Heat exchanging element
a technology of heat exchanger and element, which is applied in the direction of laminated elements, heating types, lighting and heating apparatus, etc., can solve the problems of reducing the effective area of the heat exchanger plate, difficult to make them uniform, and reducing the heat exchange efficiency, so as to achieve the effect of reducing air passage drift, high heat exchange efficiency, and maintaining structural strength
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
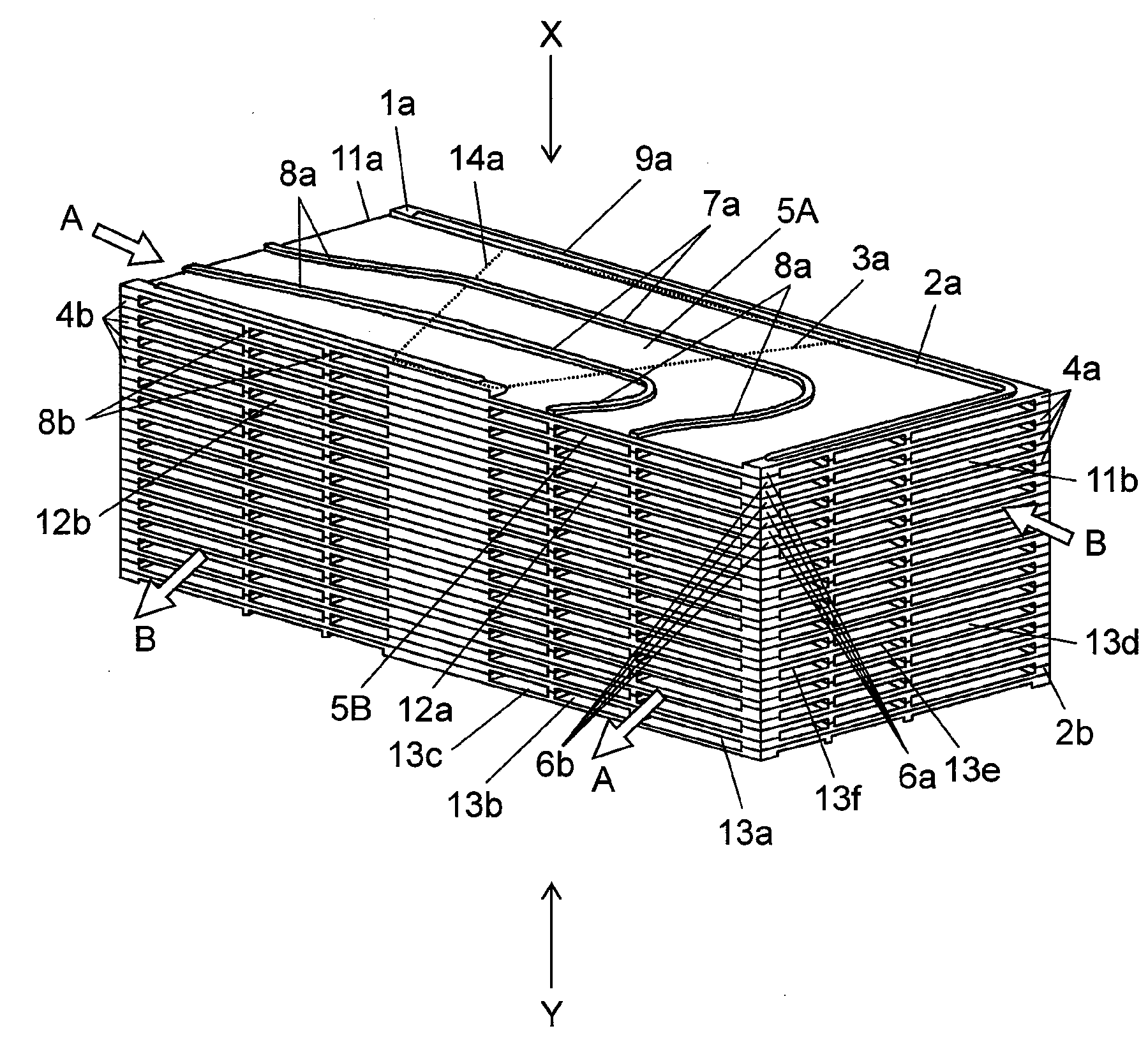
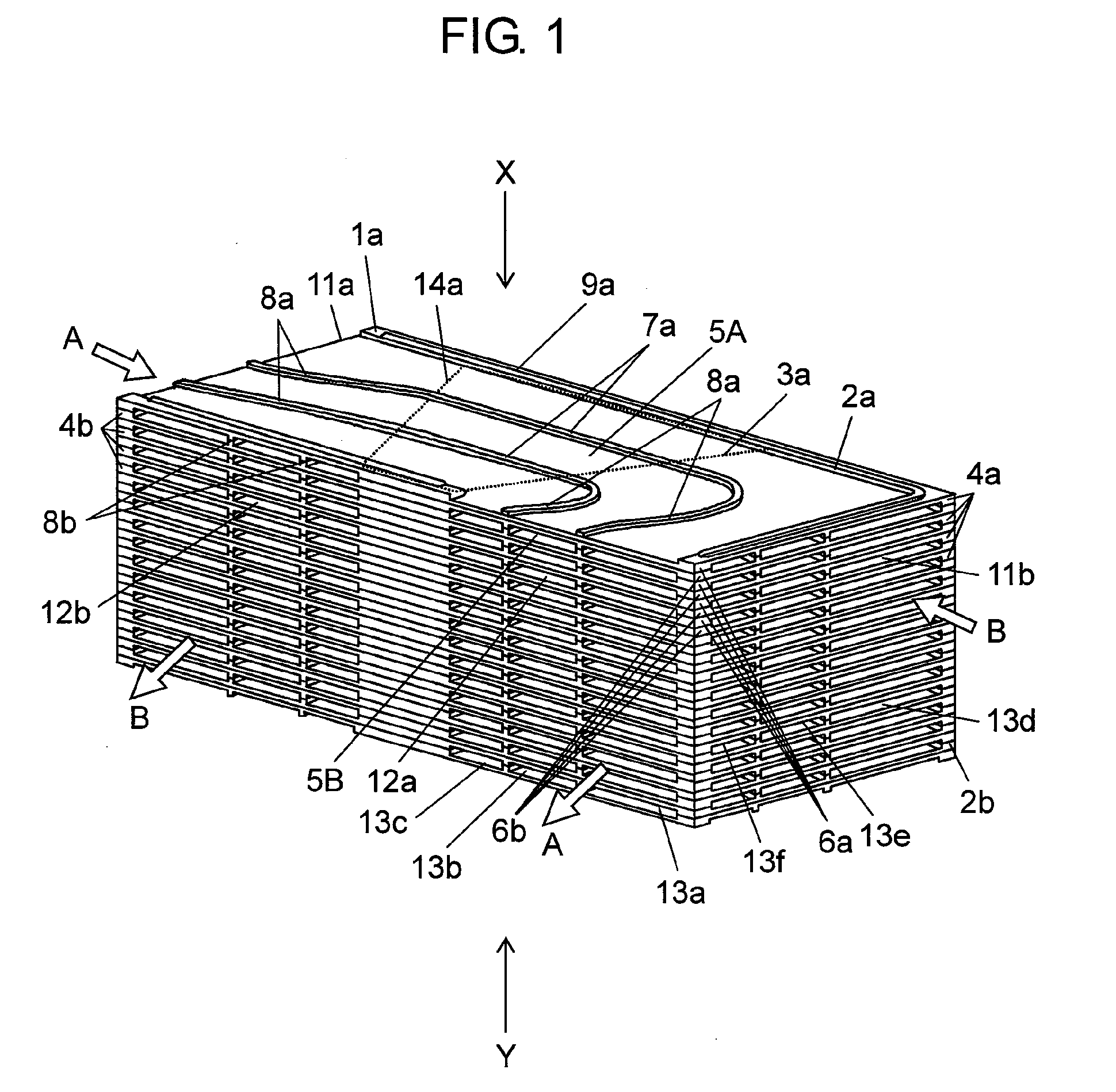
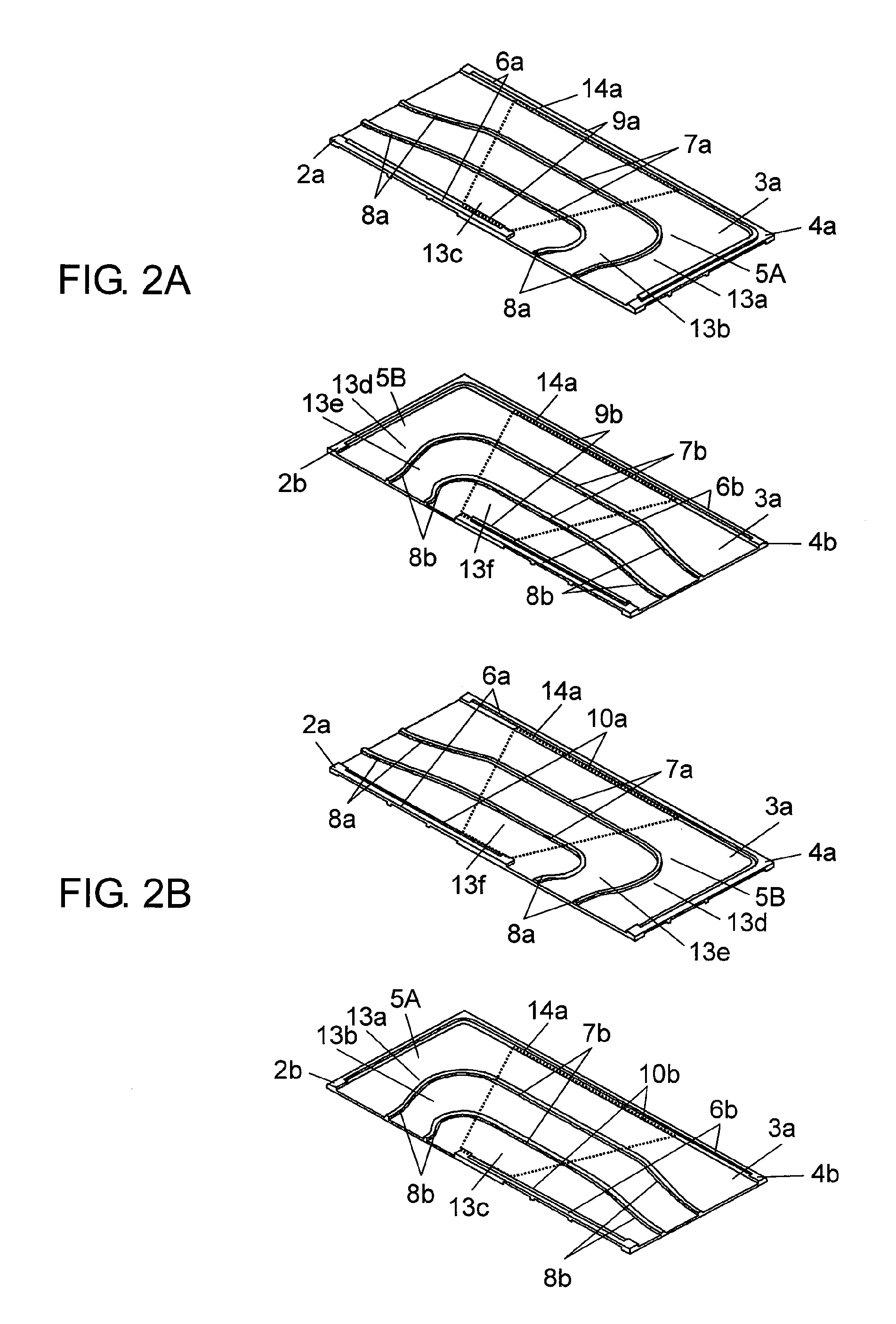
[0091]FIG. 1 is a schematic perspective view of a heat exchanging element according to a first embodiment of the present invention. FIG. 2A is a schematic perspective view of one unit element as a component of the heat exchanging element seen in a direction X of FIG. 1. FIG. 2B is a schematic perspective view of one unit element as a component of the heat exchanging element seen in a direction Y of FIG. 1. FIG. 3 is a schematic production flowchart of the heat exchanging element.
[0092]As shown in FIGS. 1, 2A, and 2B, heat exchanging element 1a includes unit elements 4a and unit elements 4b alternately laminated on each other. Each unit element 4a includes heat exchanger plate 3a integrally molded with resin frame 2a. Each unit element 4b includes heat exchanger plate 3a integrally molded with resin frame 2b. Each heat exchanger plate 3a includes air passage 5A on its top surface and air passage 5B on its bottom surface. Heat exchanging element 1a circulates primary airflow “A” throu...
second embodiment
[0116]FIG. 4 is a schematic perspective view of a heat exchanging element according to a second embodiment of the present invention. FIG. 5A is a schematic perspective view of one unit element as a component of the heat exchanging element seen in a direction X of FIG. 4. FIG. 5B is a schematic perspective view of one unit element as a component of the heat exchanging element seen in a direction Y of FIG. 4. Like components are labeled with like reference numerals with respect to the first embodiment, and these components are not described again in detail.
[0117]As shown in FIGS. 4, 5A, and 5B, heat exchanging element 1b according to the second embodiment includes unit elements 4c and unit elements 4d alternately laminated on each other. Each unit element 4c includes heat exchanger plate 3b integrally molded with resin frame 2c. Each unit element 4d includes heat exchanger plate 3b integrally molded with resin frame 2d. Each heat exchanger plate 3b includes air passage 5C on its top s...
third embodiment
[0141]FIG. 6 is a schematic perspective view of a heat exchanging element according to a third embodiment of the present invention. FIG. 7 is a schematic perspective view of one unit element as a component of the heat exchanging element seen in a direction X of FIG. 6. FIG. 8 is a schematic production flowchart of the heat exchanging element. Like components are labeled with like reference numerals with respect to the first and second embodiments, and these components are not described again in detail.
[0142]As shown in FIGS. 6 and 7, heat exchanging element 1c includes unit elements 4e and unit elements 4f alternately laminated on each other. Each unit element 4e includes shield portions 6e, flow channel division portions 7e, rectification portions 8e, and spaced projections 19a, which are formed by providing an uneven surface structure on heat exchanger plate 3c. Each unit element 4f includes shield portions 6f, flow channel division portions 7f, rectification portions 8f, and spac...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com