Virtualization and dynamic resource allocation aware storage level reordering
a virtual and dynamic resource technology, applied in memory allocation/allocation/relocation, multi-programming arrangements, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of high resource and link usage, energy overhead, and hammer the effectiveness of joint operations, so as to reduce the performance overhead of vm reprovisioning or repositioning actions, the effect of reducing recovery operations
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
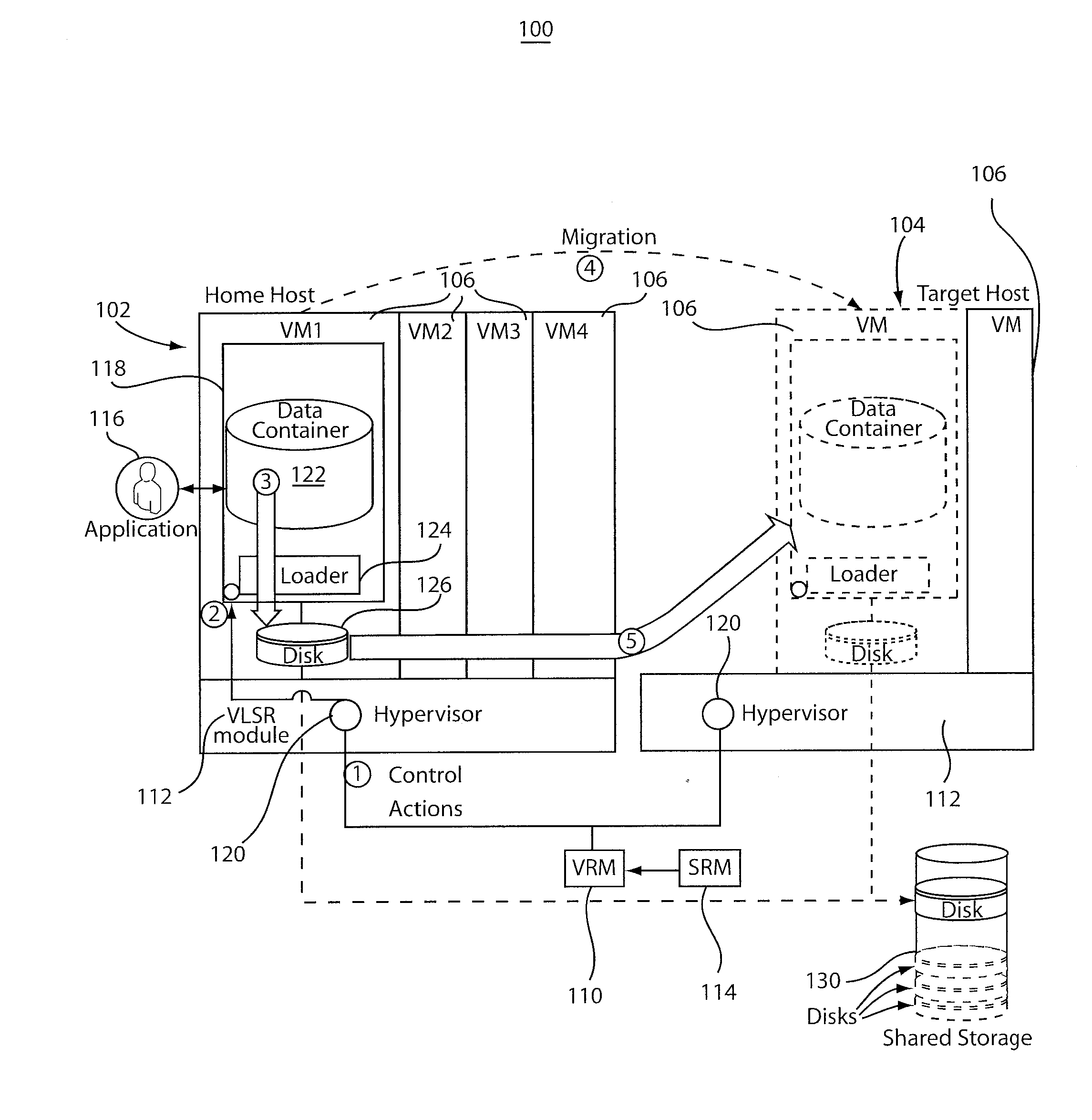
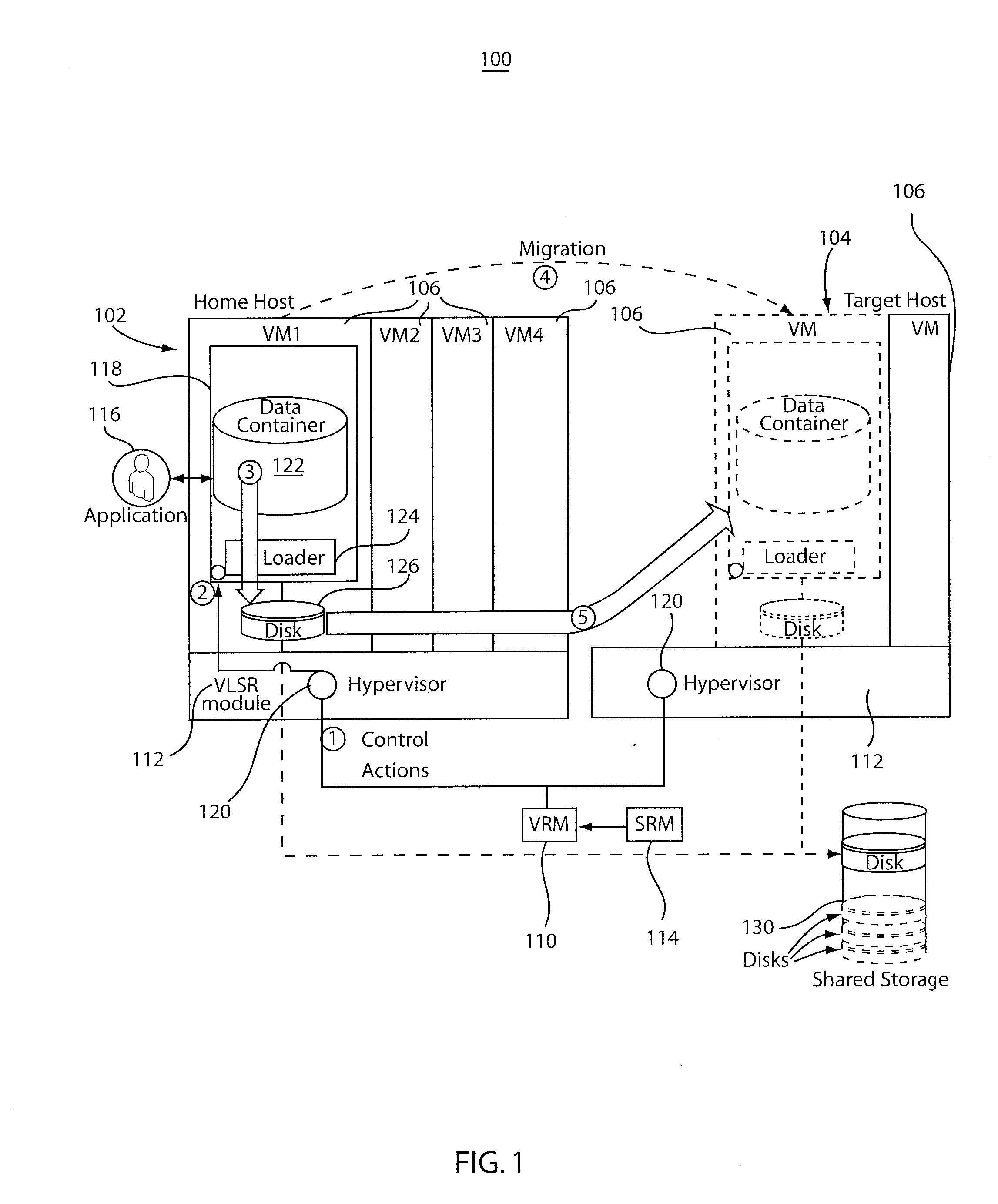
[0018]The present principles provide a system having multi-level data storage including a low latency / high bandwidth storage medium, e.g., RAM, and a higher latency / lower bandwidth storage medium, e.g., disk, which operate in a hierarchical fashion. In the context of, e.g., in-memory data grid (IMDG) appliances, a storage level with best latency / size ratio is considered primary and hence has the highest priority in the hierarchy. For example, IMDG technologies, such as ObjectGrid™, operate primarily on RAM and rely on disk storage to respond to overflow conditions.
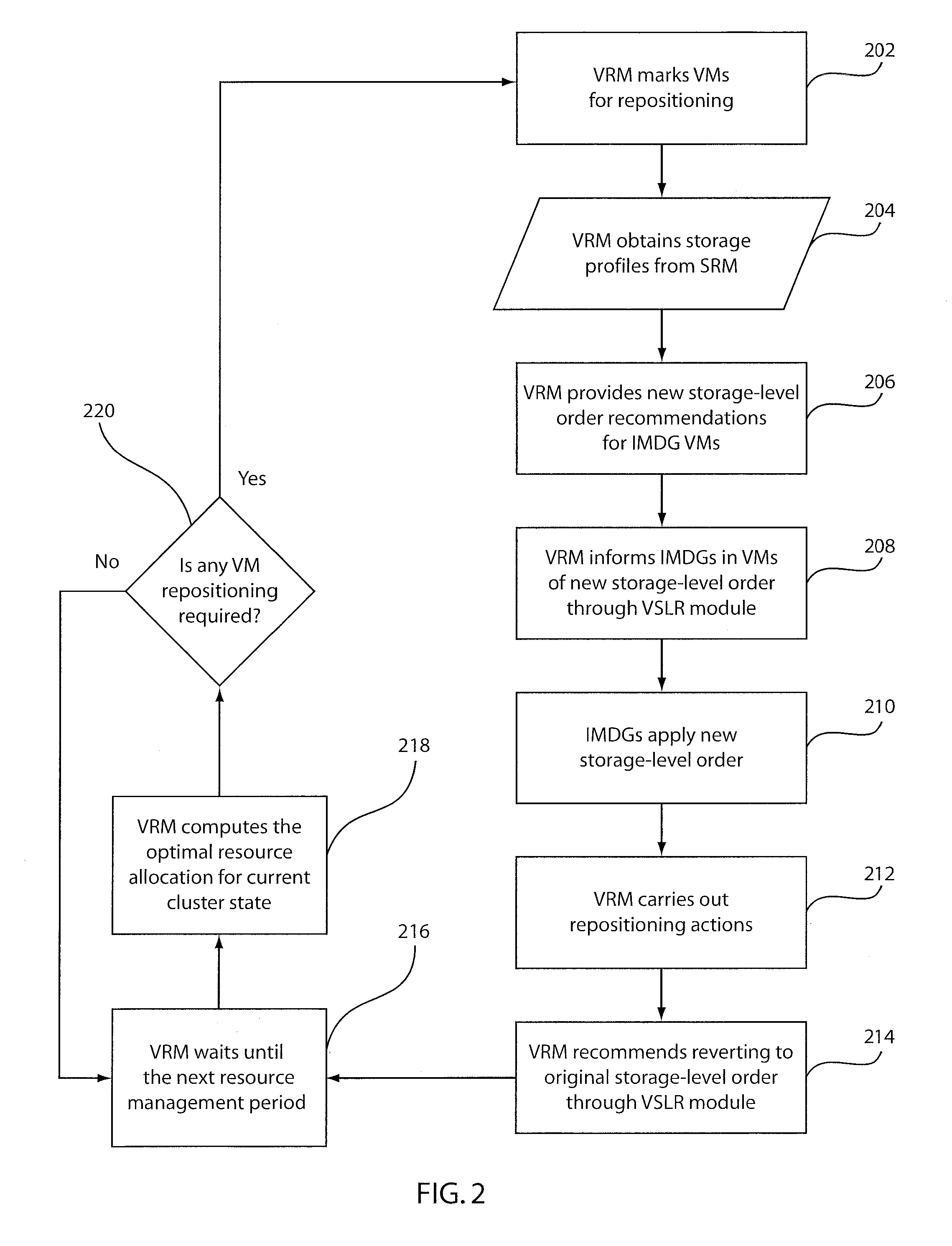
[0019]A virtualization- and dynamic-resource-allocation-aware storage level reordering (VSLR) module permits applications such as IMDGs to work in conjunction with a system virtual resource manager (VRM) to mitigate overhead resulting from virtual machine (VM) migration by effectively reducing live state data of a hosting VM to be migrated. Reducing the active state of these applications can lead to several orders of reduc...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com