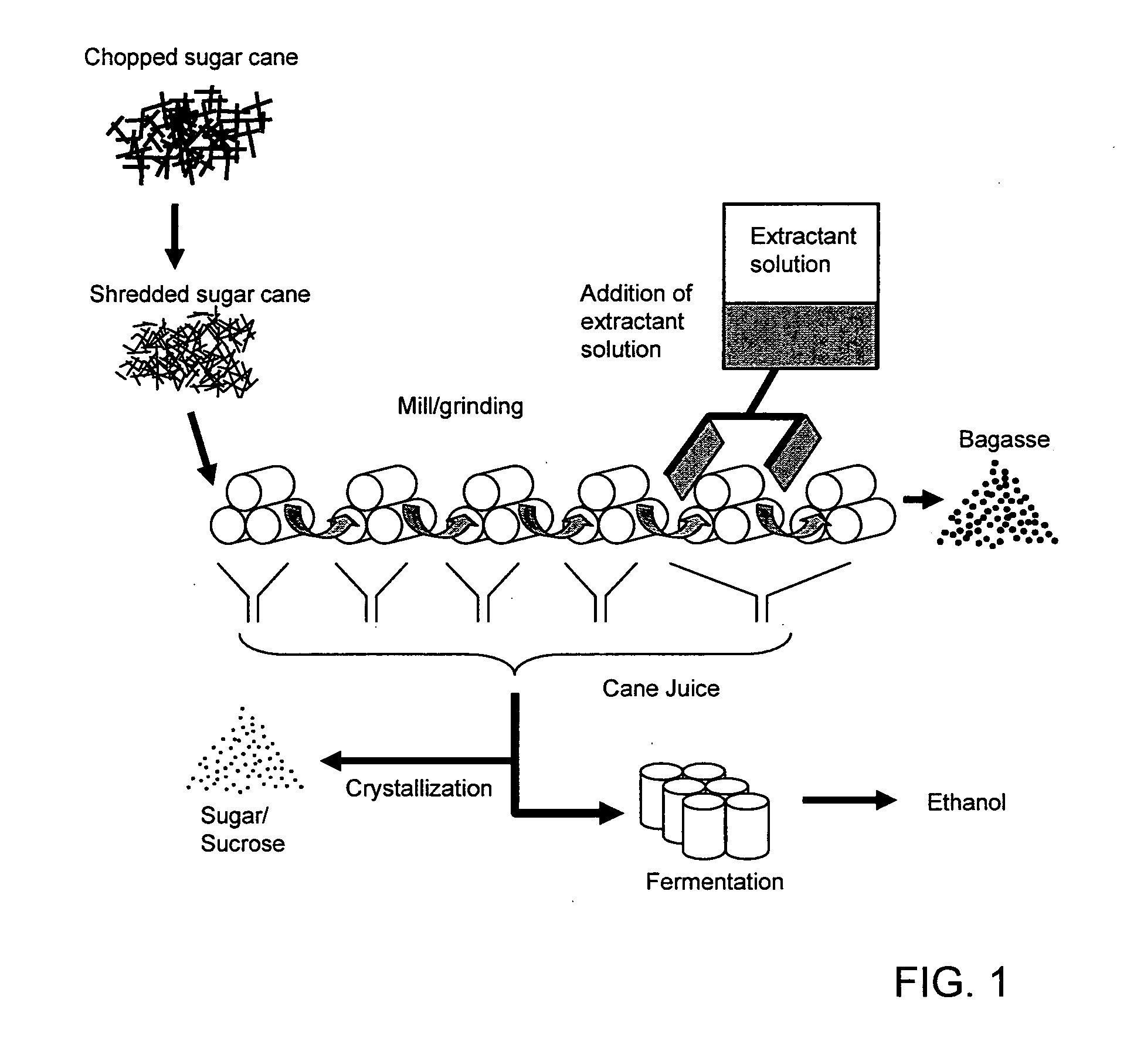
Processes for Extraction of Sugar From Sugar-Bearing Plant Material
a technology of plant material and process, which is applied in the field of sugar production, can solve the problems of insufficient extraction, high cost of equipment, and severe limitations of processes, and achieves the effect of achieving maximum extraction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Properties of an Exemplary Surfactant
[0048]The sample of Nonionic Surfactant PO / EO Block Copolymer Having 20% EO Capping used in these Examples was determined to have the following physical properties:
Molecular weight:4050 g / mol, as calculated from themolecular weight of the initiator and theoxide units.Specific Gravity:1.024 g / mL at 25° C. as determined usingASTM D 892Pour point:−8° C. as determined using ASTM D 97Flash point:>180° C. (open cup), as determined usingASTM D 92Cloud points:23° C. at 1% aqueous14° C. at 10% aqueous49° C. for a solution of 5 g of surfactant in20 g of a solution of 25% diethyleneglycol butyl ether in waterAll cloud points determined using ASTM D 2024Viscosities:850 cSt at 25° C.386 cSt at 40° C.63 cSt at 100° C.All viscosities determined using ASTM 445 / 446
example 2
Formulation of a Concentrated Surfactant Solution
[0049]A concentrated surfactant solution was prepared by combining 15 parts by weight ethanol with 50 parts by weight Nonionic Surfactant PO / EO Block Copolymer Having 20% EO Capping. To this mixture was added 35 parts by weight water. The resulting concentrated surfactant solution had the following properties:
Specific Gravity:0.9998 g / mL at 25° C. as determined usingASTM D 892Pour point:−18° C. as determined using ASTM D 97Flash point:50° C. (open cup) as determined usingASTM D 9230° C. (closed cup), as determined usingASTM D 93Cloud points:46.2° C. at for 0.5% aqueous solution ofthe concentrated surfactant solutionNone determined over the range of 25° C.-90° C.for a solution of 5 g of the concentratedsurfactant solution in 20 g of a solution of25% diethylene glycol butyl ether in water78.0° C. for a solution of 12.7 g of theconcentrated surfactant solution in 11.2 gof 50% aqueous isopropanolAll cloud points determined using ASTM D 20...
example 3
Extraction of Sugar from Bagasse Samples from Mill #1
[0050]Bagasse samples were taken from Mill # 1, a sugar cane processing facility in Brazil. At Mill # 1, sugar cane material is subjected to six milling steps. Imbibition water is added only in the fifth and sixth milling steps. Samples 1A-1H of fresh bagasse were taken from the output of the fourth milling step, and used in an extraction study.
[0051]For each sample, the bagasse (200 g wet weight) was mixed by hand for about two minutes with water (61 g at 50° C.), with different amounts of the concentrated surfactant solution of Example 2 added thereto: 0 ppm (control), 25 ppm, 50 ppm and 100 ppm concentrated surfactant solution, all based on the mass of the water. (100 ppm concentrated surfactant solution is equivalent to about 50 ppm surfactant). The mixtures were pressed in a 125 kgf / cm2 press for 1 minute to extract juice. The extracted liquid was analyzed to determine sugar content using standard analytical processes of the ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| wt % | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| wt % | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| wt % | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com