Method and System for in-Cup Dispensing, Mixing and Foaming Hot and Cold Beverages From Liquid Concentrate
a technology of liquid concentrate and in-cup dispensing, which is applied in the direction of liquid dispensing, liquid transferring device, packaging, etc., can solve the problems of labor-intensive and costly, high cost of systems such as this type, and inability to meet the needs of consumers,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
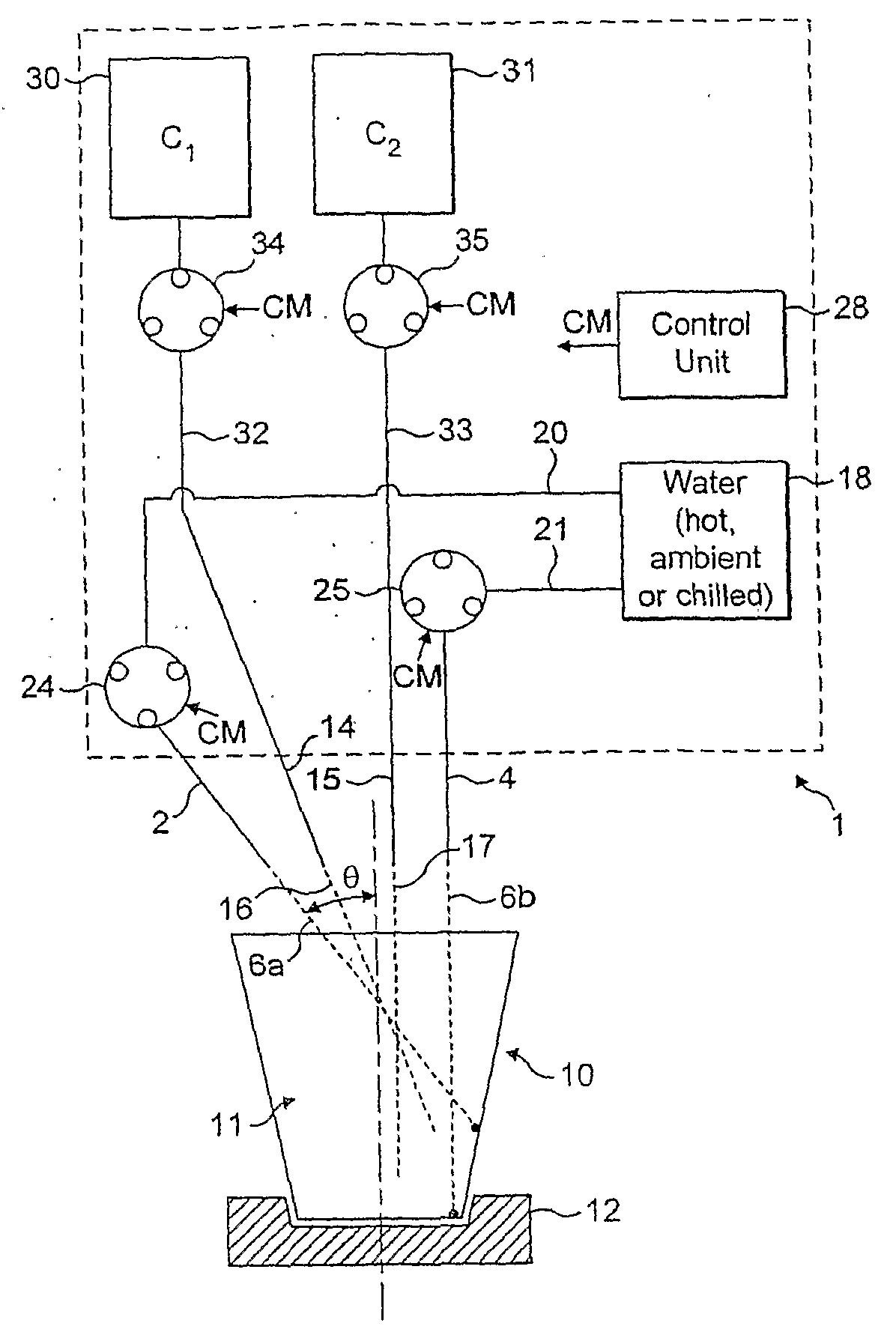
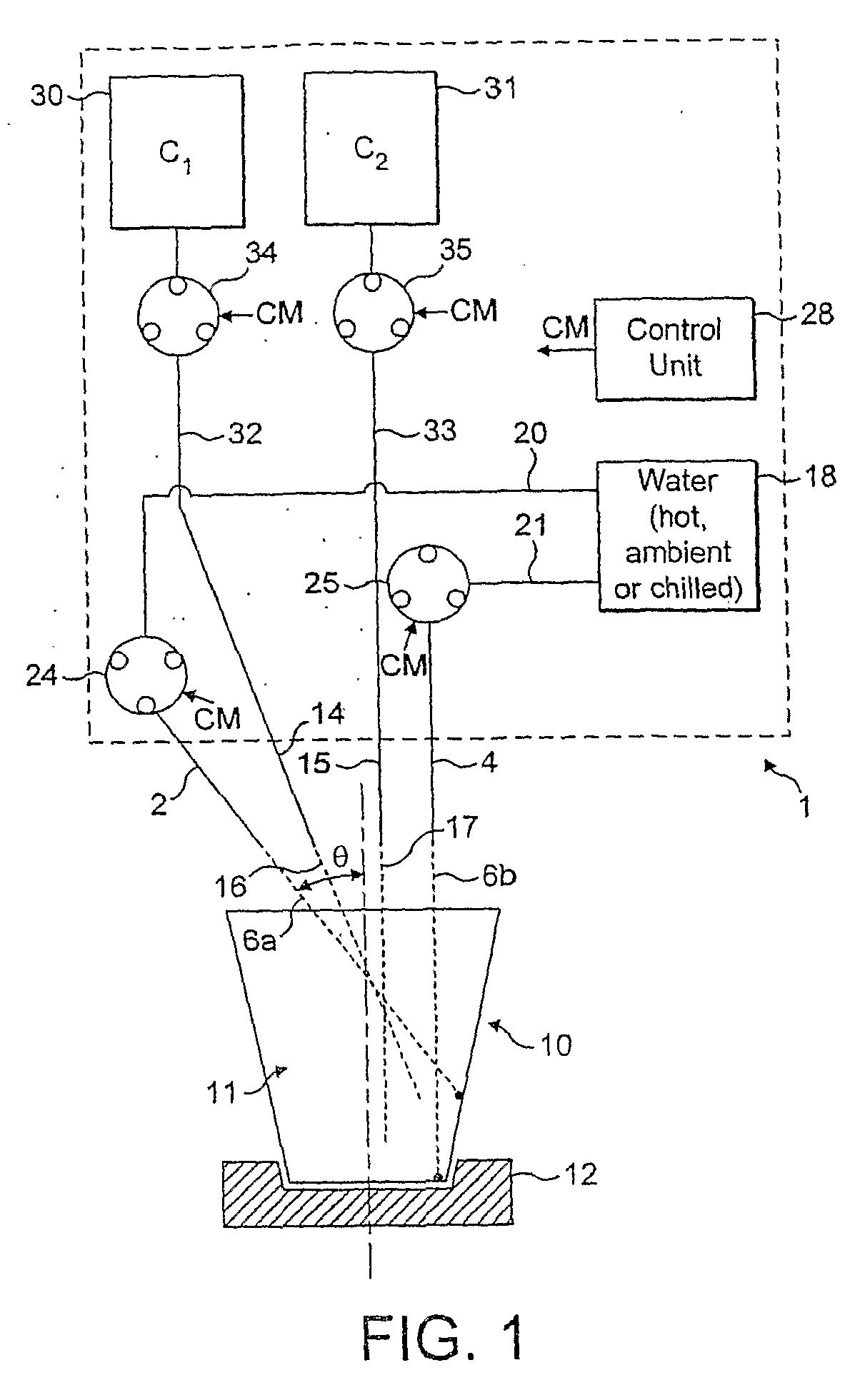
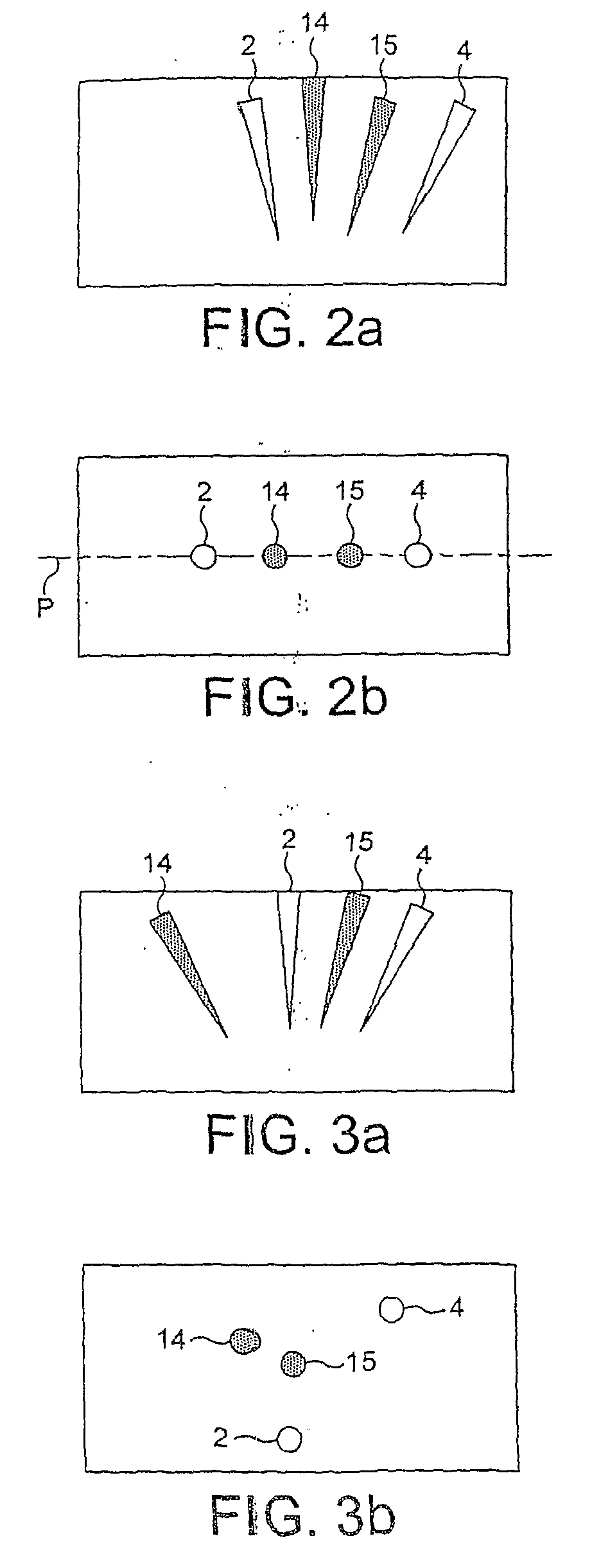
[0075]A cappuccino beverage was prepared using two water jets. The position of water jets are: first jet is 15 degree (from vertical) in one plane and angled by 20 degree in the direction of the plane perpendicular to the first one; second jet was vertical in both perpendicular planes. Flow rate and linear velocity of water jets were 20 ml / s and ˜1800 cm / s, respectively. A liquid concentrate containing milk proteins, sugar and coffee was dispensed at 10 ml / s flow rate with linear velocity of ˜35 cm / s. Viscosity of the liquid concentrate was ˜600 cP. Water temperature was 85° C.; the concentrate was kept at ambient temperature.
[0076]No liquid stratification, and high foam-to-liquid ratio (about 0.7) were visually observed. Further, foam was very stable and stiff, and desirable appearance with a uniform distribution of small bubbles was observed in dispensed cappuccino drink. No splashing from the cup was observed.
example 2
[0077]A mochaccino beverage was prepared using two water jets. The position of water jets are: first jet is 15 degree (from vertical) in one plane and angled by 20 degree in the direction of the plane perpendicular to the first one; second jet was vertical in both perpendicular planes. Flow rate and linear velocity of water jets were 20 ml / s and about 1800 cm / s, respectively. A liquid concentrate containing milk proteins, sugar and cocoa was dispensed at 4.5 ml / s flow rate with linear velocity of about 15 cm / s. Viscosity of the liquid concentrate was about 5,000 cP. Water temperature was 85° C.; the concentrate was kept at ambient temperature.
[0078]Stiff foam with high foam-to-liquid ratio and no liquid stratification was observed in the dispensed drink. Also, no splashing from the cup was observed.
example 3
[0079]A mochaccino beverage was prepared under conditions provided by Example 2 but with flow rate and linear velocity of water jets of 30 ml / s and ˜2750 cm / s, respectively.
[0080]Stiff foam with high foam-to-liquid ratio and no liquid stratification were observed. Foam bubble sizes were acceptable but larger than in Example 1. Also, no splashing from the cup was observed.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com