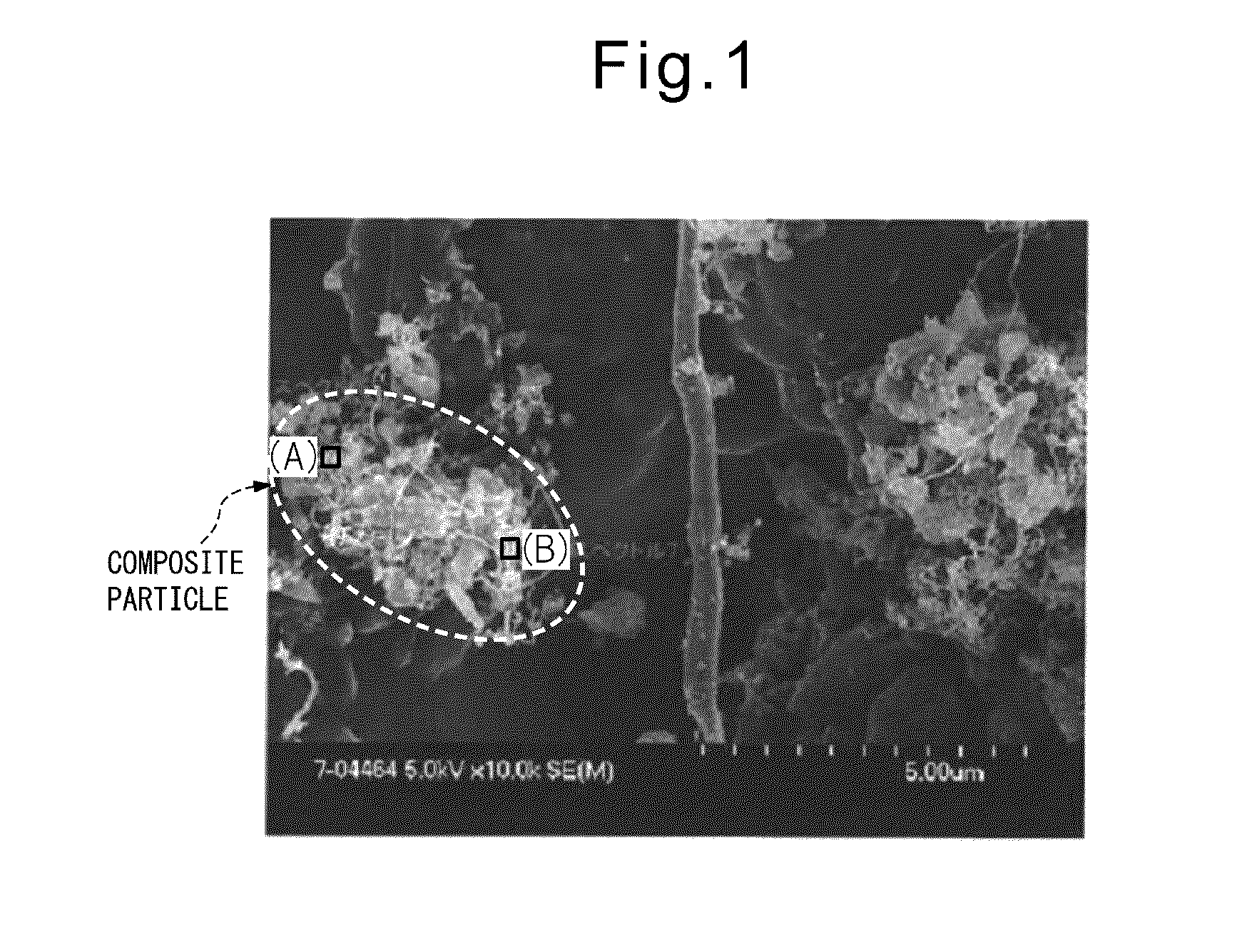
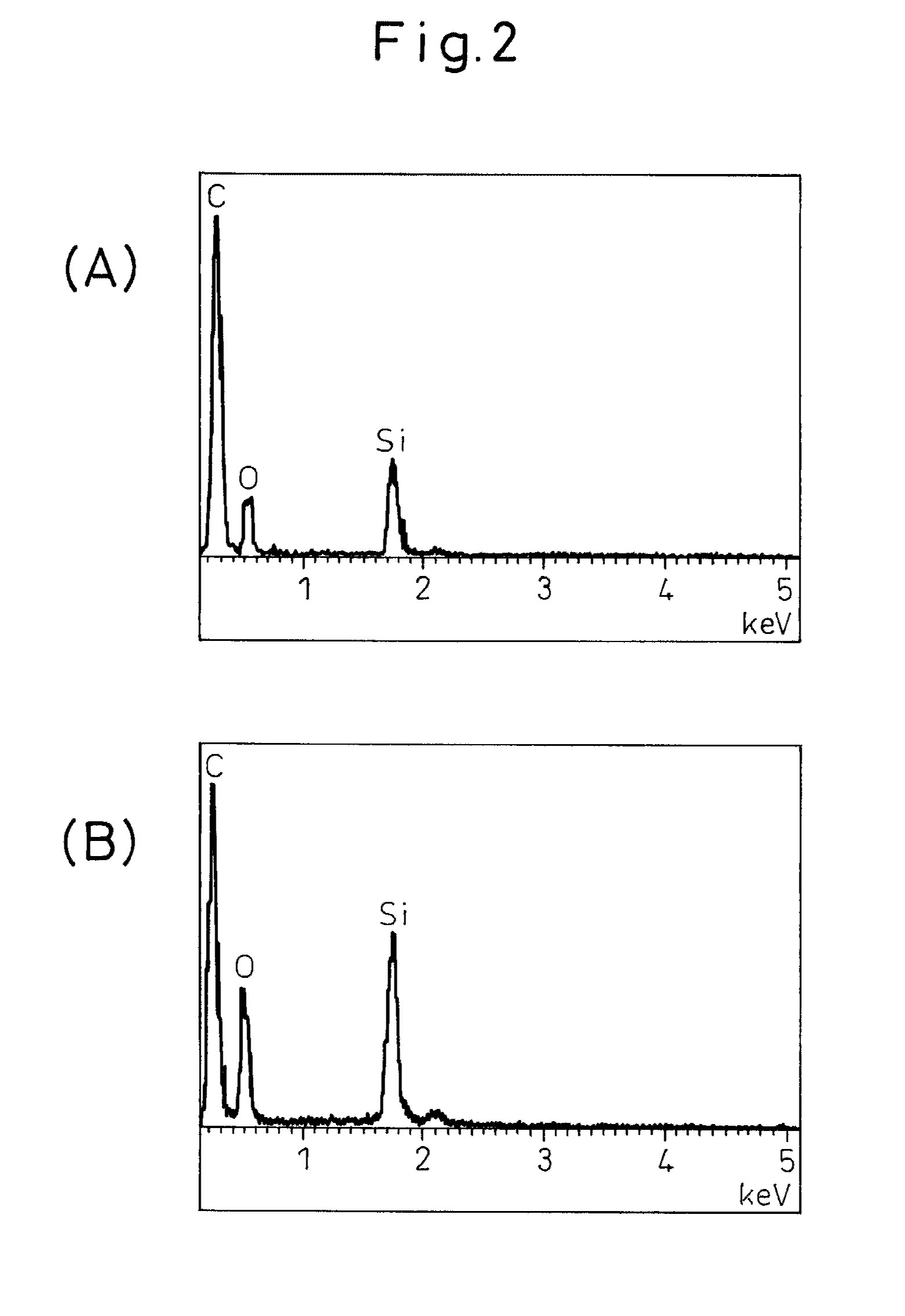
Anodic carbon material for lithium secondary battery, lithium secondary battery anode, lithium secondary battery, and method for manufacturing anodic carbon material for lithium secondary battery
a lithium secondary battery and anodic carbon technology, which is applied in the field of anodic carbon material for lithium secondary batteries, can solve the problems of inability to completely prevent the disintegration of the anode, and cannot be said that the lithium secondary battery anode disclosed in any of the above patent documents has satisfactory charge/discharge cycle characteristics, etc., to achieve enhanced charge/discharge cycle characteristics, prevent degradation of the conductivity of carbon materials, and excellent charge/discharge cycle characteristics
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
working example 1
[0061]First, 135 parts by mass of a novolac-type phenol resin (PR-50237 manufactured by Sumitomo Bakelite) and 25 parts by mass of hexamethylene tetramine (manufactured by Mitsubishi Gas Chemical) were dissolved in a four-necked flask containing 20 parts by mass of methanol; then, 50 parts by mass of silicon monoxide (average particle diameter: 1.2 μm) were added, and the mixture was stirred for 2 hours. After stirring, the resulting slurry was cured by heating at 200° C. for 5 hours. After curing, the temperature was raised under a nitrogen atmosphere until the temperature reached 500° C., at which carbonization was performed for 1 hour. The carbon material thus obtained was ground to an average particle diameter of 11 μm, and the temperature was further raised until the temperature reached 1100° C., at which the ground carbon material was subjected to carbonization for 10 hours to obtain a carbon material for a secondary battery. When this carbon material was measured by the follo...
working example 2
[0089]First, 135 parts by mass of a novolac-type phenol resin (PR-50237 manufactured by Sumitomo Bakelite) and 25 parts by mass of hexamethylene tetramine (manufactured by Mitsubishi Gas Chemical) were dissolved in a four-necked flask containing 30 parts by mass of acetone; then, 30 parts by mass of silicon monoxide (average particle diameter: 3.3 μm) were added, and the mixture was stirred for 3 hours. After stirring, the resulting slurry was cured by heating at 200° C. for 3 hours. After curing, the temperature was raised under a nitrogen atmosphere until the temperature reached 550° C., at which carbonization was performed for 1 hour. The carbon material thus obtained was ground to an average particle diameter of 7 μm, and the temperature was further raised until the temperature reached 1150° C., at which the ground carbon material was subjected to carbonization for 10 hours to obtain a carbon material for a secondary battery. The pore volume of pores in the 0.25 to 0.45 nm range...
working example 3
[0090]First, 135 parts by mass of a novolac-type phenol resin (PR-50237 manufactured by Sumitomo Bakelite) and 25 parts by mass of hexamethylene tetramine (manufactured by Mitsubishi Gas Chemical) were dissolved in a four-necked flask containing 45 parts by mass of acetone; then, 45 parts by mass of silicon monoxide (average particle diameter: 0.7 μm) were added, and the mixture was stirred for 5 hours. After stirring, the resulting slurry was cured by heating at 200° C. for 3 hours. After curing, the temperature was raised under a nitrogen atmosphere until the temperature reached 500° C., at which carbonization was performed for 3 hours. The carbon material thus obtained was ground to an average particle diameter of 11 μm, and the temperature was further raised until the temperature reached 1100° C., at which the ground carbon material was subjected to carbonization for 5 hours to obtain a carbon material for a secondary battery. When this carbon material was evaluated in the same ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore diameters | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com