Method and Device for Sealing
a magnetic hysteresis and sealing technology, applied in the field of methods and devices for magnetic hysteresis sealing, can solve problems such as loss of magnetic hysteresis, achieve high speed, prevent overheating of packaging material laminates, and save energy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
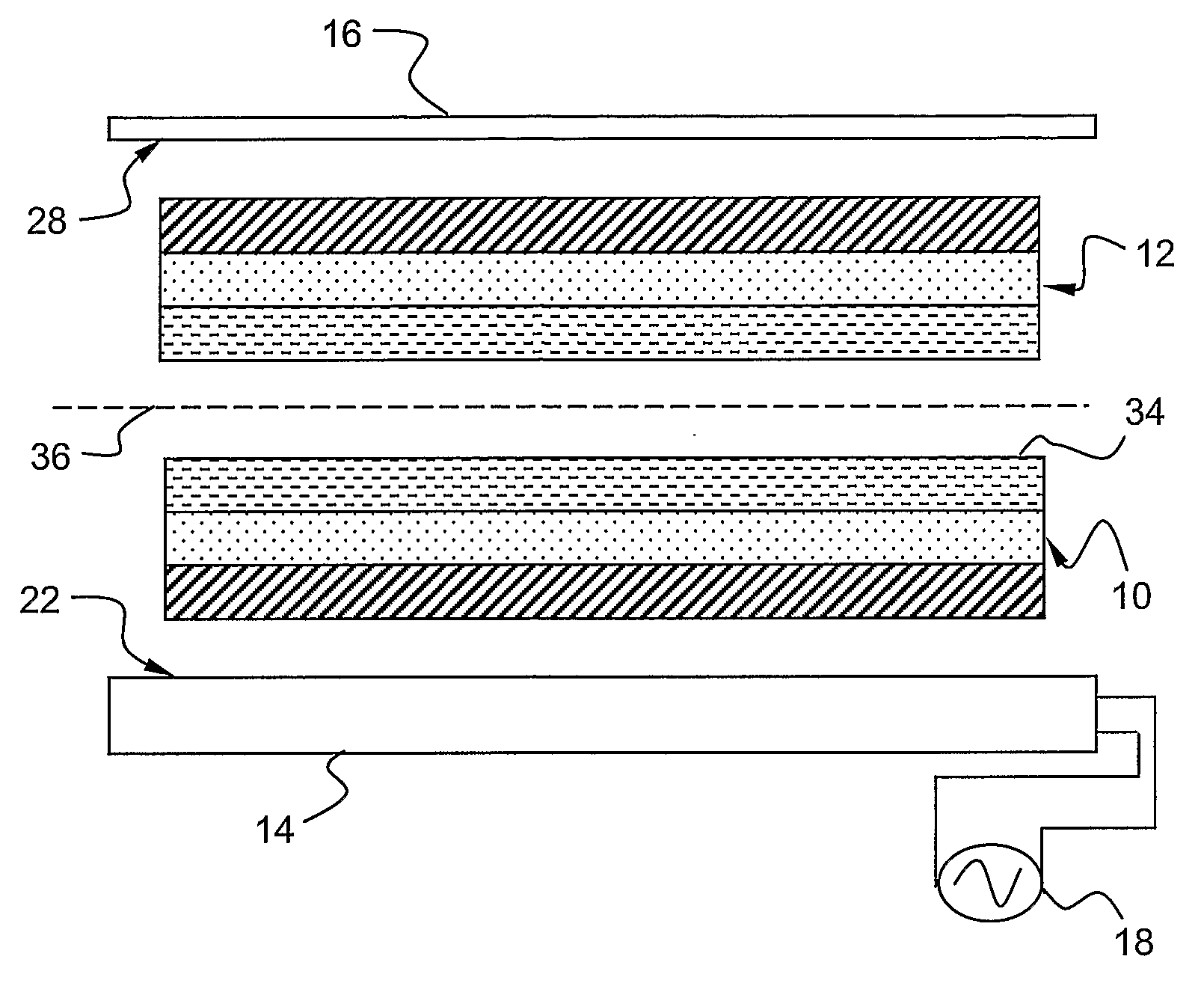
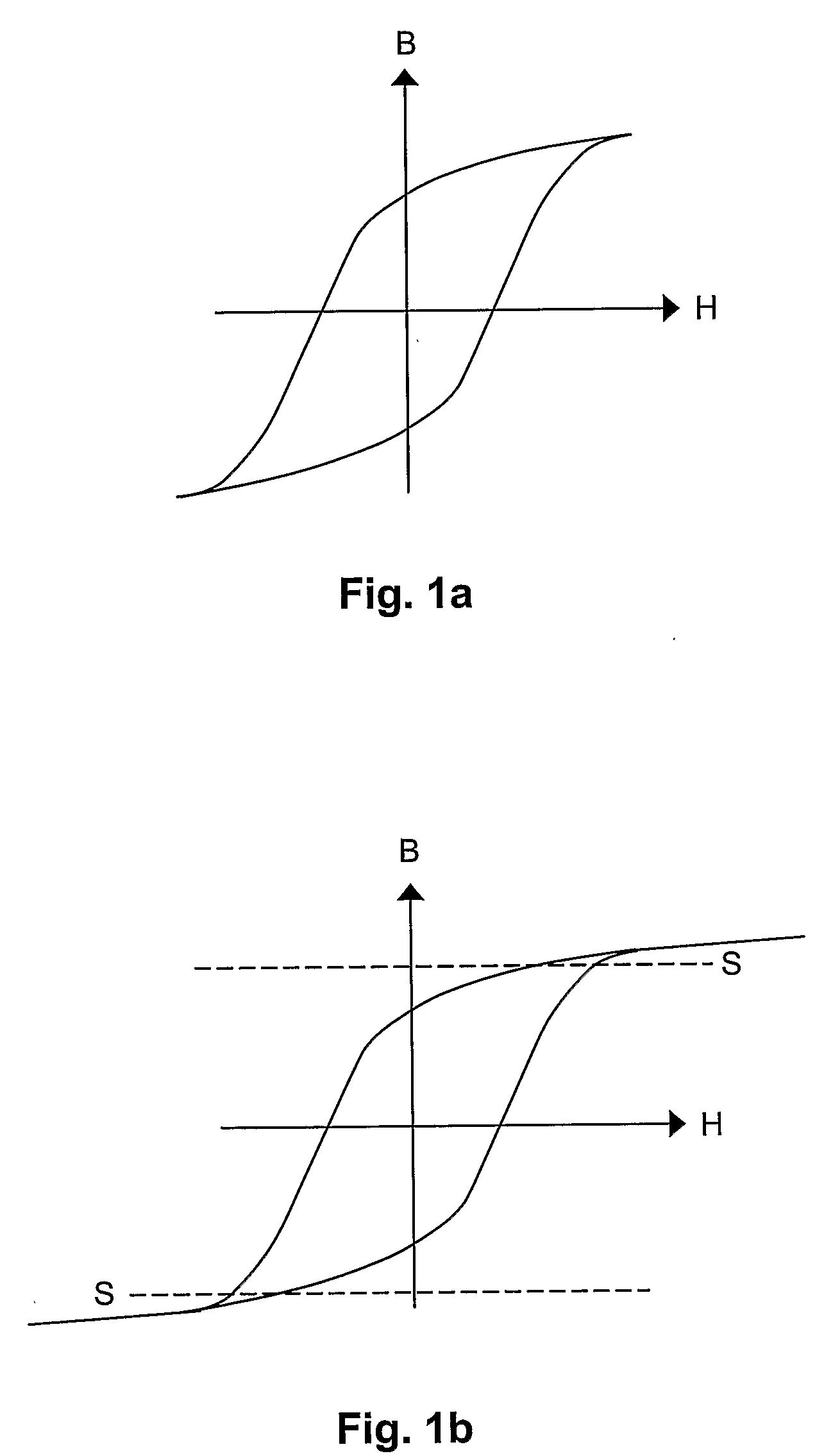
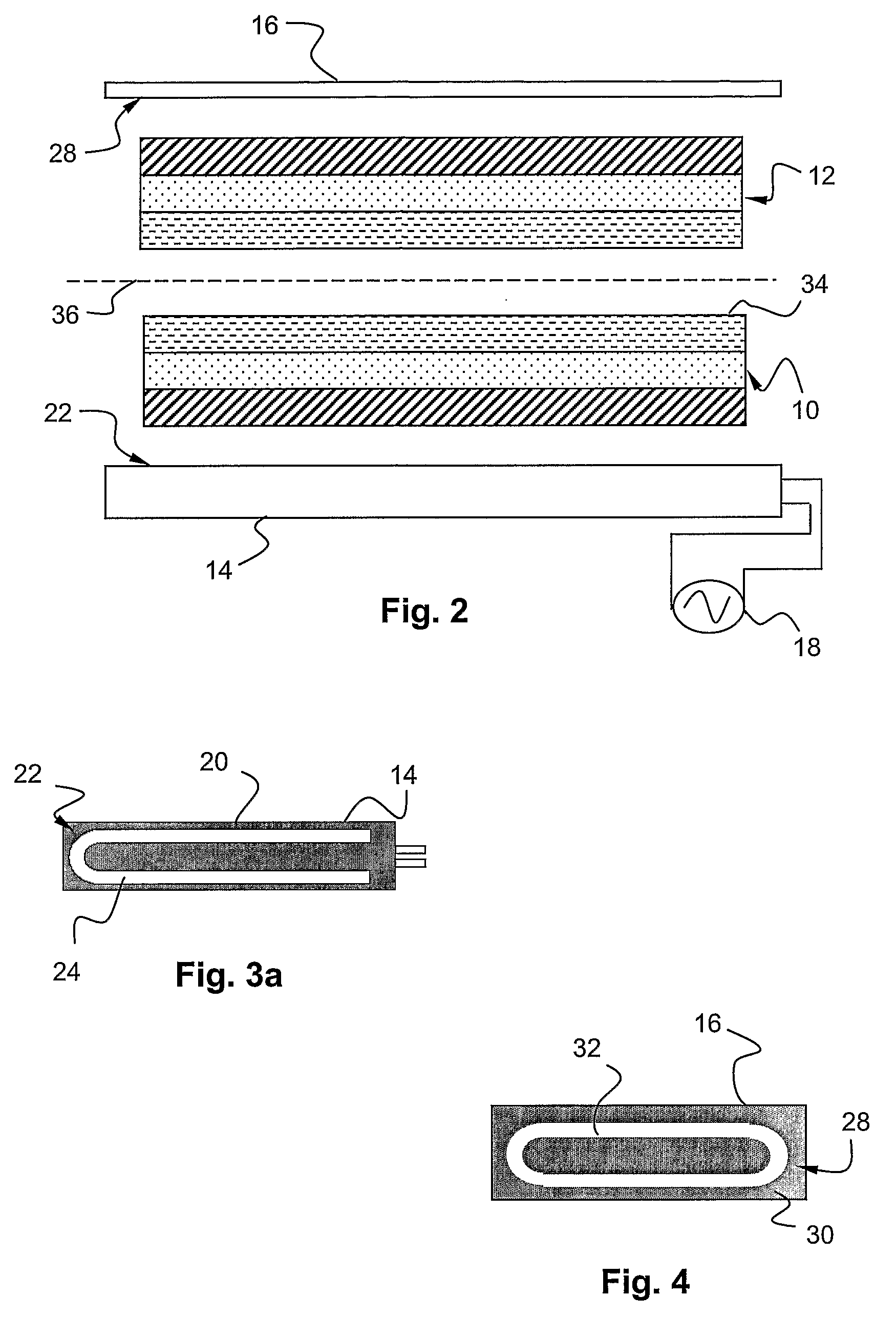
[0035]FIG. 2 shows a presently preferred embodiment of the invention. A first and a second packaging material laminate 10, 12 to be sealed together in a joint by means of a sealing jaw 14 and an anvil 16. In the joint shown the two laminates are abutting each other with their inside surfaces facing each other. In this presently preferred embodiment the sealing jaw 14 is an inductor similar to the ones used for induction sealing (where the laminate comprises aluminum foil that generate heat). The inductor 14 is here coupled to an alternating current supply 18. The alternating current is preferably in the range of 75-300 A and the power needed from the power supply is a few kW. A preferred interval is 2-10 kW. The frequency is preferably in the MHz range, and a preferred frequency interval is 0.5-5 MHz. A most preferred interval is 1-4 MHz. The frequencies that are prohibited for common use due to authority regulations are of course, in practice, excluded from said intervals.
[0036]The...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| frequency | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| frequency | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| mean size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com