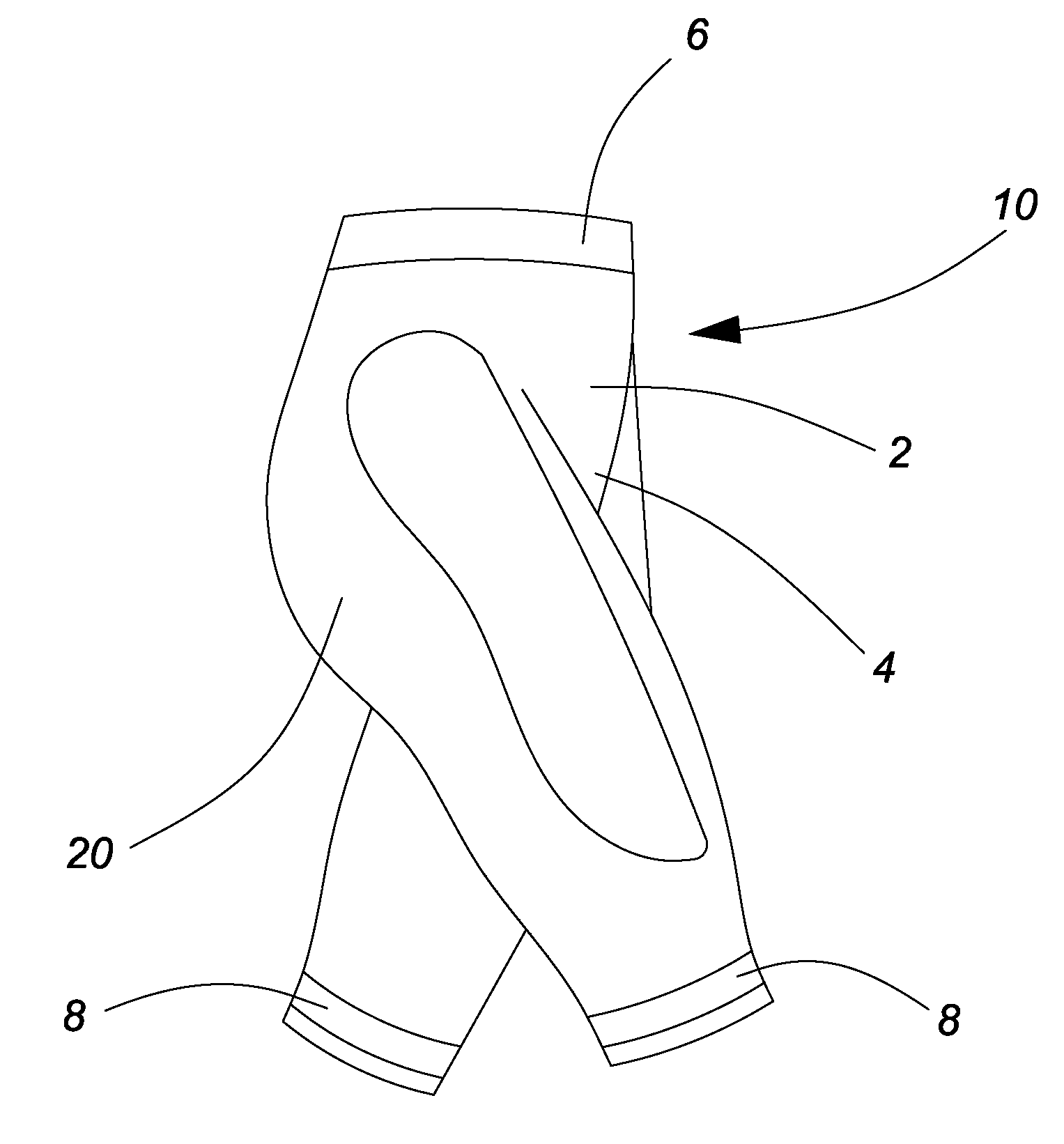
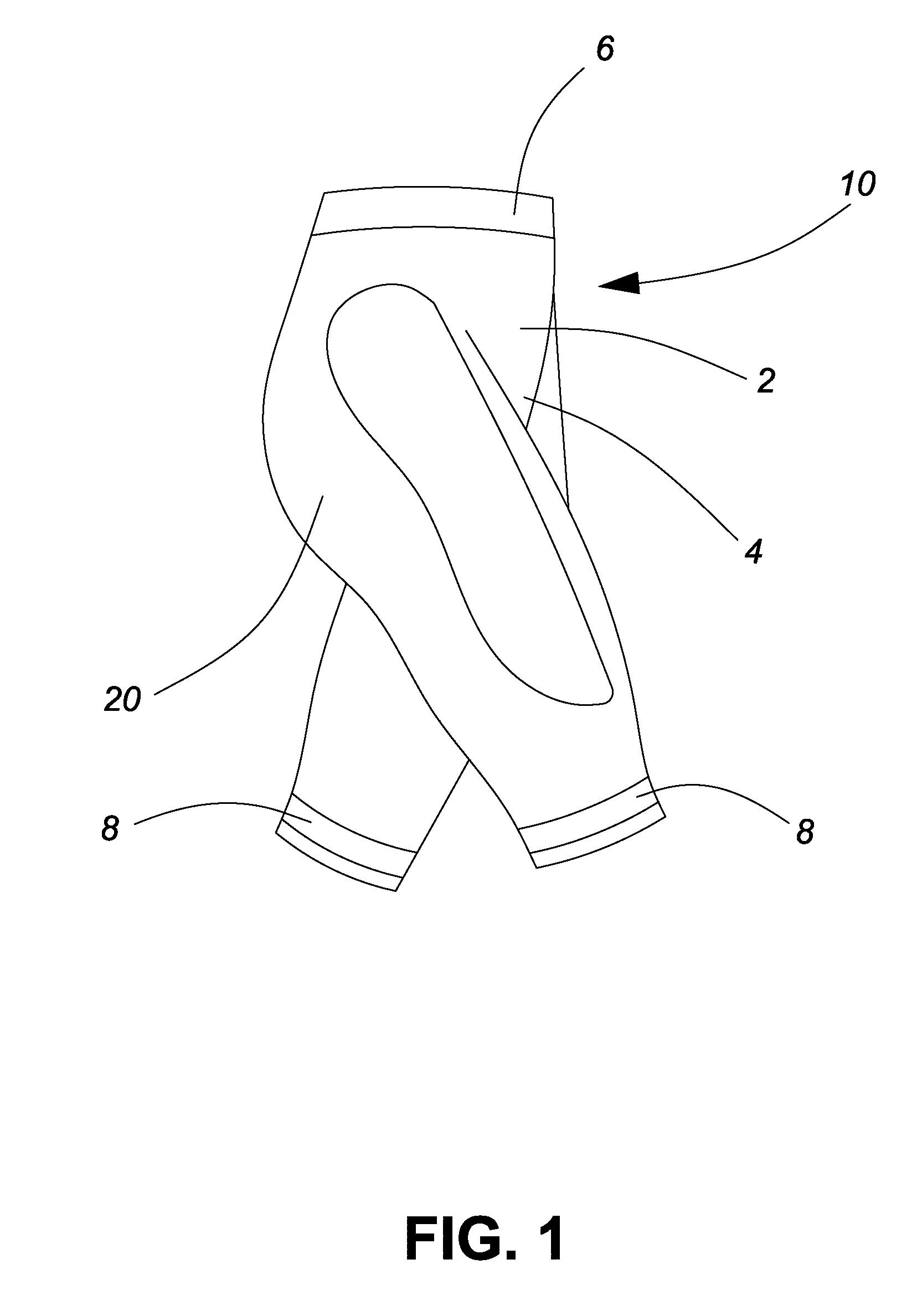
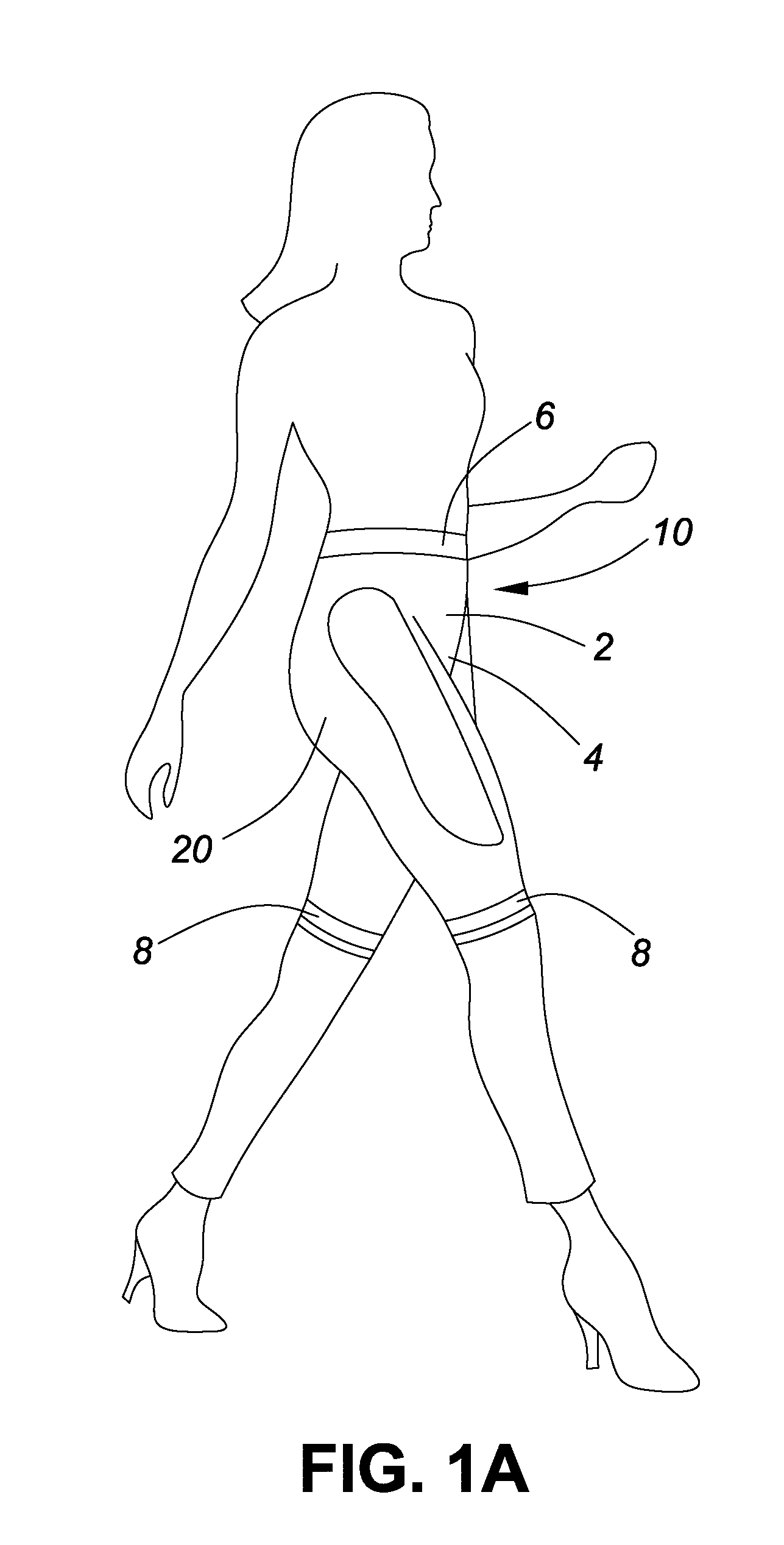
Caloric burn garment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Biomechanical Concept of Muscle Effort in Human Locomotion
All muscular efforts lead to an elevation of the energetic metabolism that varies with the intensity of the effort. The greater the effort, the greater the degree of solicitation to the muscle fiber engaged with the effort. This in turn leads to a greater need for energy, and therefore to an increase in energy consumption.
The mechanical work accomplished by the muscles during locomotion can be divided in to 2 components:
Wext=the external work accomplished by the muscles in order to move the center of gravity of the body (CG) in relationship to its environment.
Wint=the internal work accomplished by the muscles to move the whole body part in relationship to the center of gravity (Cavagna et al 1963).
The total mechanical work=tot=Wext+Wint
With each step, the CG undergoes a translation or a linear displacement upwards and forwards under the effect of the Wext. This is accomplished by the muscles that modify the energy potential ...
example 2
Typical Day for a 35-45 Year Old Female Living in the USA (Body Weight 163 pounds and 64 inches)
Background about Calories Required in a “Typical” Day
During rest (lying comfortably, essentially no activity) the body's tissues require about one-fourth of a liter of oxygen. The oxygen powers all bodily functions for the nervous system, digestion, brain and muscle activity, temperature regulation, and so on. In effect, the oxygen keeps the trillions of cells functioning while in the resting state. Oxygen use is related to heat production in a very precise manner. Every 1 liter of oxygen “burned” releases 5 calories (kilocalories) of heat energy. Thus, oxygen use is really a measure of heat production. At rest, the body's tissues consume one-fourth of a liter, the equivalent of one-fourth of 5 kcal or 1.25 kcal for each minute at rest. There are 1440 minutes in a day, so if a person did nothing all day long (remained in the resting state), 1440×1.25 kcal=1800 kcal would still be “burned....
example 3
Independent Study Conducted at the University of Virginia: Impact of a Lightweight Nylon Fiber Undergarment on the Energy Cost of Walking in Middle-Aged Women
PURPOSE: The energy deficit required to prevent weight gain in most adults averages approximately 100 kcal daily. As a novel approach to closing this energy gap, we examined the effects of a nylon fiber undergarment designed to gently resist hip flexion during movement on the energy cost of walking.
METHODS: Fifteen middle-age women (age=39.4+ / −6.6 yr; stature=167.9+ / −6.4 cm; body mass=74.6+ / −7.6 kg; BMI=26.4+ / −1.6 kg / m2) participated in 2×15-min treadmill walking tests separated by 15-min of rest. Treadmill velocity remained constant for each test (3.0 mph) with grade increased 5% every 5-min (0%, 5%, 10%). In a randomized order, subjects completed one test wearing the undergarment (G) and a control test with their usual undergarment (C). Indirect calorimetry assessed energy expenditure (EE; kCal / min-1) for each treadmill grade...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com