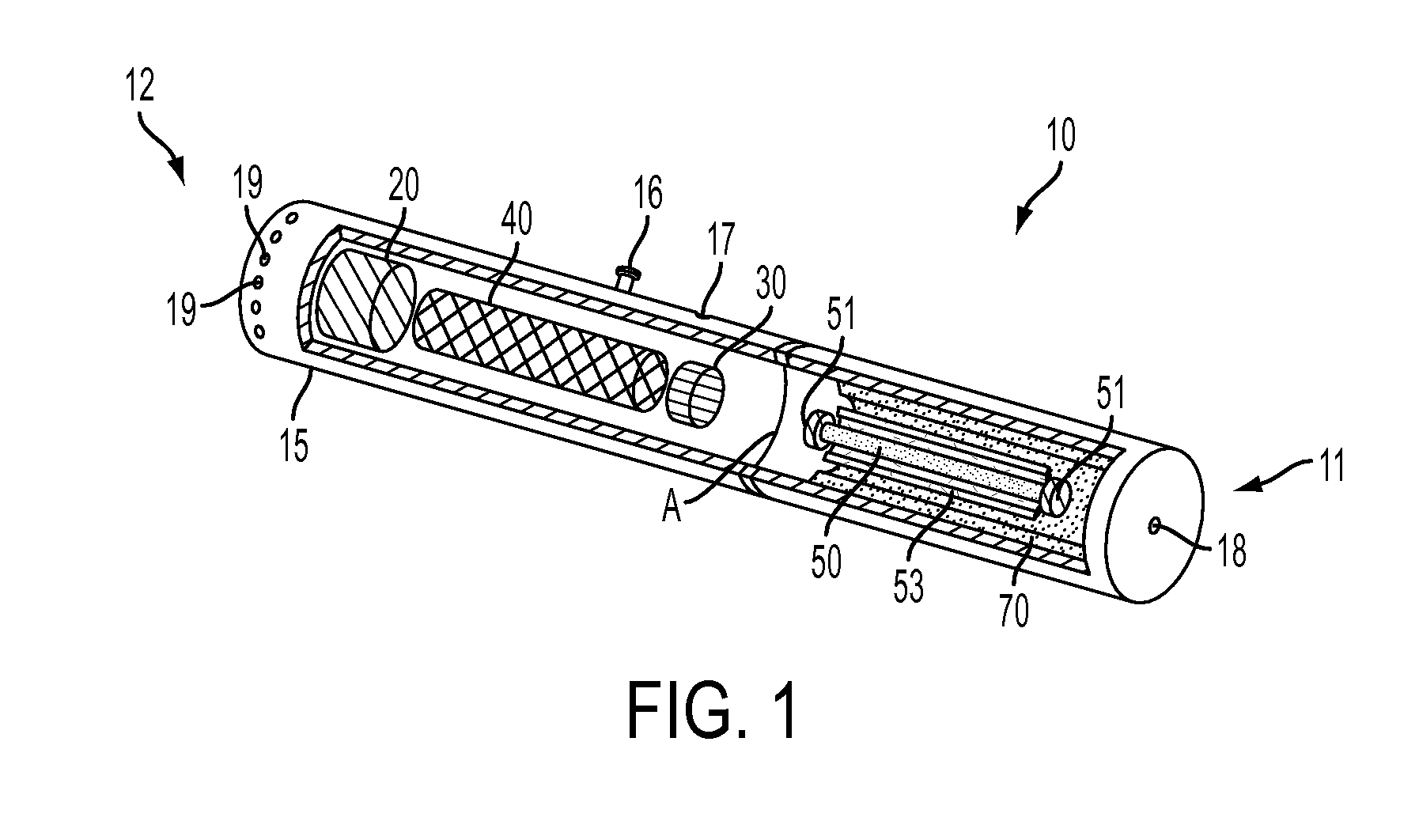
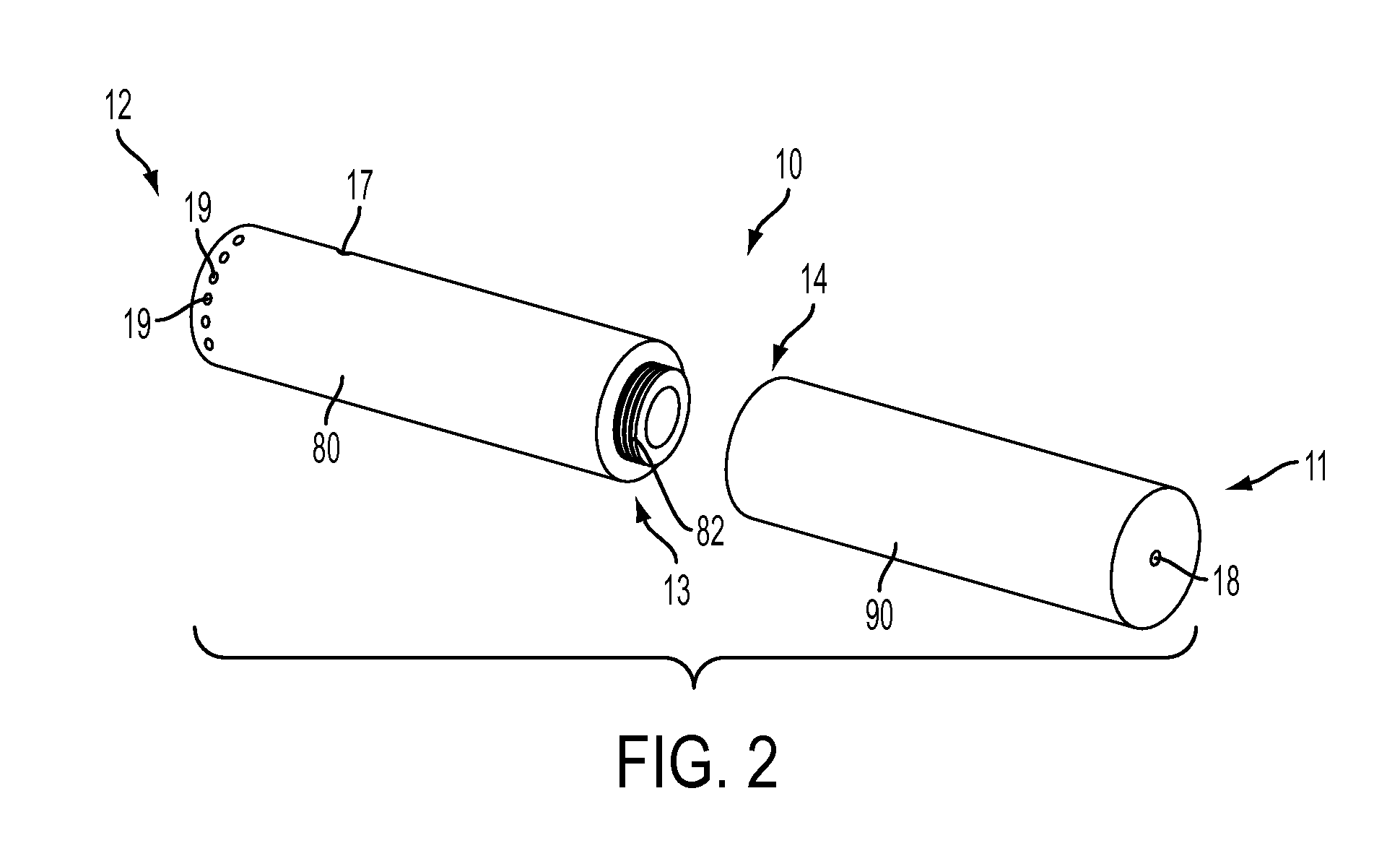
Smoking article incorporating a conductive substrate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Preparation of Conductive Substrates
[0169]Two exemplary conductive substrates were prepared for use in a smoking article according to the invention. In each case, the substrate materials were mixed and extruded to form substrates with a length of 10 mm and a diameter of 4.5 mm (Example 1a) and 4 mm (Example 1b). The formulations and measured resistance for each exemplary substrate are provided below in Table 1. Percentages are provided on a w / w basis.
TABLE 1Resistance of CalcinedExampleFormulation (wt. %)Extrudate (ohms)1aMilled Carbon (64%)2.5Guar Gum (10%)Graphite (20%)Sodium Carbonate (1%)Tobacco (5%)1bCarboxymethyl cellulose (9.5%)2Graphite (90.5%)
[0170]To prepare the substrates in Example 1a and 1b, all particulate ingredients were thoroughly mixed and water was added to yield a dough-like consistency with a moisture content of 39% for example 1a and 24.9% for example 1b (on a w / w basis). The dough was extruded using a batch extruder at a pressure of 10,000 psi (68.95 MPa) to f...
example 2
Effect of Conductive Material Concentration on Electrical Resistance of Conductive Substrate
[0173]To test the effect of the electrically conductive material in the substrate on electrical resistance, multiple conductive substrates were formed (without carbonization) and tested. In general, the conductive substrates were made by extrusion of a mixture of tobacco (a 5:3:2 ratio of flue cured, Burley, and Turkish tobaccos), graphite (from Superior Graphite Company), binder (i.e., carboxymethyl cellulose), and other additives. The exact formulations are provided in Table 2A.
[0174]In each example, the dry ingredients were mixed in a Sigma Blade Mixer (from Teledyne) for approximately one hour at low speed. Liquid ingredients were added to the mix and mixing was continued for an additional 4 hours. Sufficient water was added to ensure that the plastic mix was stiff enough to hold its shape after extrusion. The moisture content of the dough at this stage was about 31-32% (w / w). For extrusi...
example 3
Effect of Calcination on Electrical Resistance of Conductive Substrate
[0177]To test the effect of calcinations on the resistance of the substrate, various substrates were formed using the same methods described in Example 2. The resistance of the substrates was measured before and after undergoing calcination. The formulations, calcination conditions, and resistance values are discussed below. The tobacco blend was 50% flue cured, 30% Burley, and 20% Turkish tobacco by weight unless otherwise indicated.
[0178]3a: Rods of 100 mm length and 4 mm diameter were prepared from a formulation of 19 g tobacco blend, 180 g graphite, 20 g CMC, 1 g copper powder, and 40 g glycerol. The non-carbonized rods exhibited a resistance of about 27 ohms. After calcination at 300° C. for 1 hour, the rods exhibited a resistance of about 3.5 ohms.
[0179]3b: Rods of 10 mm length and 4 mm diameter were prepared from a formulation of 180 g graphite, 20 g CMC, 10 g copper powder, and 40 g glycerol. The non-carbo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com