Ex vivo cell stimulation
a cell and ex vivo technology, applied in the field of ex vivo cell stimulation, can solve the problems of adverse effects on biological efficacy and therapeutic potential, difficult to ascertain the nature of such side effects in advance, and the general inability to predict the therapeutic potential of any drug or composition with any confidence. , to achieve the effect of enhancing the function
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
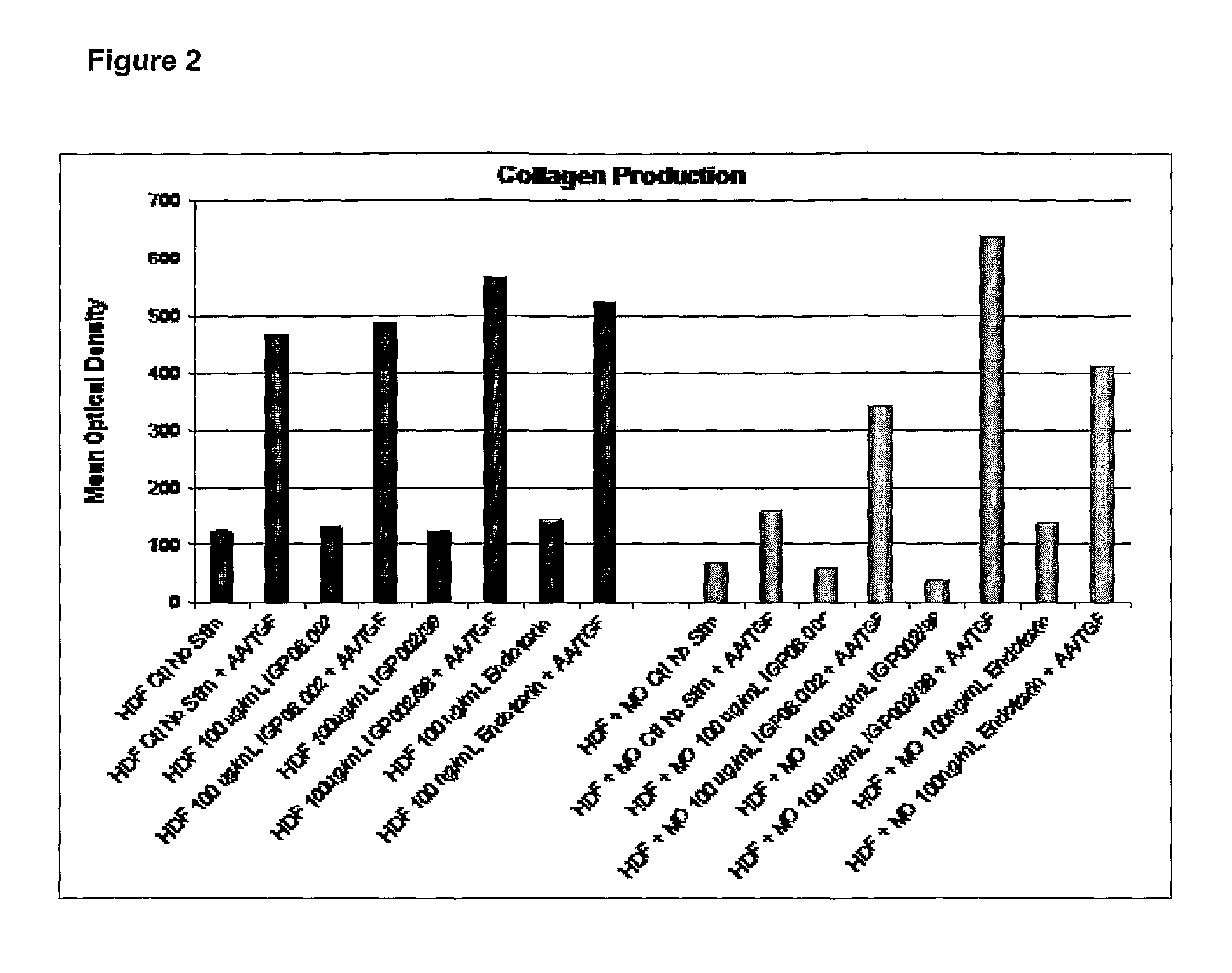
Stimulation of Collagen Production by Fibroblasts
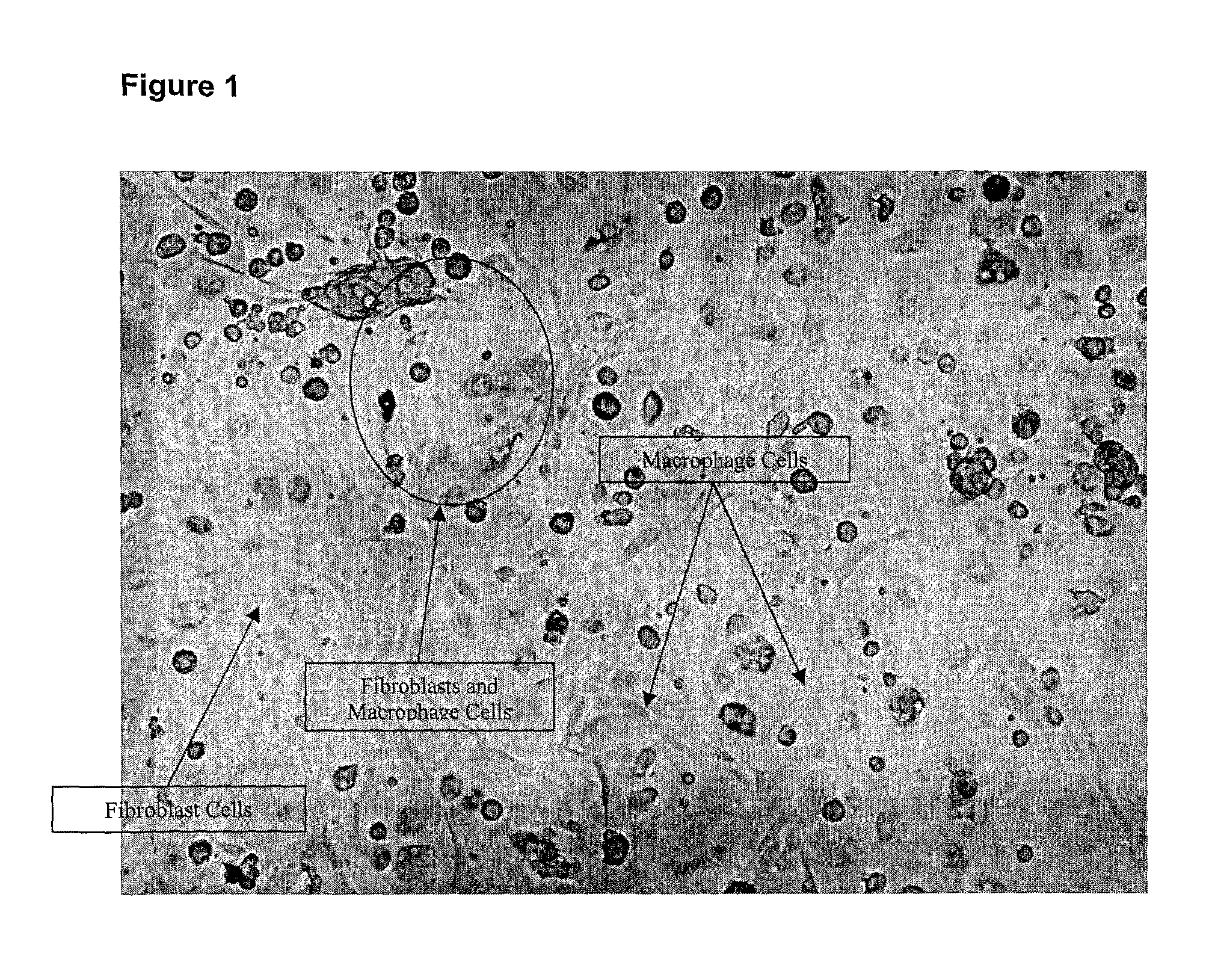
[0111]Monocytes from human blood were isolated and differentiated into macrophages (MØ) and activated by yeast microparticulate beta-(1,3)(1,6) (Glucoprime™ as described in U.S. Pat. No. 6,242,594, the disclosure of which is incorporated herein) and other glucans. Neonatal Human Fibroblasts (NHDF) were introduced to the MØ population to determine if MØ cells activated by Glucoprime™ stimulated collagen production in NHDF.
Preparation of 4 mM HCl with 0.1% Bovine Serum Albumin
[0112]1.0 mL of 12N Hydrochloric Acid (HCl) (Sigma H41758) was added to 11.0 mL of Water for Cell Culture Applications (Cambrex 17-724Q) resulting in an intermediate stock of 1.0M. The intermediate stock was further diluted by adding 0.06 mL of the stock to 14.94 mL of Water for Cell Culture Applications for a final concentration of 4 mM. 0.015 g of Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) (Sigma A-7906) was added to the 15.0 mL of 4 mM HCl for a final concentration of 0.1% of B...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Biological properties | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Therapeutic | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com