Cross-flow electrochemical batteries
a cross-flow electrochemical and battery technology, applied in the direction of secondary cell servicing/maintenance, cell components, electrolyte stream management, etc., can solve the problems of limiting the electric current in conventional cells and batteries, certain time-dependent processes, and not all faradaic surfaces exposed to electrolyte may contribute to cell charge or discharge current, etc., to achieve robust cfeb, promote ion mobility, and increase the mass transport of ions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
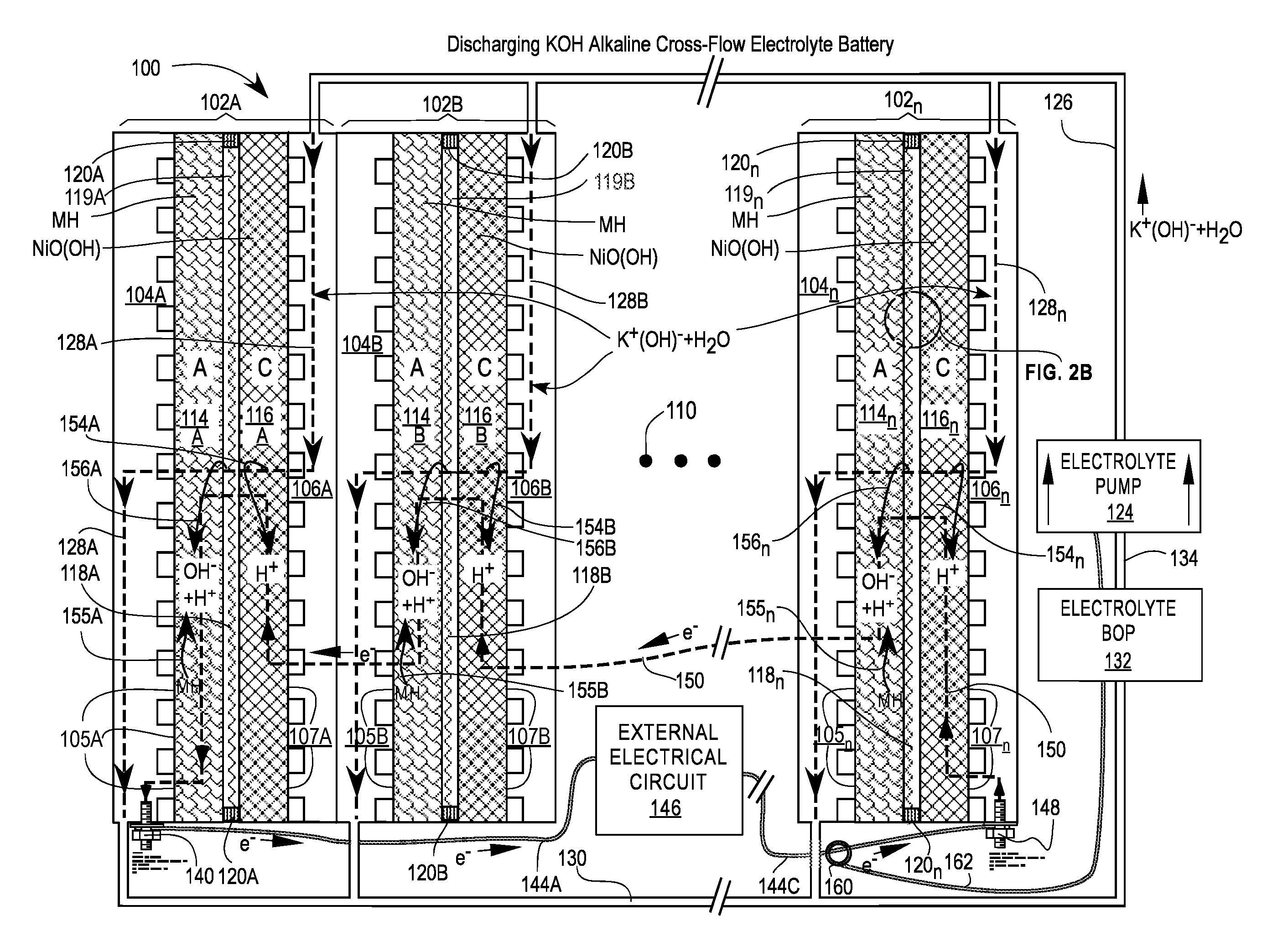
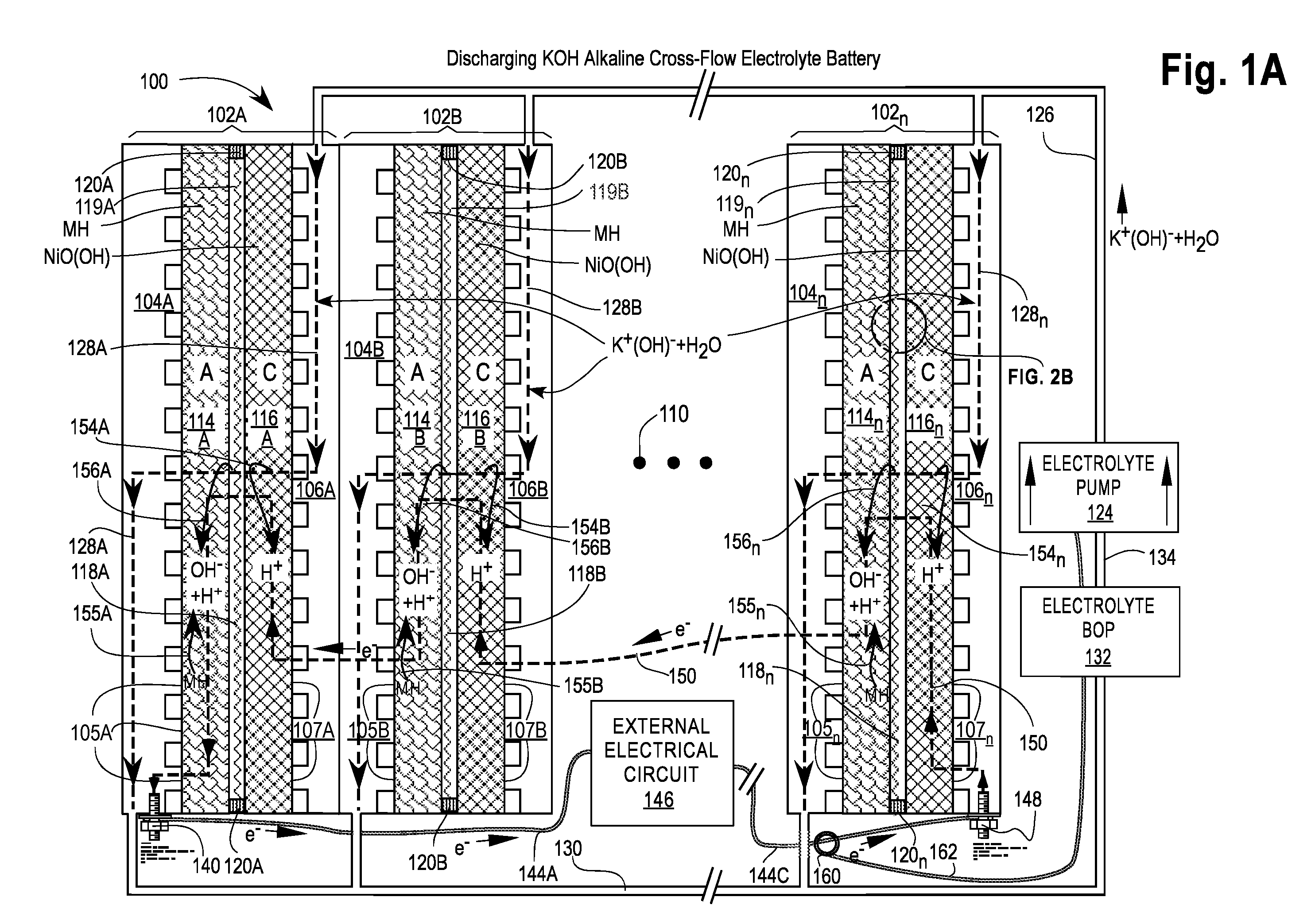
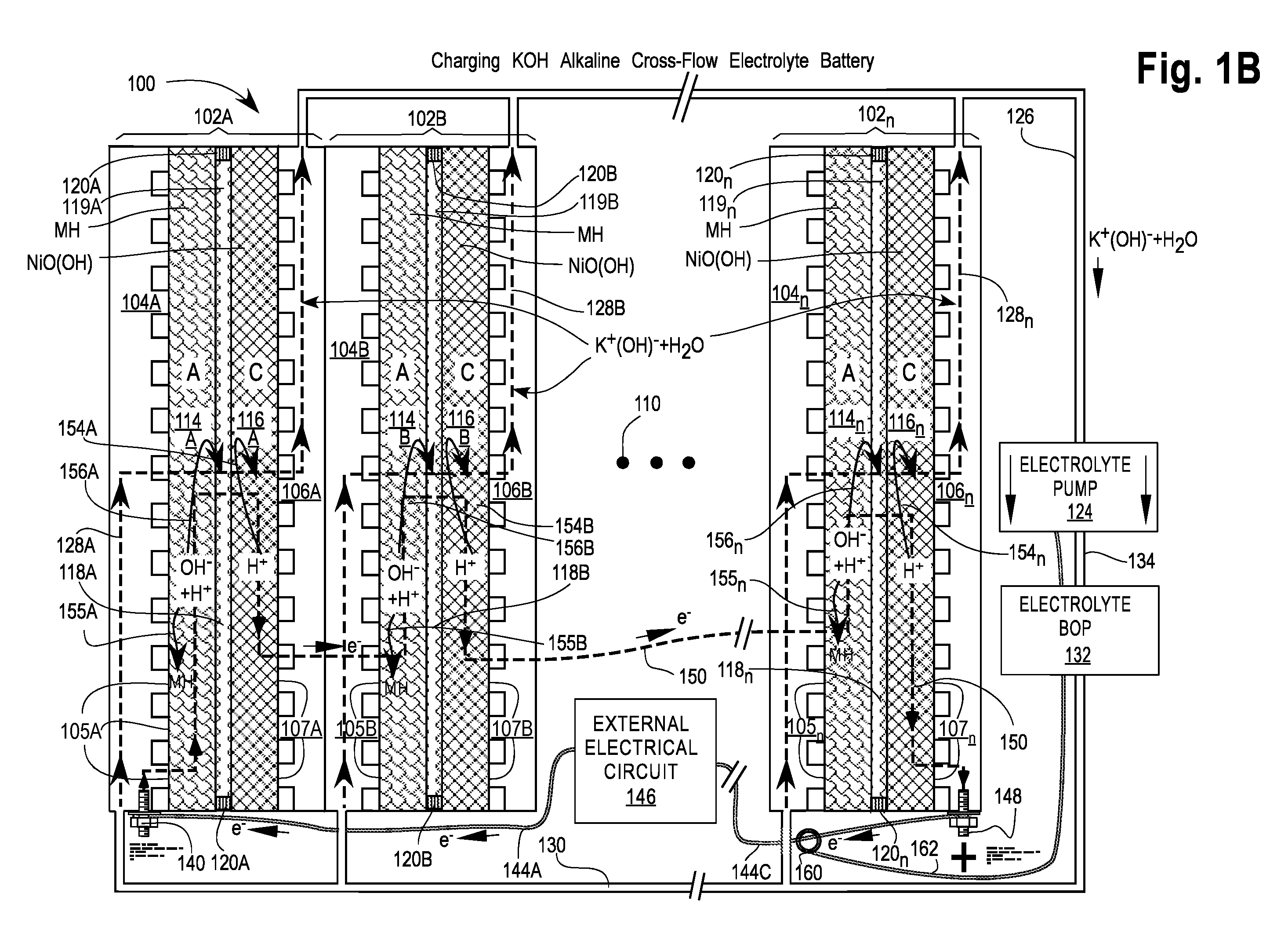
[0082]FIGS. 1A and 1B are cross-sectional views of a first embodiment of a Cross-Flow Electrochemical Battery 100 comprising a series of connected cross-flow cells 102A, 102B, . . . , 102n with separate metal anode electrolyte chambers 104A, 104B, . . . , 104n having anode contact surfaces 105A, 105B, . . . , 105n and metal cathode electrolyte chambers 106A, 106B, . . . , 106n having cathode contact surfaces 107A, 107B, . . . , 107n for each cell 102x, where 102x may be any or all of the cells 102A, 102B, . . . , 102n and n is the Roman alphabetic character of the numerical equivalent of the last cell 102n in the series (e.g., 5=E). Ellipsis 110 is a placeholder for additional cells 102C . . . 102n-1, if any.
[0083]Each of the cells 102x comprises an anode 114x—also labeled A—in electrical contact with its adjacent electrolyte chamber 104x at the anode contact surfaces 105x; a cathode 116x—also labeled C—in electrical contact with its adjacent electrolyte chamber 106x at the cathode ...
second embodiment
[0134]FIG. 2 is cross-sectional view of a second embodiment of a Cross-Flow Electrochemical Battery 200. This is a special-purpose configuration that may be preferred where energy or power density per size or weight must be maximized or the CFEB 200 need only be charged and discharged once or stored in a discharged state for rapid recharge and immediate reuse. Most of manifold hardware bulk and mass found in the first embodiment has been eliminated to reduce size and weight. The second embodiment can be stored for long periods in a stable, discharged condition and quickly charged for use. The battery's limitation is that once its external electrical source or load is removed or pumping is stopped, the battery will self-discharge. In use, self-discharge is prevented by electrolyte cross-flow.
[0135]The CFEB 200 comprises a series of connected cross-flow cells 202A, 202B, 202C, . . . , 202n. Instead of separate electrolyte chambers for each cell as incorporated in CFEB 100 of the first...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameters | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com