Method for polishing silicon wafer, method for producing silicon wafer, apparatus for polishing disk-shaped workpiece, and silicon wafer
a technology of silicon wafers and polishing methods, applied in the direction of lapping machines, manufacturing tools, transportation and packaging, etc., to achieve the effect of not reducing the resistivity of the epitaxial layer, reducing the amount of spherical particles generated in the processing of wafers, and reducing the amount of spherical particles
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
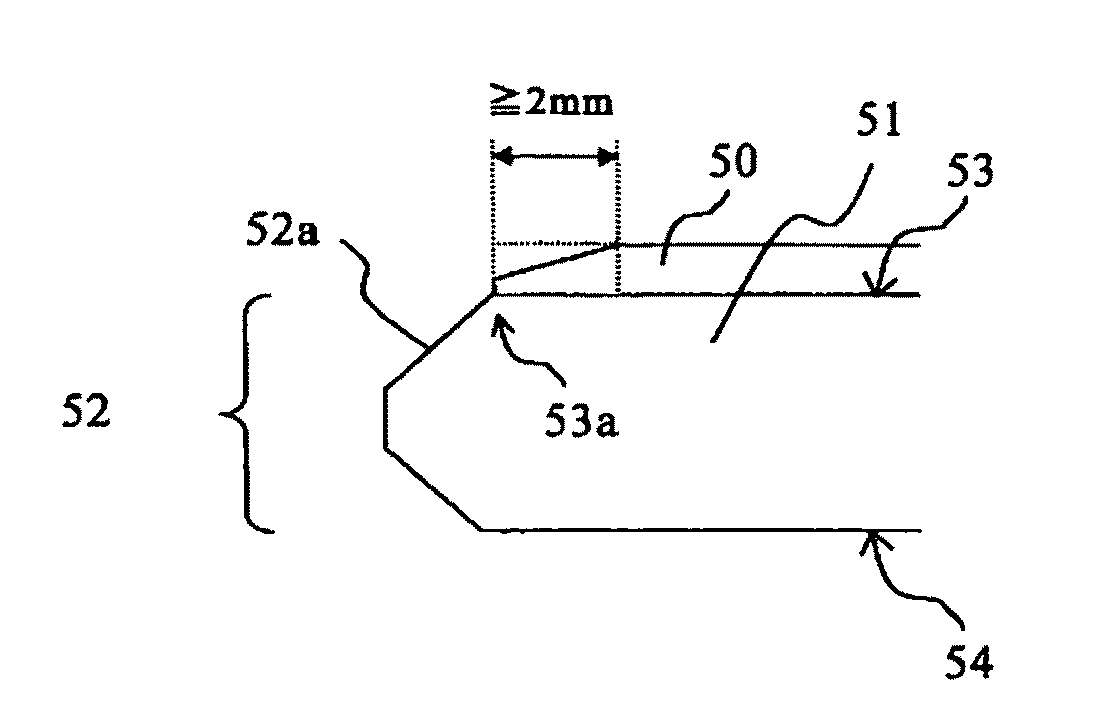
[0070]A silicon wafer (P type 0.01 Ω·cm: ) with a diameter of 300 mm produced by Czochralski method in which an oxide film was formed on a back surface and a chamfered portion was prepared, and the oxide film (thickness: 350 nm) on a peripheral portion of the back surface and the chamfered portion of the wafer was polished under the following conditions by using the polishing apparatus according to the present invention as shown in FIG. 2.
(Polishing Conditions)
[0071]Polishing pad: Suba400 (manufactured by Rodel, Inc.), ASKER C 61, thickness 1.27 mm)[0072]Angle with regard to polishing pad α: 70°, β: 90°[0073]Polishing pressure: 18 kgf[0074]Polishing agent: EDGE MIRROR V (manufactured by Fujimi Incorporated)[0075]Rotating rate of rotating body: 600 rpm[0076]Polishing time: 45 sec
[0077]The peripheral portion of the back surface and the chamfered portion of the back surface side were polished under the above-described conditions, subsequently the wafer was sucked to a holder with the f...
examples 2 and 3
[0078]Polishing was performed under the same conditions as Example 1, except that each polishing pressure was set at 12 kgf (Example 2), 6 kgf (Example 3), and each polishing time was set at 30 sec (Example 2) and 20 sec (Example 3).
examples 4-5
, Comparative Examples 4-6
[0096]Next, in order to confirm the effects of the polishing apparatus according to the present invention, polishing was performed with the angles α and β with regard to the polishing pad changed as follows. The polishing conditions were the same as Example 1 except for the angles.
Comparative example 4 α: 30°, β: 90°Example 4α: 40°, β: 90°Comparative example 5α: 80°, β: 90°Comparative example 6α: 70°, β: 120°Example 5α: 70°, β: 110°
[0097]Each wafer polished under the above-described conditions was transferred with a robot transfer device for five times, then the thickness of the oxide films on the chamfered portions and the peripheral portions of the back surfaces was measured with film thickness measuring device of interference fringe type (TFM120). Further, the number of particles on each wafer surface was measured with a particle counter (LS6500). The results are shown in Table 1.
TABLE 1Measurementresults ofthe numbersMeasurement results of oxide filmsof...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com