Image display apparatus and image display method
a technology of image display and subfield lighting, applied in the direction of instruments, television systems, static indicating devices, etc., to achieve the effect of reducing dynamic false contours, motion judder, or moving image blur, and reducing image degradation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
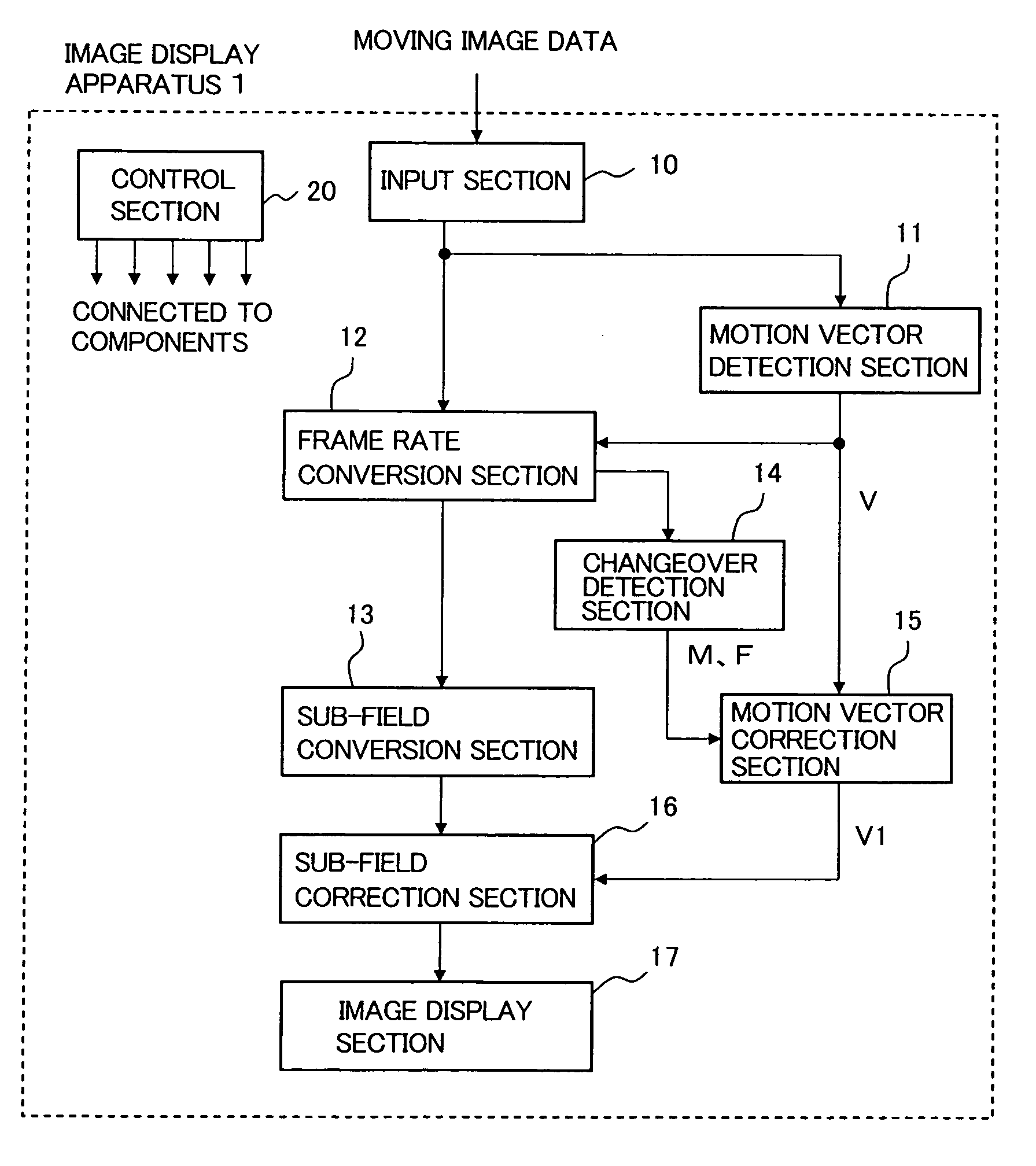
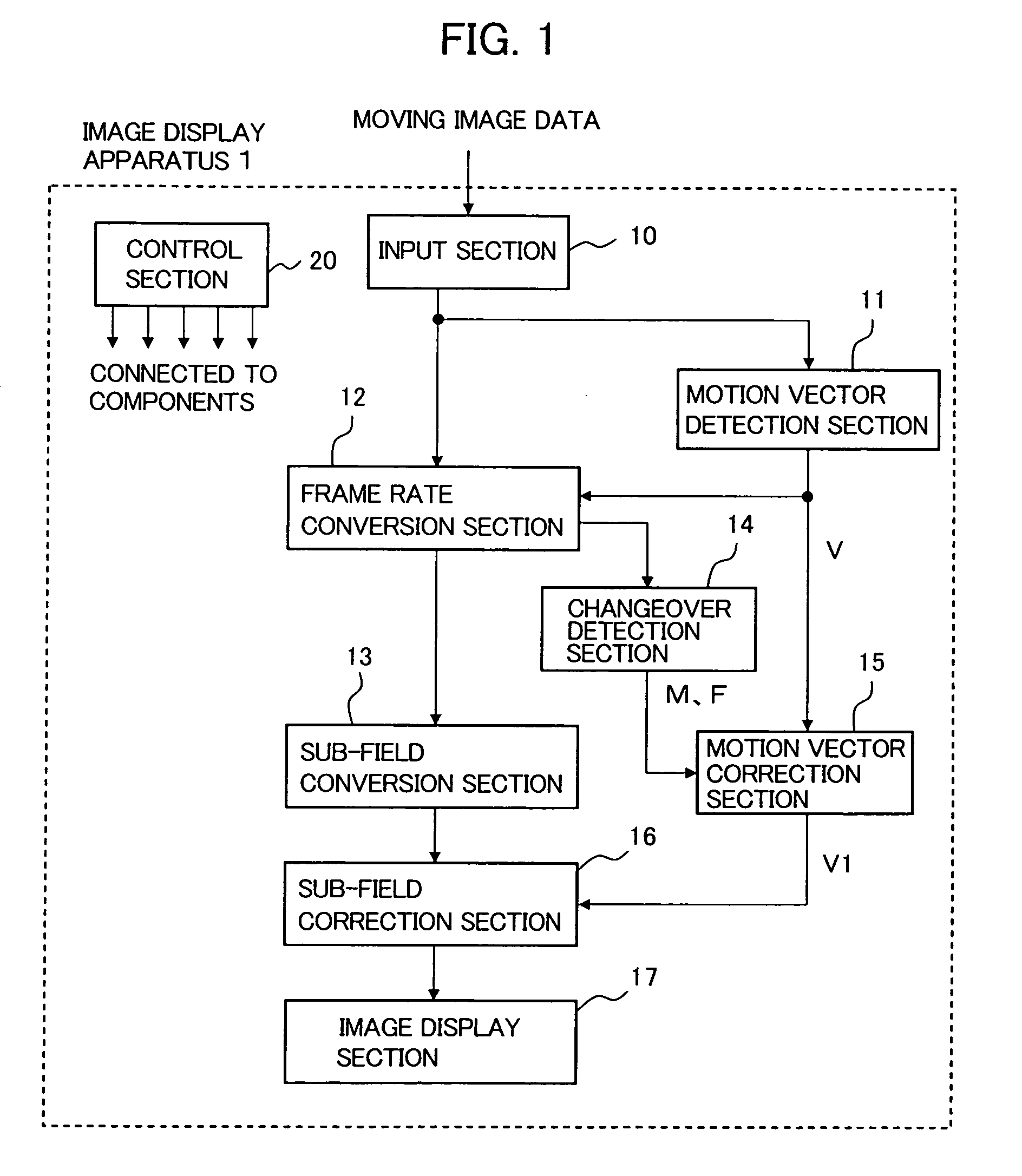
[0033]FIG. 1 is a block diagram showing the image display apparatus according to the first embodiment of the invention. An image display apparatus 1 includes an input section 10, a motion vector detection section 11, a frame rate conversion section 12, a sub-field conversion section 13, a changeover detection section 14, a motion vector correction section 15, a sub-field correction section 16, an image display section 17, and a control section 20.
[0034]The following describes the operation of each of the above sections. The input section 10 is supplied with moving image data. For example, the input section 10 may include an image input terminal or a network connection terminal or may include a TV broadcasting tuner. The input section 10 applies image preprocessing to the input moving image data as needed. The input section 10 outputs the processed display data to the motion vector detection section 11 and the frame rate conversion section 12.
[0035]The motion vector detection section...
second embodiment
[0075]The image display apparatus according to the second embodiment has the same configuration as that shown in FIG. 1 according to the first embodiment except that operations of the motion vector correction section 15 are changed. When the frame rate conversion (FRC) changes its conversion mode from ON (first conversion mode) to OFF (second conversion mode) or from OFF to ON, an image motion may become discontinuous before and after the mode change and the image may oscillate. To solve this problem, the motion vector correction section 15 according to the second embodiment performs the correction so as to smooth a motion vector change when the FRC mode changes.
[0076]The sub-field correction section 16 relocates sub-fields using the corrected motion vector. Specifically, the motion vector correction section 15 assumes the correction (V×α) using the equation (1) to be correction amount 100%. The motion vector correction section 15 further adjusts the correction amount using an adjus...
third embodiment
[0091]FIG. 9 is a block diagram of the image display apparatus according to the third embodiment of the invention. The image display apparatus 1 according to the third embodiment is compliant with a modification of the configuration of FIG. 1 according to the first embodiment by removing the changeover detection section 14 and newly adding a frame rate conversion setup section 18.
[0092]The frame rate conversion setup section 18 is equivalent to one of television screen setup menus. The frame rate conversion setup section 18 allows a user to specify the frame rate conversion (FRC) mode ON or OFF using a remote controller. FRC setup value T is set to 1 when FRC=ON (first conversion mode) is selected. FRC setup value T is set to 2 when FRC=OFF (second conversion mode) is selected.
[0093]According to the FRC setup value T, the frame rate conversion section 12 changes the conversion operation, creates an interpolation frame, and outputs it. The information about the FRC setup value T is i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com